Ace Your Professional Data Engineer with Practice Exams.
Google Cloud Certified – Professional Data Engineer – Practice Exam (Question 205)
Question 01
Your company built a TensorFlow neural network model with a large number of neurons and layers.
The model fits well for the training data. However, when tested against new data, it performs poorly.
What method can you employ to address this?
- A. Threading
- B. Serialization
- C. Dropout Methods
- D. Dimensionality Reduction
Answer: C
Question 02
You are building a model to make clothing recommendations.
You know a user’s fashion preference is likely to change over time, so you build a data pipeline to stream new data back to the model as it becomes available.
How should you use this data to train the model?
- A. Continuously retrain the model on just the new data.
- B. Continuously retrain the model on a combination of existing data and the new data.
- C. Train on the existing data while using the new data as your test set.
- D. Train on the new data while using the existing data as your test set.
Answer: B
Question 03
You designed a database for patient records as a pilot project to cover a few hundred patients in three clinics.
Your design used a single database table to represent all patients and their visits, and you used self-joins to generate reports. The server resource utilization was at 50%. Since then, the scope of the project has expanded. The database must now store 100 times more patient records. You can no longer run the reports, because they either take too long or they encounter errors with insufficient compute resources.
How should you adjust the database design?
- A. Add capacity (memory and disk space) to the database server by the order of 200.
- B. Shard the tables into smaller ones based on date ranges, and only generate reports with prespecified date ranges.
- C. Normalize the master patient-record table into the patient table and the visits table, and create other necessary tables to avoid self-join.
- D. Partition the table into smaller tables, with one for each clinic. Run queries against the smaller table pairs, and use unions for consolidated reports.
Answer: C
Question 04
You create an important report for your large team in Google Data Studio 360.
The report uses Google BigQuery as its data source. You notice that visualizations are not showing data that is less than 1 hour old.
What should you do?
- A. Disable caching by editing the report settings.
- B. Disable caching in BigQuery by editing table details.
- C. Refresh your browser tab showing the visualizations.
- D. Clear your browser history for the past hour then reload the tab showing the virtualizations.
Answer: A
Reference:
Manage data freshness – Looker Studio Help
Question 05
An external customer provides you with a daily dump of data from their database.
The data flows into Google Cloud Storage GCS as comma-separated values (CSV) files. You want to analyze this data in Google BigQuery, but the data could have rows that are formatted incorrectly or corrupted.
How should you build this pipeline?
- A. Use federated data sources, and check data in the SQL query.
- B. Enable BigQuery monitoring in Google Stackdriver and create an alert.
- C. Import the data into BigQuery using the gcloud CLI and set max_bad_records to 0.
- D. Run a Google Cloud Dataflow batch pipeline to import the data into BigQuery, and push errors to another dead-letter table for analysis.
Answer: D
Question 06
Your weather app queries a database every 15 minutes to get the current temperature.
The frontend is powered by Google App Engine and serves millions of users.
How should you design the frontend to respond to a database failure?
- A. Issue a command to restart the database servers.
- B. Retry the query with exponential backoff, up to a cap of 15 minutes.
- C. Retry the query every second until it comes back online to minimize staleness of data.
- D. Reduce the query frequency to once every hour until the database comes back online.
Answer: B
Question 07
You are creating a model to predict housing prices.
Due to budget constraints, you must run it on a single resource-constrained virtual machine.
Which learning algorithm should you use?
- A. Linear regression
- B. Logistic classification
- C. Recurrent neural network
- D. Feedforward neural network
Answer: A
Question 08
You are building a new real-time data warehouse for your company and will use Google BigQuery streaming inserts.
There is no guarantee that data will only be sent in once but you do have a unique ID for each row of data and an event timestamp. You want to ensure that duplicates are not included while interactively querying data.
Which query type should you use?
- A. Include ORDER BY DESK on the timestamp column and LIMIT to 1.
- B. Use GROUP BY on the unique ID column and timestamp column and SUM on the values.
- C. Use the LAG window function with PARTITION by unique ID along with WHERE LAG IS NOT NULL.
- D. Use the ROW_NUMBER window function with PARTITION by unique ID along with WHERE row equals 1.
Answer: D
Question 09
Your company is using WILDCARD tables to query data across multiple tables with similar names.
The SQL statement is currently failing with the following error:
# Syntax error : Expected end of statement but got "-" at [4:11]
SELECT age -
FROM -
bigquery-public-data.noaa_gsod.gsod
WHERE -
age != 99
AND_TABLE_SUFFIX = "˜1929'
ORDER BY -
age DESCWhich table name will make the SQL statement work correctly?
- A. ‘bigquery-public-data.noaa_gsod.gsod’
- B. bigquery-public-data.noaa_gsod.gsod*
- C. ‘bigquery-public-data.noaa_gsod.gsod’*
- D. ‘bigquery-public-data.noaa_gsod.gsod*`
Answer: D
Reference:
Query multiple tables using a wildcard table | BigQuery | Google Cloud
Question 10
Your company is in a highly regulated industry.
One of your requirements is to ensure individual users have access only to the minimum amount of information required to do their jobs. You want to enforce this requirement with Google BigQuery.
Which three approaches can you take? (Choose three.)
- A. Disable writes to certain tables.
- B. Restrict access to tables by role.
- C. Ensure that the data is encrypted at all times.
- D. Restrict BigQuery API access to approved users.
- E. Segregate data across multiple tables or databases.
- F. Use Google Stackdriver Audit Logging to determine policy violations.
Answer: B, D, F
Question 11
You are designing a basket abandonment system for an ecommerce company.
The system will send a message to a user based on these rules:
・No interaction by the user on the site for 1 hour
・Has added more than $30 worth of products to the basket
・Has not completed a transaction
You use Google Cloud Dataflow to process the data and decide if a message should be sent.
How should you design the pipeline?
- A. Use a fixed-time window with a duration of 60 minutes.
- B. Use a sliding time window with a duration of 60 minutes.
- C. Use a session window with a gap time duration of 60 minutes.
- D. Use a global window with a time based trigger with a delay of 60 minutes.
Answer: C
Question 12
Your company handles data processing for a number of different clients.
Each client prefers to use their own suite of analytics tools, with some allowing direct query access via Google BigQuery. You need to secure the data so that clients cannot see each other’s data. You want to ensure appropriate access to the data.
Which three steps should you take? (Choose three.)
- A. Load data into different partitions.
- B. Load data into a different dataset for each client.
- C. Put each client’s BigQuery dataset into a different table.
- D. Restrict a client’s dataset to approved users.
- E. Only allow a service account to access the datasets.
- F. Use the appropriate identity and access management (IAM) roles for each client’s users.
Answer: B, D, F
Question 13
You want to process payment transactions in a point-of-sale application that will run on Google Cloud Platform.
Your user base could grow exponentially, but you do not want to manage infrastructure scaling.
Which Google database service should you use?
- A. Cloud SQL
- B. BigQuery
- C. Cloud Bigtable
- D. Cloud Datastore
Answer: D
Reference:
Transactions | Cloud Datastore Documentation
Question 14
You want to use a database of information about tissue samples to classify future tissue samples as either normal or mutated.
You are evaluating an unsupervised anomaly detection method for classifying the tissue samples.
Which two characteristics support this method? (Choose two.)
- A. There are very few occurrences of mutations relative to normal samples.
- B. There are roughly equal occurrences of both normal and mutated samples in the database.
- C. You expect future mutations to have different features from the mutated samples in the database.
- D. You expect future mutations to have similar features to the mutated samples in the database.
- E. You already have labels for which samples are mutated and which are normal in the database.
Answer: A, D
Question 15
You need to store and analyze social media postings in Google BigQuery at a rate of 10,000 messages per minute in near real-time.
Initially, design the application to use streaming inserts for individual postings. Your application also performs data aggregations right after the streaming inserts. You discover that the queries after streaming inserts do not exhibit strong consistency, and reports from the queries might miss in-flight data.
How can you adjust your application design?
- A. Re-write the application to load accumulated data every 2 minutes.
- B. Convert the streaming insert code to batch load for individual messages.
- C. Load the original message to Google Cloud SQL, and export the table every hour to BigQuery via streaming inserts.
- D. Estimate the average latency for data availability after streaming inserts, and always run queries after waiting twice as long.
Answer: D
Question 16
Your startup has never implemented a formal security policy.
Currently, everyone in the company has access to the datasets stored in Google BigQuery. Teams have freedom to use the service as they see fit, and they have not documented their use cases. You have been asked to secure the data warehouse. You need to discover what everyone is doing.
What should you do first?
- A. Use Google Stackdriver Audit Logs to review data access.
- B. Get the identity and access management IIAM) policy of each table
- C. Use Stackdriver Monitoring to see the usage of BigQuery query slots.
- D. Use the Google Cloud Billing API to see what account the warehouse is being billed to.
Answer: A
Question 17
Your company is migrating their 30-node Apache Hadoop cluster to the cloud.
They want to re-use Hadoop jobs they have already created and minimize the management of the cluster as much as possible. They also want to be able to persist data beyond the life of the cluster.
What should you do?
- A. Create a Google Cloud Dataflow job to process the data.
- B. Create a Google Cloud Dataproc cluster that uses persistent disks for HDFS.
- C. Create a Hadoop cluster on Google Compute Engine that uses persistent disks.
- D. Create a Cloud Dataproc cluster that uses the Google Cloud Storage connector.
- E. Create a Hadoop cluster on Google Compute Engine that uses Local SSD disks.
Answer: D
Question 18
Business owners at your company have given you a database of bank transactions.
Each row contains the user ID, transaction type, transaction location, and transaction amount. They ask you to investigate what type of machine learning can be applied to the data.
Which three machine learning applications can you use? (Choose three.)
- A. Supervised learning to determine which transactions are most likely to be fraudulent.
- B. Unsupervised learning to determine which transactions are most likely to be fraudulent.
- C. Clustering to divide the transactions into N categories based on feature similarity.
- D. Supervised learning to predict the location of a transaction.
- E. Reinforcement learning to predict the location of a transaction.
- F. Unsupervised learning to predict the location of a transaction.
Answer: B, C, E
Question 19
Your company’s on-premises Apache Hadoop servers are approaching end-of-life, and IT has decided to migrate the cluster to Google Cloud Dataproc.
A like-for- like migration of the cluster would require 50 TB of Google Persistent Disk per node. The CIO is concerned about the cost of using that much block storage. You want to minimize the storage cost of the migration.
What should you do?
- A. Put the data into Google Cloud Storage.
- B. Use preemptible virtual machines (VMs) for the Cloud Dataproc cluster.
- C. Tune the Cloud Dataproc cluster so that there is just enough disk for all data.
- D. Migrate some of the cold data into Google Cloud Storage, and keep only the hot data in Persistent Disk.
Answer: A
Question 20
You work for a car manufacturer and have set up a data pipeline using Google Cloud Pub/Sub to capture anomalous sensor events.
You are using a push subscription in Cloud Pub/Sub that calls a custom HTTPS endpoint that you have created to take action of these anomalous events as they occur. Your custom HTTPS endpoint keeps getting an inordinate amount of duplicate messages.
What is the most likely cause of these duplicate messages?
- A. The message body for the sensor event is too large.
- B. Your custom endpoint has an out-of-date SSL certificate.
- C. The Cloud Pub/Sub topic has too many messages published to it.
- D. Your custom endpoint is not acknowledging messages within the acknowledgement deadline.
Answer: D
Reference:
Troubleshooting | Cloud Pub/Sub Documentation
Question 21
Your company uses a proprietary system to send inventory data every 6 hours to a data ingestion service in the cloud.
Transmitted data includes a payload of several fields and the timestamp of the transmission. If there are any concerns about a transmission, the system re-transmits the data.
How should you deduplicate the data most efficiently?
- A. Assign global unique identifiers (GUID) to each data entry.
- B. Compute the hash value of each data entry, and compare it with all historical data.
- C. Store each data entry as the primary key in a separate database and apply an index.
- D. Maintain a database table to store the hash value and other metadata for each data entry.
Answer: A
Question 22
Your company has hired a new data scientist who wants to perform complicated analyses across very large datasets stored in Google Cloud Storage and in a Cassandra cluster on Google Compute Engine.
The scientist primarily wants to create labelled datasets for machine learning projects, along with some visualization tasks. She reports that her laptop is not powerful enough to perform her tasks and it is slowing her down. You want to help her perform her tasks.
What should you do?
- A. Run a local version of Jupiter on the laptop.
- B. Grant the user access to Google Cloud Shell.
- C. Host a visualization tool on a VM on Google Compute Engine.
- D. Deploy Google Cloud Datalab to a virtual machine (VM) on Google Compute Engine.
Answer: D
Reference:
Managing the lifecycle of a Cloud Datalab instance
Cloud Datalab Documentation
Question 23
You are deploying 10,000 new Internet of Things devices to collect temperature data in your warehouses globally.
You need to process, store and analyze these very large datasets in real time.
What should you do?
- A. Send the data to Google Cloud Datastore and then export to BigQuery.
- B. Send the data to Google Cloud Pub/Sub, stream Cloud Pub/Sub to Google Cloud Dataflow, and store the data in Google BigQuery.
- C. Send the data to Cloud Storage and then spin up an Apache Hadoop cluster as needed in Google Cloud Dataproc whenever analysis is required.
- D. Export logs in batch to Google Cloud Storage and then spin up a Google Cloud SQL instance, import the data from Cloud Storage, and run an analysis as needed.
Answer: B
Question 24
You have spent a few days loading data from comma-separated values (CSV) files into the Google BigQuery table CLICK_STREAM.
The column DT stores the epoch time of click events. For convenience, you chose a simple schema where every field is treated as the STRING type. Now, you want to compute web session durations of users who visit your site, and you want to change its data type to TIMESTAMP. You want to minimize the migration effort without making future queries computationally expensive.
What should you do?
- A. Delete the table CLICK_STREAM, and then recreate it such that the column DT is of the TIMESTAMP type. Reload the data.
- B. Add a column TS of the TIMESTAMP type to the table CLICK_STREAM, and populate the numeric values from the column TS for each row. Reference the column TS instead of the column DT from now on.
- C. Create a view CLICK_STREAM_V, where strings from the column DT are cast into TIMESTAMP values. Reference the view CLICK_STREAM_V instead of the table CLICK_STREAM from now on.
- D. Add two columns to the table CLICK STREAM: TS of the TIMESTAMP type and IS_NEW of the BOOLEAN type. Reload all data in append mode. For each appended row, set the value of IS_NEW to true. For future queries, reference the column TS instead of the column DT, with the WHERE clause ensuring that the value of IS_NEW must be true.
- E. Construct a query to return every row of the table CLICK_STREAM, while using the built-in function to cast strings from the column DT into TIMESTAMP values. Run the query into a destination table NEW_CLICK_STREAM, in which the column TS is the TIMESTAMP type. Reference the table NEW_CLICK_STREAM instead of the table CLICK_STREAM from now on. In the future, new data is loaded into the table NEW_CLICK_STREAM.
Answer: E
Reference:
Modifying table schemas | BigQuery | Google Cloud
Question 25
You want to use Google Stackdriver Logging to monitor Google BigQuery usage.
You need an instant notification to be sent to your monitoring tool when new data is appended to a certain table using an insert job, but you do not want to receive notifications for other tables.
What should you do?
- A. Make a call to the Stackdriver API to list all logs, and apply an advanced filter.
- B. In the Stackdriver logging admin interface, and enable a log sink export to BigQuery.
- C. In the Stackdriver logging admin interface, enable a log sink export to Google Cloud Pub/Sub, and subscribe to the topic from your monitoring tool.
- D. Using the Stackdriver API, create a project sink with an advanced log filter to export to Pub/Sub, and subscribe to the topic from your monitoring tool.
Answer: D
Reference:
Build queries by using the Logging query language | Google Cloud
Question 26
You are working on a sensitive project involving private user data.
You have set up a project on Google Cloud Platform to house your work internally. An external consultant is going to assist with coding a complex transformation in a Google Cloud Dataflow pipeline for your project.
How should you maintain users’ privacy?
- A. Grant the consultant the Viewer role on the project.
- B. Grant the consultant the Cloud Dataflow Developer role on the project.
- C. Create a service account and allow the consultant to log on with it.
- D. Create an anonymized sample of the data for the consultant to work with in a different project.
Answer: D
Reference:
Access control with IAM | Cloud Dataflow
Question 27
You are building a model to predict whether or not it will rain on a given day.
You have thousands of input features and want to see if you can improve training speed by removing some features while having a minimum effect on model accuracy.
What can you do?
- A. Eliminate features that are highly correlated to the output labels.
- B. Combine highly co-dependent features into one representative feature.
- C. Instead of feeding in each feature individually, average their values in batches of 3.
- D. Remove the features that have null values for more than 50% of the training records.
Answer: B
Question 28
Your company is performing data preprocessing for a learning algorithm in Google Cloud Dataflow.
Numerous data logs are being generated during this step, and the team wants to analyze them. Due to the dynamic nature of the campaign, the data is growing exponentially every hour.The data scientists have written the following code to read the data for new key features in the logs.
Google BigQueryIO.Read -
.named("ReadLogData")
.from("clouddataflow-readonly:samples.log_data")You want to improve the performance of this data read.
What should you do?
- A. Specify the TableReference object in the code.
- B. Use the .fromQuery operation to read specific fields from the table.
- C. Use of both the Google BigQuery TableSchema and TableFieldSchema classes.
- D. Call a transform that returns TableRow objects, where each element in the PCollection represents a single row in the table.
Answer: B
Reference:
Control costs in BigQuery | Google Cloud
Question 29
Your company is streaming real-time sensor data from their factory floor into Bigtable and they have noticed extremely poor performance.
How should the row key be redesigned to improve Bigtable performance on queries that populate real-time dashboards?
- A. Use a row key of the form <timestamp>.
- B. Use a row key of the form <sensorid>.
- C. Use a row key of the form <timestamp>#<sensorid>.
- D. Use a row key of the form >#<sensorid>#<timestamp>.
Answer: D
Question 30
Your company’s customer and order databases are often under heavy load.
This makes performing analytics against them difficult without harming operations. The databases are in a MySQL cluster, with nightly backups taken using mysqldump. You want to perform analytics with minimal impact on operations.
What should you do?
- A. Add a node to the MySQL cluster and build an OLAP cube there.
- B. Use an ETL tool to load the data from MySQL into Google BigQuery.
- C. Connect an on-premises Apache Hadoop cluster to MySQL and perform ETL.
- D. Mount the backups to Google Cloud SQL, and then process the data using Google Cloud Dataproc.
Answer: B
Question 31
You have Google Cloud Dataflow streaming pipeline running with a Google Cloud Pub/Sub subscription as the source.
You need to make an update to the code that will make the new Cloud Dataflow pipeline incompatible with the current version. You do not want to lose any data when making this update.
What should you do?
- A. Update the current pipeline and use the drain flag.
- B. Update the current pipeline and provide the transform mapping JSON object.
- C. Create a new pipeline that has the same Cloud Pub/Sub subscription and cancel the old pipeline.
- D. Create a new pipeline that has a new Cloud Pub/Sub subscription and cancel the old pipeline.
Answer: A
Reference:
Update an existing pipeline | Cloud Dataflow
Question 32
Your company is running their first dynamic campaign, serving different offers by analyzing real-time data during the holiday season.
The data scientists are collecting terabytes of data that rapidly grows every hour during their 30-day campaign. They are using Google Cloud Dataflow to preprocess the data and collect the feature (signals) data that is needed for the machine learning model in Google Cloud Bigtable. The team is observing suboptimal performance with reads and writes of their initial load of 10 TB of data. They want to improve this performance while minimizing cost.
What should they do?
- A. Redefine the schema by evenly distributing reads and writes across the row space of the table.
- B. The performance issue should be resolved over time as the site of the BigDate cluster is increased.
- C. Redesign the schema to use a single row key to identify values that need to be updated frequently in the cluster.
- D. Redesign the schema to use row keys based on numeric IDs that increase sequentially per user viewing the offers.
Answer: A
Question 33
Your software uses a simple JSON format for all messages.
These messages are published to Google Cloud Pub/Sub, then processed with Google Cloud Dataflow to create a real-time dashboard for the CFO. During testing, you notice that some messages are missing in the dashboard. You check the logs, and all messages are being published to Cloud Pub/Sub successfully.
What should you do next?
- A. Check the dashboard application to see if it is not displaying correctly.
- B. Run a fixed dataset through the Cloud Dataflow pipeline and analyze the output.
- C. Use Google Stackdriver Monitoring on Cloud Pub/Sub to find the missing messages.
- D. Switch Cloud Dataflow to pull messages from Cloud Pub/Sub instead of Cloud Pub/Sub pushing messages to Cloud Dataflow.
Answer: B
Question 34
View Flowlogistic for a case study on this exam.
Flowlogistic wants to use Google BigQuery as their primary analysis system, but they still have Apache Hadoop and Spark workloads that they cannot move to BigQuery.
Flowlogistic does not know how to store the data that is common to both workloads.
What should they do?
- A. Store the common data in BigQuery as partitioned tables.
- B. Store the common data in BigQuery and expose authorized views.
- C. Store the common data encoded as Avro in Google Cloud Storage.
- D. Store the common data in the HDFS storage for a Google Cloud Dataproc cluster.
Answer: C
Question 35
View Flowlogistic for a case study on this exam.
Flowlogistic’s management has determined that the current Apache Kafka servers cannot handle the data volume for their real-time inventory tracking system.
You need to build a new system on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) that will feed the proprietary tracking software. The system must be able to ingest data from a variety of global sources, process and query in real-time, and store the data reliably.
Which combination of GCP products should you choose?
- A. Cloud Pub/Sub, Cloud Dataflow, and Cloud Storage
- B. Cloud Pub/Sub, Cloud Dataflow, and Local SSD
- C. Cloud Pub/Sub, Cloud SQL, and Cloud Storage
- D. Cloud Load Balancing, Cloud Dataflow, and Cloud Storage
Answer: A
Question 36
View Flowlogistic for a case study on this exam.
Flowlogistic’s CEO wants to gain rapid insight into their customer base so his sales team can be better informed in the field.
This team is not very technical, so they’ve purchased a visualization tool to simplify the creation of BigQuery reports. However, they’ve been overwhelmed by all the data in the table, and are spending a lot of money on queries trying to find the data they need. You want to solve their problem in the most cost-effective way.
What should you do?
- A. Export the data into a Google Sheet for virtualization.
- B. Create an additional table with only the necessary columns.
- C. Create a view on the table to present to the virtualization tool.
- D. Create identity and access management (IAM) roles on the appropriate columns, so only they appear in a query.
Answer: C
Question 37
View Flowlogistic for a case study on this exam.
Flowlogistic is rolling out their real-time inventory tracking system.
The tracking devices will all send package-tracking messages, which will now go to a single Google Cloud Pub/Sub topic instead of the Apache Kafka cluster. A subscriber application will then process the messages for real-time reporting and store them in Google BigQuery for historical analysis. You want to ensure the package data can be analyzed over time.
Which approach should you take?
- A. Attach the timestamp on each message in the Cloud Pub/Sub subscriber application as they are received.
- B. Attach the timestamp and Package ID on the outbound message from each publisher device as they are sent to Cloud Pub/Sub.
- C. Use the NOW () function in BigQuery to record the event’s time.
- D. Use the automatically generated timestamp from Cloud Pub/Sub to order the data.
Answer: B
Question 38
View MJTelco for a case study on this exam.
MJTelco’s Google Cloud Dataflow pipeline is now ready to start receiving data from the 50,000 installations.
You want to allow Cloud Dataflow to scale its compute power up as required.
Which Cloud Dataflow pipeline configuration setting should you update?
- A. The zone
- B. The number of workers
- C. The disk size per worker
- D. The maximum number of workers
Answer: D
Reference:
Pipeline options | Cloud Dataflow
Question 39
View MJTelco for a case study on this exam.
You need to compose visualizations for operations teams with the following requirements:
・The report must include telemetry data from all 50,000 installations for the most recent 6 weeks (sampling once every minute).
・The report must not be more than 3 hours delayed from live data.
・The actionable report should only show suboptimal links.
・Most suboptimal links should be sorted to the top.
・Suboptimal links can be grouped and filtered by regional geography.
・User response time to load the report must be <5 seconds.
Which approach meets the requirements?
- A. Load the data into Google Sheets, use formulas to calculate a metric, and use filters/sorting to show only suboptimal links in a table.
- B. Load the data into Google BigQuery tables, write Google Apps Script that queries the data, calculates the metric, and shows only suboptimal rows in a table in Google Sheets.
- C. Load the data into Google Cloud Datastore tables, write a Google App Engine Application that queries all rows, applies a function to derive the metric, and then renders results in a table using the Google charts and visualization API.
- D. Load the data into Google BigQuery tables, write a Google Data Studio 360 report that connects to your data, calculates a metric, and then uses a filter expression to show only suboptimal rows in a table.
Answer: D
Question 40
View MJTelco for a case study on this exam.
You create a new report for your large team in Google Data Studio 360. The report uses Google BigQuery as its data source.
It is company policy to ensure employees can view only the data associated with their region, so you create and populate a table for each region. You need to enforce the regional access policy to the data.
Which two actions should you take? (Choose two.)
- A. Ensure all the tables are included in the global dataset.
- B. Ensure each table is included in a dataset for a region.
- C. Adjust the settings for each table to allow a related region-based security group view access.
- D. Adjust the settings for each view to allow a related region-based security group view access.
- E. Adjust the settings for each dataset to allow a related region-based security group view access.
Answer: B, E
Question 41
View MJTelco for a case study on this exam.
MJTelco needs you to create a schema in Google Bigtable that will allow for the historical analysis of the last 2 years of records.
Each record that comes in is sent every 15 minutes, and contains a unique identifier of the device and a data record. The most common query is for all the data for a given device for a given day.
Which schema should you use?
- A. Rowkey: date#device_id Column data: data_point
- B. Rowkey: date Column data: device_id, data_point
- C. Rowkey: device_id Column data: date, data_point
- D. Rowkey: data_point Column data: device_id, date
- E. Rowkey: date#data_point Column data: device_id
Answer: A
Question 42
Your company has recently grown rapidly and now ingesting data at a significantly higher rate than it was previously.
You manage the daily batch MapReduce analytics jobs in Apache Hadoop. However, the recent increase in data has meant the batch jobs are falling behind. You were asked to recommend ways the development team could increase the responsiveness of the analytics without increasing costs.
What should you recommend they do?
- A. Rewrite the job in Pig.
- B. Rewrite the job in Apache Spark.
- C. Increase the size of the Hadoop cluster.
- D. Decrease the size of the Hadoop cluster but also rewrite the job in Hive.
Answer: B
Question 43
You work for a large fast food restaurant chain with over 400,000 employees.
You store employee information in Google BigQuery in a Users table consisting of a FirstName field and a LastName field. A member of IT is building an application and asks you to modify the schema and data in BigQuery so the application can query a FullName field consisting of the value of the FirstName field concatenated with a space, followed by the value of the LastName field for each employee.
How can you make that data available while minimizing cost?
- A. Create a view in BigQuery that concatenates the FirstName and LastName field values to produce the FullName.
- B. Add a new column called FullName to the Users table. Run an UPDATE statement that updates the FullName column for each user with the concatenation of the FirstName and LastName values.
- C. Create a Google Cloud Dataflow job that queries BigQuery for the entire Users table, concatenates the FirstName value and LastName value for each user, and loads the proper values for FirstName, LastName, and FullName into a new table in BigQuery.
- D. Use BigQuery to export the data for the table to a CSV file. Create a Google Cloud Dataproc job to process the CSV file and output a new CSV file containing the proper values for FirstName, LastName and FullName. Run a BigQuery load job to load the new CSV file into BigQuery.
Answer: B
Question 44
You are deploying a new storage system for your mobile application, which is a media streaming service.
You decide the best fit is Google Cloud Datastore. You have entities with multiple properties, some of which can take on multiple values. For example, in the entity Movie the property actors and the property tags have multiple values but the property date released does not. A typical query would ask for all movies with actor=<actorname> ordered by date_released or all movies with tag=Comedy ordered by date_released.
How should you avoid a combinatorial explosion in the number of indexes?
- A. Manually configure the index in your index config as follows:
Indexes:
-kind: Movie
Properties:
-name: actors
name date_released
-kind: Movie
Properties:
-name: tags
name: date_released- B. Manually configure the index in your index config as follows:
Indexes:
-kind: Movie
Properties:
-name: actors
-name: date_published- C. Set the following in your entity options: exclude_from_indexes = actors, tags
- D. Set the following in your entity options: exclude_from_indexes = date_published
Answer: A
Question 45
You work for a manufacturing plant that batches application log files together into a single log file once a day at 2:00 AM.
You have written a Google Cloud Dataflow job to process that log file. You need to make sure the log file is processed once per day as inexpensively as possible.
What should you do?
- A. Change the processing job to use Google Cloud Dataproc instead.
- B. Manually start the Cloud Dataflow job each morning when you get into the office.
- C. Create a cron job with Google App Engine Cron Service to run the Cloud Dataflow job.
- D. Configure the Cloud Dataflow job as a streaming job so that it processes the log data immediately.
Answer: C
Question 46
You work for an economic consulting firm that helps companies identify economic trends as they happen.
As part of your analysis, you use Google BigQuery to correlate customer data with the average prices of the 100 most common goods sold, including bread, gasoline, milk, and others. The average prices of these goods are updated every 30 minutes. You want to make sure this data stays up to date so you can combine it with other data in BigQuery as cheaply as possible.
What should you do?
- A. Load the data every 30 minutes into a new partitioned table in BigQuery.
- B. Store and update the data in a regional Google Cloud Storage bucket and create a federated data source in BigQuery
- C. Store the data in Google Cloud Datastore. Use Google Cloud Dataflow to query BigQuery and combine the data programmatically with the data stored in Cloud Datastore
- D. Store the data in a file in a regional Google Cloud Storage bucket. Use Cloud Dataflow to query BigQuery and combine the data programmatically with the data stored in Google Cloud Storage.
Answer: B
Question 47
You are designing the database schema for a machine learning-based food ordering service that will predict what users want to eat.
Here is some of the information you need to store:
・The user profile: What the user likes and doesn’t like to eat
・The user account information: Name, address, preferred meal times
・The order information: When orders are made, from where, to whom
The database will be used to store all the transactional data of the product. You want to optimize the data schema.
Which Google Cloud Platform product should you use?
- A. BigQuery
- B. Cloud SQL
- C. Cloud Bigtable
- D. Cloud Datastore
Answer: A
Question 48
Your company is loading comma-separated values (CSV) files into Google BigQuery.
The data is fully imported successfully; however, the imported data is not matching byte-to-byte to the source file.
What is the most likely cause of this problem?
- A. The CSV data loaded in BigQuery is not flagged as CSV.
- B. The CSV data has invalid rows that were skipped on import.
- C. The CSV data loaded in BigQuery is not using BigQuery’s default encoding.
- D. The CSV data has not gone through an ETL phase before loading into BigQuery.
Answer: C
Question 49
Your company produces 20,000 files every hour.
Each data file is formatted as a comma separated values (CSV) file that is less than 4 KB. All files must be ingested on Google Cloud Platform before they can be processed. Your company site has a 200 ms latency to Google Cloud, and your Internet connection bandwidth is limited as 50 Mbps. You currently deploy a secure FTP (SFTP) server on a virtual machine in Google Compute Engine as the data ingestion point. A local SFTP client runs on a dedicated machine to transmit the CSV files as is. The goal is to make reports with data from the previous day available to the executives by 10:00 a.m. each day. This design is barely able to keep up with the current volume, even though the bandwidth utilization is rather low.
You are told that due to seasonality, your company expects the number of files to double for the next three months.
Which two actions should you take? (Choose two.)
- A. Introduce data compression for each file to increase the rate file of file transfer.
- B. Contact your internet service provider (ISP) to increase your maximum bandwidth to at least 100 Mbps.
- C. Redesign the data ingestion process to use gsutil tool to send the CSV files to a storage bucket in parallel.
- D. Assemble 1,000 files into a tape archive (TAR) file. Transmit the TAR files instead, and disassemble the CSV files in the cloud upon receiving them.
- E. Create an S3-compatible storage endpoint in your network, and use Google Cloud Storage Transfer Service to transfer on-premises data to the designated storage bucket.
Answer: C, D
Question 50
You are choosing a NoSQL database to handle telemetry data submitted from millions of Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices.
The volume of data is growing at 100 TB per year, and each data entry has about 100 attributes. The data processing pipeline does not require atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability (ACID). However, high availability and low latency are required. You need to analyze the data by querying against individual fields.
Which three databases meet your requirements? (Choose three.)
- A. Redis
- B. HBase
- C. MySQL
- D. MongoDB
- E. Cassandra
- F. HDFS with Hive
Answer: B, D, E
Question 51
You are training a spam classifier.
You notice that you are overfitting the training data.
Which three actions can you take to resolve this problem? (Choose three.)
- A. Get more training examples
- B. Reduce the number of training examples
- C. Use a smaller set of features
- D. Use a larger set of features
- E. Increase the regularization parameters
- F. Decrease the regularization parameters
Answer: A, C, E
Question 52
You are implementing security best practices on your data pipeline.
Currently, you are manually executing jobs as the Project Owner. You want to automate these jobs by taking nightly batch files containing non-public information from Google Cloud Storage, processing them with a Spark Scala job on a Google Cloud Dataproc cluster, and depositing the results into Google BigQuery.
How should you securely run this workload?
- A. Restrict the Google Cloud Storage bucket so only you can see the files.
- B. Grant the Project Owner role to a service account, and run the job with it.
- C. Use a service account with the ability to read the batch files and to write to BigQuery.
- D. Use a user account with the Project Viewer role on the Cloud Dataproc cluster to read the batch files and write to BigQuery.
Answer: C
Question 53
You are using Google BigQuery as your data warehouse.
Your users report that the following simple query is running very slowly, no matter when they run the query:
SELECT country, state, city FROM [myproject:mydataset.mytable] GROUP BY country.
You check the query plan for the query and see the following output in the Read section of Stage:1:

What is the most likely cause of the delay for this query?
- A. Users are running too many concurrent queries in the system.
- B. The [myproject:mydataset.mytable] table has too many partitions.
- C. Either the state or the city columns in the [myproject:mydataset.mytable] table have too many NULL values.
- D. Most rows in the [myproject:mydataset.mytable] table have the same value in the country column, causing data skew.
Answer: D
Question 54
Your globally distributed auction application allows users to bid on items.
Occasionally, users place identical bids at nearly identical times, and different application servers process those bids. Each bid event contains the item, amount, user, and timestamp. You want to collate those bid events into a single location in real time to determine which user bid first.
What should you do?
- A. Create a file on a shared file and have the application servers write all bid events to that file. Process the file with Apache Hadoop to identify which user bid first.
- B. Have each application server write the bid events to Cloud Pub/Sub as they occur. Push the events from Cloud Pub/Sub to a custom endpoint that writes the bid event information into Cloud SQL.
- C. Set up a MySQL database for each application server to write bid events into. Periodically query each of those distributed MySQL databases and update a master MySQL database with bid event information.
- D. Have each application server write the bid events to Google Cloud Pub/Sub as they occur. Use a pull subscription to pull the bid events using Google Cloud Dataflow. Give the bid for each item to the user in the bid event that is processed first.
Answer: B
Question 55
Your organization has been collecting and analyzing data in Google BigQuery for 6 months.
The majority of the data analyzed is placed in a time-partitioned table named events_partitioned. To reduce the cost of queries, your organization created a view called events, which queries only the last 14 days of data. The view is described in legacy SQL. Next month, existing applications will be connecting to BigQuery to read the events data via an ODBC connection. You need to ensure the applications can connect.
Which two actions should you take? (Choose two.)
- A. Create a new view over events using standard SQL.
- B. Create a new partitioned table using a standard SQL query.
- C. Create a new view over events_partitioned using standard SQL.
- D. Create a service account for the ODBC connection to use for authentication.
- E. Create a Google Cloud Identity and Access Management (Cloud IAM) role for the ODBC connection and shared events.
Answer: C, D
Question 56
You have enabled the free integration between Firebase Analytics and Google BigQuery.
Firebase now automatically creates a new table daily in BigQuery in the format app_events_YYYYMMDD. You want to query all of the tables for the past 30 days in legacy SQL.
What should you do?
- A. Use the TABLE_DATE_RANGE function
- B. Use the WHERE_PARTITIONTIME pseudo column
- C. Use WHERE date BETWEEN YYYY-MM-DD AND YYYY-MM-DD
- D. Use SELECT IF.(date >= YYYY-MM-DD AND date <= YYYY-MM-DD
Answer: A
Reference:
Using BigQuery and Firebase Analytics to understand your mobile app | Google Cloud Blog
Question 57
Your company is currently setting up data pipelines for their campaign.
For all the Google Cloud Pub/Sub streaming data, one of the important business requirements is to be able to periodically identify the inputs and their timings during their campaign. Engineers have decided to use windowing and transformation in Google Cloud Dataflow for this purpose. However, when testing this feature, they find that the Cloud Dataflow job fails for the all streaming insert.
What is the most likely cause of this problem?
- A. They have not assigned the timestamp, which causes the job to fail.
- B. They have not set the triggers to accommodate the data coming in late, which causes the job to fail.
- C. They have not applied a global windowing function, which causes the job to fail when the pipeline is created.
- D. They have not applied a non-global windowing function, which causes the job to fail when the pipeline is created.
Answer: D
Question 58
You architect a system to analyze seismic data.
Your extract, transform, and load (ETL) process runs as a series of MapReduce jobs on an Apache Hadoop cluster. The ETL process takes days to process a data set because some steps are computationally expensive. Then you discover that a sensor calibration step has been omitted.
How should you change your ETL process to carry out sensor calibration systematically in the future?
- A. Modify the transformMapReduce jobs to apply sensor calibration before they do anything else.
- B. Introduce a new MapReduce job to apply sensor calibration to raw data, and ensure all other MapReduce jobs are chained after this.
- C. Add sensor calibration data to the output of the ETL process, and document that all users need to apply sensor calibration themselves.
- D. Develop an algorithm through simulation to predict variance of data output from the last MapReduce job based on calibration factors, and apply the correction to all data.
Answer: B
Question 59
An online retailer has built their current application on Google App Engine.
A new initiative at the company mandates that they extend their application to allow their customers to transact directly via the application. They need to manage their shopping transactions and analyze combined data from multiple datasets using a business intelligence (BI) tool. They want to use only a single database for this purpose.
Which Google Cloud database should they choose?
- A. BigQuery
- B. Cloud SQL
- C. Cloud BigTable
- D. Cloud Datastore
Answer: B
Question 60
You launched a new gaming app almost three years ago.
You have been uploading log files from the previous day to a separate Google BigQuery table with the table name format LOGS_yyyymmdd. You have been using table wildcard functions to generate daily and monthly reports for all time ranges. Recently, you discovered that some queries that cover long date ranges are exceeding the limit of 1,000 tables and failing.
How can you resolve this issue?
- A. Convert all daily log tables into date-partitioned tables.
- B. Convert the sharded tables into a single partitioned table.
- C. Enable query caching so you can cache data from previous months.
- D. Create separate views to cover each month, and query from these views.
Answer: B
Question 61
Your analytics team wants to build a simple statistical model to determine which customers are most likely to work with your company again, based on a few different metrics.
They want to run the model on Apache Spark, using data housed in Google Cloud Storage, and you have recommended using Google Cloud Dataproc to execute this job. Testing has shown that this workload can run in approximately 30 minutes on a 15-node cluster, outputting the results into Google BigQuery. The plan is to run this workload weekly.
How should you optimize the cluster for cost?
- A. Migrate the workload to Google Cloud Dataflow.
- B. Use preemptible virtual machines (VMs) for the cluster.
- C. Use a higher-memory node so that the job runs faster.
- D. Use SSDs on the worker nodes so that the job can run faster.
Answer: B
Question 62
Your company receives both batch- and stream-based event data.
You want to process the data using Google Cloud Dataflow over a predictable time period. However, you realize that in some instances data can arrive late or out of order.
How should you design your Cloud Dataflow pipeline to handle data that is late or out of order?
- A. Set a single global window to capture all the data.
- B. Set sliding windows to capture all the lagged data.
- C. Use watermarks and timestamps to capture the lagged data.
- D. Ensure every datasource type (stream or batch) has a timestamp, and use the timestamps to define the logic for lagged data.
Answer: C
Question 63
You have some data, which is shown in the graphic below.
The two dimensions are X and Y, and the shade of each dot represents what class it is. You want to classify this data accurately using a linear algorithm. To do this you need to add a synthetic feature.
What should the value of that feature be?
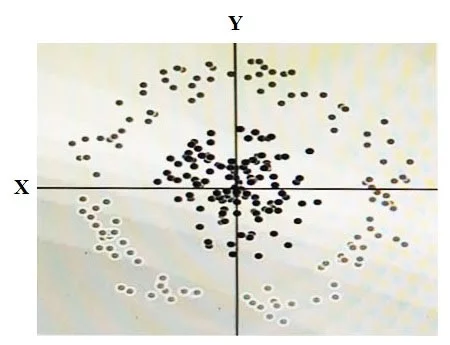
- A. X2+Y2
- B. X2
- C. Y2
- D. cos(X)
Answer: A
Question 64
You are integrating one of your internal IT applications and Google BigQuery, so users can query BigQuery from the application’s interface.
You do not want individual users to authenticate to BigQuery and you do not want to give them access to the dataset. You need to securely access BigQuery from your IT application.
What should you do?
- A. Create groups for your users and give those groups access to the dataset.
- B. Integrate with a single sign-on (SSO) platform, and pass each user’s credentials along with the query request.
- C. Create a service account and grant dataset access to that account. Use the service account’s private key to access the dataset.
- D. Create a dummy user and grant dataset access to that user. Store the username and password for that user in a file on the files system, and use those credentials to access the BigQuery dataset.
Answer: C
Question 65
You are building a data pipeline on Google Cloud.
You need to prepare data using a causal method for a machine-learning process. You want to support a logistic regression model. You also need to monitor and adjust for null values, which must remain real-valued and cannot be removed.
What should you do?
- A. Use Cloud Dataprep to find null values in sample source data. Convert all nulls to ‘none’ using a Cloud Dataproc job.
- B. Use Cloud Dataprep to find null values in sample source data. Convert all nulls to 0 using a Cloud Dataprep job.
- C. Use Cloud Dataflow to find null values in sample source data. Convert all nulls to ‘none’ using a Cloud Dataprep job.
- D. Use Cloud Dataflow to find null values in sample source data. Convert all nulls to 0 using a custom script.
Answer: B
Question 66
You set up a streaming data insert into a Redis cluster via a Kafka cluster.
Both clusters are running on Compute Engine instances. You need to encrypt data at rest with encryption keys that you can create, rotate, and destroy as needed.
What should you do?
- A. Create a dedicated service account, and use encryption at rest to reference your data stored in your Compute Engine cluster instances as part of your API service calls.
- B. Create encryption keys in Cloud Key Management Service. Use those keys to encrypt your data in all of the Compute Engine cluster instances.
- C. Create encryption keys locally. Upload your encryption keys to Cloud Key Management Service. Use those keys to encrypt your data in all of the Compute Engine cluster instances.
- D. Create encryption keys in Cloud Key Management Service. Reference those keys in your API service calls when accessing the data in your Compute Engine cluster instances.
Answer: B
Question 67
You are developing an application that uses a recommendation engine on Google Cloud.
Your solution should display new videos to customers based on past views. Your solution needs to generate labels for the entities in videos that the customer has viewed. Your design must be able to provide very fast filtering suggestions based on data from other customer preferences on several TB of data.
What should you do?
- A. Build and train a complex classification model with Spark MLlib to generate labels and filter the results. Deploy the models using Cloud Dataproc. Call the model from your application.
- B. Build and train a classification model with Spark MLlib to generate labels. Build and train a second classification model with Spark MLlib to filter results to match customer preferences. Deploy the models using Cloud Dataproc. Call the models from your application.
- C. Build an application that calls the Cloud Video Intelligence API to generate labels. Store data in Cloud Bigtable, and filter the predicted labels to match the user’s viewing history to generate preferences.
- D. Build an application that calls the Cloud Video Intelligence API to generate labels. Store data in Cloud SQL, and join and filter the predicted labels to match the user’s viewing history to generate preferences.
Answer: C
Question 68
You are selecting services to write and transform JSON messages from Cloud Pub/Sub to BigQuery for a data pipeline on Google Cloud.
You want to minimize service costs. You also want to monitor and accommodate input data volume that will vary in size with minimal manual intervention.
What should you do?
- A. Use Cloud Dataproc to run your transformations. Monitor CPU utilization for the cluster. Resize the number of worker nodes in your cluster via the command line.
- B. Use Cloud Dataproc to run your transformations. Use the diagnose command to generate an operational output archive. Locate the bottleneck and adjust cluster resources.
- C. Use Cloud Dataflow to run your transformations. Monitor the job system lag with Stackdriver. Use the default auto scaling setting for worker instances.
- D. Use Cloud Dataflow to run your transformations. Monitor the total execution time for a sampling of jobs. Configure the job to use non-default Compute Engine machine types when needed.
Answer: C
Question 69
Your infrastructure includes a set of YouTube channels.
You have been tasked with creating a process for sending the YouTube channel data to Google Cloud for analysis. You want to design a solution that allows your world-wide marketing teams to perform ANSI SQL and other types of analysis on up-to-date YouTube channels log data.
How should you set up the log data transfer into Google Cloud?
- A. Use Storage Transfer Service to transfer the offsite backup files to a Cloud Storage Multi-Regional storage bucket as a final destination.
- B. Use Storage Transfer Service to transfer the offsite backup files to a Cloud Storage Regional bucket as a final destination.
- C. Use BigQuery Data Transfer Service to transfer the offsite backup files to a Cloud Storage Multi-Regional storage bucket as a final destination.
- D. Use BigQuery Data Transfer Service to transfer the offsite backup files to a Cloud Storage Regional storage bucket as a final destination.
Answer: A
Question 70
You are designing storage for very large text files for a data pipeline on Google Cloud.
You want to support ANSI SQL queries. You also want to support compression and parallel load from the input locations using Google recommended practices.
What should you do?
- A. Transform text files to compressed Avro using Cloud Dataflow. Use BigQuery for storage and query.
- B. Transform text files to compressed Avro using Cloud Dataflow. Use Cloud Storage and BigQuery permanent linked tables for query.
- C. Compress text files to gzip using the Grid Computing Tools. Use BigQuery for storage and query.
- D. Compress text files to gzip using the Grid Computing Tools. Use Cloud Storage, and then import into Cloud Bigtable for query.
Answer: B
Question 71
You are developing an application on Google Cloud that will automatically generate subject labels for users’ blog posts.
You are under competitive pressure to add this feature quickly, and you have no additional developer resources. No one on your team has experience with machine learning.
What should you do?
- A. Call the Cloud Natural Language API from your application. Process the generated Entity Analysis as labels.
- B. Call the Cloud Natural Language API from your application. Process the generated Sentiment Analysis as labels.
- C. Build and train a text classification model using TensorFlow. Deploy the model using Cloud Machine Learning Engine. Call the model from your application and process the results as labels.
- D. Build and train a text classification model using TensorFlow. Deploy the model using a Kubernetes Engine cluster. Call the model from your application and process the results as labels.
Answer: A
Question 72
You are designing storage for 20 TB of text files as part of deploying a data pipeline on Google Cloud.
Your input data is in CSV format. You want to minimize the cost of querying aggregate values for multiple users who will query the data in Cloud Storage with multiple engines.
Which storage service and schema design should you use?
- A. Use Cloud Bigtable for storage. Install the HBase shell on a Compute Engine instance to query the Cloud Bigtable data.
- B. Use Cloud Bigtable for storage. Link as permanent tables in BigQuery for query.
- C. Use Cloud Storage for storage. Link as permanent tables in BigQuery for query.
- D. Use Cloud Storage for storage. Link as temporary tables in BigQuery for query.
Answer: C
Question 73
You are designing storage for two relational tables that are part of a 10-TB database on Google Cloud.
You want to support transactions that scale horizontally. You also want to optimize data for range queries on non-key columns.
What should you do?
- A. Use Cloud SQL for storage. Add secondary indexes to support query patterns.
- B. Use Cloud SQL for storage. Use Cloud Dataflow to transform data to support query patterns.
- C. Use Cloud Spanner for storage. Add secondary indexes to support query patterns.
- D. Use Cloud Spanner for storage. Use Cloud Dataflow to transform data to support query patterns.
Answer: C
Question 74
Your financial services company is moving to cloud technology and wants to store 50 TB of financial time-series data in the cloud.
This data is updated frequently and new data will be streaming in all the time. Your company also wants to move their existing Apache Hadoop jobs to the cloud to get insights into this data.
Which product should they use to store the data?
- A. Cloud Bigtable
- B. Google BigQuery
- C. Google Cloud Storage
- D. Google Cloud Datastore
Answer: A
Reference:
Schema design for time series data | Cloud Bigtable Documentation
Question 75
An organization maintains a Google BigQuery dataset that contains tables with user-level data.
They want to expose aggregates of this data to other Google Cloud projects, while still controlling access to the user-level data. Additionally, they need to minimize their overall storage cost and ensure the analysis cost for other projects is assigned to those projects.
What should they do?
- A. Create and share an authorized view that provides the aggregate results.
- B. Create and share a new dataset and view that provides the aggregate results.
- C. Create and share a new dataset and table that contains the aggregate results.
- D. Create dataViewer Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles on the dataset to enable sharing.
Answer: B
Reference:
Create an authorized view | BigQuery | Google Cloud
Question 76
Government regulations in your industry mandate that you have to maintain an auditable record of access to certain types of data.
Assuming that all expiring logs will be archived correctly, where should you store data that is subject to that mandate?
- A. Encrypted on Cloud Storage with user-supplied encryption keys. A separate decryption key will be given to each authorized user.
- B. In a BigQuery dataset that is viewable only by authorized personnel, with the Data Access log used to provide the auditability.
- C. In Cloud SQL, with separate database user names to each user. The Cloud SQL Admin activity logs will be used to provide the auditability.
- D. In a bucket on Cloud Storage that is accessible only by an AppEngine service that collects user information and logs the access before providing a link to the bucket.
Answer: B
Question 77
Your neural network model is taking days to train.
You want to increase the training speed.
What can you do?
- A. Subsample your test dataset.
- B. Subsample your training dataset.
- C. Increase the number of input features to your model.
- D. Increase the number of layers in your neural network.
Answer: B
Reference:
Improving the Performance of a Neural Network | by Rohith Gandhi | Towards Data Science
Question 78
You are responsible for writing your company’s ETL pipelines to run on an Apache Hadoop cluster.
The pipeline will require some checkpointing and splitting pipelines.
Which method should you use to write the pipelines?
- A. PigLatin using Pig
- B. HiveQL using Hive
- C. Java using MapReduce
- D. Python using MapReduce
Answer: A
Question 79
Your company maintains a hybrid deployment with GCP, where analytics are performed on your anonymized customer data.
The data is imported to Cloud Storage from your data center through parallel uploads to a data transfer server running on GCP. Management informs you that the daily transfers take too long and have asked you to fix the problem. You want to maximize transfer speeds.
Which action should you take?
- A. Increase the CPU size on your server.
- B. Increase the size of the Google Persistent Disk on your server.
- C. Increase your network bandwidth from your datacenter to GCP.
- D. Increase your network bandwidth from Compute Engine to Cloud Storage.
Answer: C
Question 80
View MJTelco for a case study on this exam.
MJTelco is building a custom interface to share data. They have these requirements:
1. They need to do aggregations over their petabyte-scale datasets.
2. They need to scan specific time range rows with a very fast response time (milliseconds).
Which combination of Google Cloud Platform products should you recommend?
- A. Cloud Datastore and Cloud Bigtable
- B. Cloud Bigtable and Cloud SQL
- C. BigQuery and Cloud Bigtable
- D. BigQuery and Cloud Storage
Answer: C
Question 81
View MJTelco for a case study on this exam.
You need to compose visualization for operations teams with the following requirements:
・Telemetry must include data from all 50,000 installations for the most recent 6 weeks (sampling once every minute)
・The report must not be more than 3 hours delayed from live data.
・The actionable report should only show suboptimal links.
・Most suboptimal links should be sorted to the top.
Suboptimal links can be grouped and filtered by regional geography.
・User response time to load the report must be <5 seconds.
You create a data source to store the last 6 weeks of data, and create visualizations that allow viewers to see multiple date ranges, distinct geographic regions, and unique installation types. You always show the latest data without any changes to your visualizations. You want to avoid creating and updating new visualizations each month.
What should you do?
- A. Look through the current data and compose a series of charts and tables, one for each possible combination of criteria.
- B. Look through the current data and compose a small set of generalized charts and tables bound to criteria filters that allow value selection.
- C. Export the data to a spreadsheet, compose a series of charts and tables, one for each possible combination of criteria, and spread them across multiple tabs.
- D. Load the data into relational database tables, write a Google App Engine application that queries all rows, summarizes the data across each criteria, and then renders results using the Google Charts and visualization API.
Answer: D
Question 82
View MJTelco for a case study on this exam.
Given the record streams MJTelco is interested in ingesting per day, they are concerned about the cost of Google BigQuery increasing.
MJTelco asks you to provide a design solution. They require a single large data table called tracking_table. Additionally, they want to minimize the cost of daily queries while performing fine-grained analysis of each day’s events. They also want to use streaming ingestion.
What should you do?
- A. Create a table called tracking_table and include a DATE column.
- B. Create a partitioned table called tracking_table and include a TIMESTAMP column.
- C. Create sharded tables for each day following the pattern tracking_table_YYYYMMDD.
- D. Create a table called tracking_table with a TIMESTAMP column to represent the day.
Answer: B
Question 83
View Flowlogistic for a case study on this exam.
Flowlogistic’s management has determined that the current Apache Kafka servers cannot handle the data volume for their real-time inventory tracking system.
You need to build a new system on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) that will feed the proprietary tracking software. The system must be able to ingest data from a variety of global sources, process and query in real-time, and store the data reliably.
Which combination of GCP products should you choose?
- A. Cloud Pub/Sub, Cloud Dataflow, and Cloud Storage
- B. Cloud Pub/Sub, Cloud Dataflow, and Local SSD
- C. Cloud Pub/Sub, Cloud SQL, and Cloud Storage
- D. Cloud Load Balancing, Cloud Dataflow, and Cloud Storage
- E. Cloud Dataflow, Cloud SQL, and Cloud Storage
Answer: A
Question 84
After migrating ETL jobs to run on BigQuery, you need to verify that the output of the migrated jobs is the same as the output of the original.
You’ve loaded a table containing the output of the original job and want to compare the contents with output from the migrated job to show that they are identical. The tables do not contain a primary key column that would enable you to join them together for comparison.
What should you do?
- A. Select random samples from the tables using the RAND() function and compare the samples.
- B. Select random samples from the tables using the HASH() function and compare the samples.
- C. Use a Dataproc cluster and the BigQuery Hadoop connector to read the data from each table and calculate a hash from non-timestamp columns of the table after sorting. Compare the hashes of each table.
- D. Create stratified random samples using the OVER() function and compare equivalent samples from each table.
Answer: C
Question 85
You are a head of BI at a large enterprise company with multiple business units that each have different priorities and budgets.
You use on-demand pricing for BigQuery with a quota of 2K concurrent on-demand slots per project. Users at your organization sometimes don’t get slots to execute their query and you need to correct this. You’d like to avoid introducing new projects to your account.
What should you do?
- A. Convert your batch BQ queries into interactive BQ queries.
- B. Create an additional project to overcome the 2K on-demand per-project quota.
- C. Switch to flat-rate pricing and establish a hierarchical priority model for your projects.
- D. Increase the amount of concurrent slots per project at the Quotas page at the Cloud Console.
Answer: C
Reference:
Busting 12 myths about BigQuery | Google Cloud Blog
Question 86
You have an Apache Kafka cluster on-prem with topics containing web application logs.
You need to replicate the data to Google Cloud for analysis in BigQuery and Cloud Storage. The preferred replication method is mirroring to avoid deployment of Kafka Connect plugins.
What should you do?
- A. Deploy a Kafka cluster on GCE VM Instances. Configure your on-prem cluster to mirror your topics to the cluster running in GCE. Use a Dataproc cluster or Dataflow job to read from Kafka and write to GCS.
- B. Deploy a Kafka cluster on GCE VM Instances with the Pub/Sub Kafka connector configured as a Sink connector. Use a Dataproc cluster or Dataflow job to read from Kafka and write to GCS.
- C. Deploy the Pub/Sub Kafka connector to your on-prem Kafka cluster and configure Pub/Sub as a Source connector. Use a Dataflow job to read from Pub/Sub and write to GCS.
- D. Deploy the Pub/Sub Kafka connector to your on-prem Kafka cluster and configure Pub/Sub as a Sink connector. Use a Dataflow job to read from Pub/Sub and write to GCS.
Answer: A
Question 87
You’ve migrated a Hadoop job from an on-prem cluster to dataproc and Google Cloud Storage.
Your Spark job is a complicated analytical workload that consists of many shuffling operations and initial data are parquet files (on average 200-400 MB size each). You see some degradation in performance after the migration to Dataproc, so you’d like to optimize for it. You need to keep in mind that your organization is very cost-sensitive, so you’d like to continue using Dataproc on preemptible (with 2 non-preemptible workers only) for this workload.
What should you do?
- A. Increase the size of your parquet files to ensure them to be 1 GB minimum.
- B. Switch to TFRecords formats (appr. 200MB per file) instead of parquet files.
- C. Switch from HDDs to SSDs, copy initial data from GCS to HDFS, run the Spark job and copy results back to GCS.
- D. Switch from HDDs to SSDs, override the preemptible VMs configuration to increase the boot disk size.
Answer: D
Question 88
Your team is responsible for developing and maintaining ETLs in your company.
One of your Dataflow jobs is failing because of some errors in the input data, and you need to improve reliability of the pipeline (incl. being able to reprocess all failing data).
What should you do?
- A. Add a filtering step to skip these types of errors in the future, extract erroneous rows from logs.
- B. Add a try catch block to your DoFn that transforms the data, extract erroneous rows from logs.
- C. Add a try catch block to your DoFn that transforms the data, write erroneous rows to Pub/Sub PubSub directly from the DoFn.
- D. Add a try catch block to your DoFn that transforms the data, use a sideOutput to create a PCollection that can be stored to Pub/Sub later.
Answer: C
Question 89
You’re training a model to predict housing prices based on an available dataset with real estate properties.
Your plan is to train a fully connected neural net, and you’ve discovered that the dataset contains latitude and longitude of the property. Real estate professionals have told you that the location of the property is highly influential on price, so you’d like to engineer a feature that incorporates this physical dependency.
What should you do?
- A. Provide latitude and longitude as input vectors to your neural net.
- B. Create a numeric column from a feature cross of latitude and longitude.
- C. Create a feature cross of latitude and longitude, bucketize it at the minute level and use L1 regularization during optimization.
- D. Create a feature cross of latitude and longitude, bucketize it at the minute level and use L2 regularization during optimization.
Answer: C
Reference:
Working with geospatial data | BigQuery | Google Cloud
Question 90
You are deploying MariaDB SQL databases on GCE VM Instances and need to configure monitoring and alerting.
You want to collect metrics including network connections, disk IO and replication status from MariaDB with minimal development effort and use StackDriver for dashboards and alerts.
What should you do?
- A. Install the OpenCensus Agent and create a custom metric collection application with a StackDriver exporter.
- B. Place the MariaDB instances in an Instance Group with a Health Check.
- C. Install the StackDriver Logging Agent and configure fluentd in_tail plugin to read MariaDB logs.
- D. Install the StackDriver Agent and configure the MySQL plugin.
Answer: D
Question 91
You work for a bank.
You have a labelled dataset that contains information on already granted loan applications and whether these applications have been defaulted. You have been asked to train a model to predict default rates for credit applicants.
What should you do?
- A. Increase the size of the dataset by collecting additional data.
- B. Train a linear regression to predict a credit default risk score.
- C. Remove the bias from the data and collect applications that have been declined loans.
- D. Match loan applicants with their social profiles to enable feature engineering.
Answer: B
Question 92
You need to migrate a 2TB relational database to Google Cloud Platform.
You do not have the resources to significantly refactor the application that uses this database and cost to operate is of primary concern.
Which service do you select for storing and serving your data?
- A. Cloud Spanner
- B. Cloud Bigtable
- C. Cloud Firestore
- D. Cloud SQL
Answer: D
Question 93
You’re using Bigtable for a real-time application, and you have a heavy load that is a mix of reads and writes.
You’ve recently identified an additional use case and need to perform an hourly analytical job to calculate certain statistics across the whole database. You need to ensure both the reliability of your production application as well as the analytical workload.
What should you do?
- A. Export Bigtable dump to GCS and run your analytical job on top of the exported files.
- B. Add a second cluster to an existing instance with a multi-cluster routing, use live-traffic app profile for your regular workload and batch-analytics profile for the analytics workload.
- C. Add a second cluster to an existing instance with a single-cluster routing, use live-traffic app profile for your regular workload and batch-analytics profile for the analytics workload.
- D. Increase the size of your existing cluster twice and execute your analytics workload on your new resized cluster.
Answer: C
Question 94
You are designing an Apache Beam pipeline to enrich data from Cloud Pub/Sub with static reference data from BigQuery.
The reference data is small enough to fit in memory on a single worker. The pipeline should write enriched results to BigQuery for analysis.
Which job type and transforms should this pipeline use?
- A. Batch job, PubSubIO, side-inputs
- B. Streaming job, PubSubIO, JdbcIO, side-outputs
- C. Streaming job, PubSubIO, BigQueryIO, side-inputs
- D. Streaming job, PubSubIO, BigQueryIO, side-outputs
Answer: C
Question 95
You have a data pipeline that writes data to Cloud Bigtable using well-designed row keys.
You want to monitor your pipeline to determine when to increase the size of your Cloud Bigtable cluster.
Which two actions can you take to accomplish this? (Choose two.)
- A. Review Key Visualizer metrics. Increase the size of the Cloud Bigtable cluster when the Read pressure index is above 100.
- B. Review Key Visualizer metrics. Increase the size of the Cloud Bigtable cluster when the Write pressure index is above 100.
- C. Monitor the latency of write operations. Increase the size of the Cloud Bigtable cluster when there is a sustained increase in write latency.
- D. Monitor storage utilization. Increase the size of the Cloud Bigtable cluster when utilization increases above 70% of max capacity.
- E. Monitor latency of read operations. Increasing the size of the Cloud Bigtable cluster of read operations takes longer than 100 ms.
Answer: C, D
Question 96
You want to analyze hundreds of thousands of social media posts daily at the lowest cost and with the fewest steps.
You have the following requirements:
・You will batch-load the posts once per day and run them through the Cloud Natural Language API.
・You will extract topics and sentiment from the posts.
・You must store the raw posts for archiving and reprocessing.
・You will create dashboards to be shared with people both inside and outside your organization.
You need to store both the data extracted from the API to perform analysis as well as the raw social media posts for historical archiving.
What should you do?
- A. Store the social media posts and the data extracted from the API in BigQuery.
- B. Store the social media posts and the data extracted from the API in Cloud SQL.
- C. Store the raw social media posts in Cloud Storage, and write the data extracted from the API into BigQuery.
- D. Feed social media posts into the API directly from the source, and write the extracted data from the API into BigQuery.
Answer: C
Question 97
You store historic data in Cloud Storage.
You need to perform analytics on the historic data. You want to use a solution to detect invalid data entries and perform data transformations that will not require programming or knowledge of SQL.
What should you do?
- A. Use Cloud Dataflow with Beam to detect errors and perform transformations.
- B. Use Cloud Dataprep with recipes to detect errors and perform transformations.
- C. Use Cloud Dataproc with a Hadoop job to detect errors and perform transformations.
- D. Use federated tables in BigQuery with queries to detect errors and perform transformations.
Answer: B
Question 98
Your company needs to upload their historic data to Cloud Storage.
The security rules don’t allow access from external IPs to their on-premises resources. After an initial upload, they will add new data from existing on-premises applications every day.
What should they do?
- A. Execute gsutil rsync from the on-premises servers.
- B. Use Dataflow and write the data to Cloud Storage.
- C. Write a job template in Dataproc to perform the data transfer.
- D. Install an FTP server on a Compute Engine VM to receive the files and move them to Cloud Storage.
Answer: A
Question 99
You have a query that filters a BigQuery table using a WHERE clause on timestamp and ID columns.
By using bq query `”-dry_run you learn that the query triggers a full scan of the table, even though the filter on timestamp and ID selects a tiny fraction of the overall data. You want to reduce the amount of data scanned by BigQuery with minimal changes to existing SQL queries.
What should you do?
- A. Create a separate table for each ID.
- B. Use the LIMIT keyword to reduce the number of rows returned.
- C. Recreate the table with a partitioning column and clustering column.
- D. Use the bq query –maximum_bytes_billed flag to restrict the number of bytes billed.
Answer: C
Question 100
You have a requirement to insert minute-resolution data from 50,000 sensors into a BigQuery table.
You expect significant growth in data volume and need the data to be available within 1 minute of ingestion for real-time analysis of aggregated trends.
What should you do?
- A. Use bq load to load a batch of sensor data every 60 seconds.
- B. Use a Cloud Dataflow pipeline to stream data into the BigQuery table.
- C. Use the INSERT statement to insert a batch of data every 60 seconds.
- D. Use the MERGE statement to apply updates in a batch every 60 seconds.
Answer: B
Question 101
You need to copy millions of sensitive patient records from a relational database to BigQuery.
The total size of the database is 10 TB. You need to design a solution that is secure and time-efficient.
What should you do?
- A. Export the records from the database as an Avro file. Upload the file to GCS using gsutil, and then load the Avro file into BigQuery using the BigQuery web UI in the GCP Console.
- B. Export the records from the database as an Avro file. Copy the file onto a Transfer Appliance and send it to Google, and then load the Avro file into BigQuery using the BigQuery web UI in the GCP Console.
- C. Export the records from the database into a CSV file. Create a public URL for the CSV file, and then use Storage Transfer Service to move the file to Cloud Storage. Load the CSV file into BigQuery using the BigQuery web UI in the GCP Console.
- D. Export the records from the database as an Avro file. Create a public URL for the Avro file, and then use Storage Transfer Service to move the file to Cloud Storage. Load the Avro file into BigQuery using the BigQuery web UI in the GCP Console.
Answer: B
Question 102
You need to create a near real-time inventory dashboard that reads the main inventory tables in your BigQuery data warehouse.
Historical inventory data is stored as inventory balances by item and location. You have several thousand updates to inventory every hour. You want to maximize performance of the dashboard and ensure that the data is accurate.
What should you do?
- A. Leverage BigQuery UPDATE statements to update the inventory balances as they are changing.
- B. Partition the inventory balance table by item to reduce the amount of data scanned with each inventory update.
- C. Use the BigQuery streaming the stream changes into a daily inventory movement table. Calculate balances in a view that joins it to the historical inventory balance table. Update the inventory balance table nightly.
- D. Use the BigQuery bulk loader to batch load inventory changes into a daily inventory movement table. Calculate balances in a view that joins it to the historical inventory balance table. Update the inventory balance table nightly.
Answer: A
Question 103
You have data stored in BigQuery.
The data in the BigQuery dataset must be highly available. You need to define a storage, backup, and recovery strategy of this data that minimizes cost.
How should you configure the BigQuery table that has a recovery point objective (RPO) of 30 days?
- A. Set the BigQuery dataset to be regional. In the event of an emergency, use a point-in-time snapshot to recover the data.
- B. Set the BigQuery dataset to be regional. Create a scheduled query to make copies of the data to tables suffixed with the time of the backup. In the event of an emergency, use the backup copy of the table.
- C. Set the BigQuery dataset to be multi-regional. In the event of an emergency, use a point-in-time snapshot to recover the data.
- D. Set the BigQuery dataset to be multi-regional. Create a scheduled query to make copies of the data to tables suffixed with the time of the backup. In the event of an emergency, use the backup copy of the table.
Answer: C
Question 104
You used Dataprep to create a recipe on a sample of data in a BigQuery table.
You want to reuse this recipe on a daily upload of data with the same schema, after the load job with variable execution time completes.
What should you do?
- A. Create a cron schedule in Dataprep.
- B. Create an App Engine cron job to schedule the execution of the Dataprep job.
- C. Export the recipe as a Dataprep template, and create a job in Cloud Scheduler.
- D. Export the Dataprep job as a Dataflow template, and incorporate it into a Composer job.
Answer: D
Question 105
You want to automate execution of a multi-step data pipeline running on Google Cloud.
The pipeline includes Dataproc and Dataflow jobs that have multiple dependencies on each other. You want to use managed services where possible, and the pipeline will run every day.
Which tool should you use?
- A. cron
- B. Cloud Composer
- C. Cloud Scheduler
- D. Workflow Templates on Dataproc
Answer: B
Question 106
You are managing a Cloud Dataproc cluster.
You need to make a job run faster while minimizing costs, without losing work in progress on your clusters.
What should you do?
- A. Increase the cluster size with more non-preemptible workers.
- B. Increase the cluster size with preemptible worker nodes, and configure them to forcefully decommission.
- C. Increase the cluster size with preemptible worker nodes, and use Cloud Stackdriver to trigger a script to preserve work.
- D. Increase the cluster size with preemptible worker nodes, and configure them to use graceful decommissioning.
Answer: D
Reference:
Dataproc Enhanced Flexibility Mode
Question 107
You work for a shipping company that uses handheld scanners to read shipping labels.
Your company has strict data privacy standards that require scanners to only transmit tracking numbers when events are sent to Kafka topics. A recent software update caused the scanners to accidentally transmit recipients’ personally identifiable information (PII) to analytics systems, which violates user privacy rules. You want to quickly build a scalable solution using cloud-native managed services to prevent exposure of PII to the analytics systems.
What should you do?
- A. Create an authorized view in BigQuery to restrict access to tables with sensitive data.
- B. Install a third-party data validation tool on Compute Engine virtual machines to check the incoming data for sensitive information.
- C. Use Cloud Logging to analyze the data passed through the total pipeline to identify transactions that may contain sensitive information.
- D. Build a Cloud Function that reads the topics and makes a call to the Cloud Data Loss Prevention (Cloud DLP) API. Use the tagging and confidence levels to either pass or quarantine the data in a bucket for review.
Answer: D
Question 108
You have developed three data processing jobs.
One executes a Cloud Dataflow pipeline that transforms data uploaded to Cloud Storage and writes results to BigQuery. The second ingests data from on-premises servers and uploads it to Cloud Storage. The third is a Cloud Dataflow pipeline that gets information from third-party data providers and uploads the information to Cloud Storage. You need to be able to schedule and monitor the execution of these three workflows and manually execute them when needed.
What should you do?
- A. Create a Direct Acyclic Graph in Cloud Composer to schedule and monitor the jobs.
- B. Use Stackdriver Monitoring and set up an alert with a Webhook notification to trigger the jobs.
- C. Develop an App Engine application to schedule and request the status of the jobs using GCP API calls.
- D. Set up cron jobs in a Compute Engine instance to schedule and monitor the pipelines using GCP API calls.
Answer: A
Question 109
You have Cloud Functions written in Node.js that pull messages from Cloud Pub/Sub and send the data to BigQuery.
You observe that the message processing rate on the Pub/Sub topic is orders of magnitude higher than anticipated, but there is no error logged in Cloud Logging.
What are the two most likely causes of this problem? (Choose two.)
- A. Publisher throughput quota is too small.
- B. Total outstanding messages exceed the 10-MB maximum.
- C. Error handling in the subscriber code is not handling run-time errors properly.
- D. The subscriber code cannot keep up with the messages.
- E. The subscriber code does not acknowledge the messages that it pulls.
Answer: C, E
Question 110
You are creating a new pipeline in Google Cloud to stream IoT data from Cloud Pub/Sub through Cloud Dataflow to BigQuery.
While previewing the data, you notice that roughly 2% of the data appears to be corrupt. You need to modify the Cloud Dataflow pipeline to filter out this corrupt data.
What should you do?
- A. Add a SideInput that returns a Boolean if the element is corrupt.
- B. Add a ParDo transform in Cloud Dataflow to discard corrupt elements.
- C. Add a Partition transform in Cloud Dataflow to separate valid data from corrupt data.
- D. Add a GroupByKey transform in Cloud Dataflow to group all of the valid data together and discard the rest.
Answer: B
Question 111
You have historical data covering the last three years in BigQuery and a data pipeline that delivers new data to BigQuery daily.
You have noticed that when the Data Science team runs a query filtered on a date column and limited to 30`”90 days of data, the query scans the entire table. You also noticed that your bill is increasing more quickly than you expected. You want to resolve the issue as cost-effectively as possible while maintaining the ability to conduct SQL queries.
What should you do?
- A. Re-create the tables using DDL. Partition the tables by a column containing a TIMESTAMP or DATE Type.
- B. Recommend that the Data Science team export the table to a CSV file on Cloud Storage and use Cloud Datalab to explore the data by reading the files directly.
- C. Modify your pipeline to maintain the last 3090 days of data in one table and the longer history in a different table to minimize full table scans over the entire history.
- D. Write an Apache Beam pipeline that creates a BigQuery table per day. Recommend that the Data Science team use wildcards on the table name suffixes to select the data they need.
Answer: A
Question 112
You operate a logistics company, and you want to improve event delivery reliability for vehicle-based sensors.
You operate small data centers around the world to capture these events, but leased lines that provide connectivity from your event collection infrastructure to your event processing infrastructure are unreliable, with unpredictable latency. You want to address this issue in the most cost-effective way.
What should you do?
- A. Deploy small Kafka clusters in your data centers to buffer events.
- B. Have the data acquisition devices publish data to Cloud Pub/Sub.
- C. Establish a Cloud Interconnect between all remote data centers and Google.
- D. Write a Cloud Dataflow pipeline that aggregates all data in session windows.
Answer: B
Question 113
You are a retailer that wants to integrate your online sales capabilities with different in-home assistants, such as Google Home.
You need to interpret customer voice commands and issue an order to the backend systems.
Which solutions should you choose?
- A. Speech-to-Text API
- B. Cloud Natural Language API
- C. Dialogflow Enterprise Edition
- D. AutoML Natural Language
Answer: C
Question 114
Your company has a hybrid cloud initiative.
You have a complex data pipeline that moves data between cloud provider services and leverages services from each of the cloud providers.
Which cloud-native service should you use to orchestrate the entire pipeline?
- A. Cloud Dataflow
- B. Cloud Composer
- C. Cloud Dataprep
- D. Cloud Dataproc
Answer: B
Question 115
You use a dataset in BigQuery for analysis.
You want to provide third-party companies with access to the same dataset. You need to keep the costs of data sharing low and ensure that the data is current.
Which solution should you choose?
- A. Use Analytics Hub to control data access, and provide third party companies with access to the dataset.
- B. Use Cloud Scheduler to export the data on a regular basis to Cloud Storage, and provide third-party companies with access to the bucket.
- C. Create a separate dataset in BigQuery that contains the relevant data to share, and provide third-party companies with access to the new dataset.
- D. Create a Dataflow job that reads the data in frequent time intervals, and writes it to the relevant BigQuery dataset or Cloud Storage bucket for third-party companies to use.
Answer: A
Question 116
Your company is in the process of migrating its on-premises data warehousing solutions to BigQuery.
The existing data warehouse uses trigger-based change data capture (CDC) to apply updates from multiple transactional database sources on a daily basis. With BigQuery, your company hopes to improve its handling of CDC so that changes to the source systems are available to query in BigQuery in near-real time using log-based CDC streams, while also optimizing for the performance of applying changes to the data warehouse.
Which two steps should they take to ensure that changes are available in the BigQuery reporting table with minimal latency while reducing compute overhead? (Choose two.)
- A. Perform a DML INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE to replicate each individual CDC record in real time directly on the reporting table.
- B. Insert each new CDC record and corresponding operation type to a staging table in real time.
- C. Periodically DELETE outdated records from the reporting table.
- D. Periodically use a DML MERGE to perform several DML INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE operations at the same time on the reporting table.
- E. Insert each new CDC record and corresponding operation type in real time to the reporting table, and use a materialized view to expose only the newest version of each unique record.
Answer: B, D
Question 117
You are designing a data processing pipeline.
The pipeline must be able to scale automatically as load increases. Messages must be processed at least once and must be ordered within windows of 1 hour.
How should you design the solution?
- A. Use Apache Kafka for message ingestion and use Cloud Dataproc for streaming analysis.
- B. Use Apache Kafka for message ingestion and use Cloud Dataflow for streaming analysis.
- C. Use Cloud Pub/Sub for message ingestion and Cloud Dataproc for streaming analysis.
- D. Use Cloud Pub/Sub for message ingestion and Cloud Dataflow for streaming analysis.
Answer: D
Question 118
You need to set access to BigQuery for different departments within your company.
Your solution should comply with the following requirements:
・Each department should have access only to their data.
・Each department will have one or more leads who need to be able to create and update tables and provide them to their team.
・Each department has data analysts who need to be able to query but not modify data.
How should you set access to the data in BigQuery?
- A. Create a dataset for each department. Assign the department leads the role of OWNER, and assign the data analysts the role of WRITER on their dataset.
- B. Create a dataset for each department. Assign the department leads the role of WRITER, and assign the data analysts the role of READER on their dataset.
- C. Create a table for each department. Assign the department leads the role of Owner, and assign the data analysts the role of Editor on the project the table is in.
- D. Create a table for each department. Assign the department leads the role of Editor, and assign the data analysts the role of Viewer on the project the table is in.
Answer: B
Question 119
You operate a database that stores stock trades and an application that retrieves average stock price for a given company over an adjustable window of time.
The data is stored in Cloud Bigtable where the datetime of the stock trade is the beginning of the row key. Your application has thousands of concurrent users, and you notice that performance is starting to degrade as more stocks are added.
What should you do to improve the performance of your application?
- A. Change the row key syntax in your Cloud Bigtable table to begin with the stock symbol.
- B. Change the row key syntax in your Cloud Bigtable table to begin with a random number per second.
- C. Change the data pipeline to use BigQuery for storing stock trades, and update your application.
- D. Use Cloud Dataflow to write a summary of each day’s stock trades to an Avro file on Cloud Storage. Update your application to read from Cloud Storage and Cloud Bigtable to compute the responses.
Answer: A
Question 120
You are operating a Cloud Dataflow streaming pipeline.
The pipeline aggregates events from a Cloud Pub/Sub subscription source, within a window, and sinks the resulting aggregation to a Cloud Storage bucket. The source has consistent throughput. You want to monitor an alert on behavior of the pipeline with Cloud Stackdriver to ensure that it is processing data.
Which Stackdriver alerts should you create?
- A. An alert based on a decrease of subscription/num_undelivered_messages for the source and a rate of change increase of instance/storage/ used_bytes for the destination.
- B. An alert based on an increase of subscription/num_undelivered_messages for the source and a rate of change decrease of instance/storage/ used_bytes for the destination.
- C. An alert based on a decrease of instance/storage/used_bytes for the source and a rate of change increase of subscription/ num_undelivered_messages for the destination.
- D. An alert based on an increase of instance/storage/used_bytes for the source and a rate of change decrease of subscription/ num_undelivered_messages for the destination.
Answer: B
Question 121
You currently have a single on-premises Kafka cluster in a data center in the us-east region that is responsible for ingesting messages from IoT devices globally.
Because large parts of the globe have poor internet connectivity, messages sometimes batch at the edge, come in all at once, and cause a spike in load on your Kafka cluster. This is becoming difficult to manage and prohibitively expensive.
What is the Google-recommended cloud native architecture for this scenario?
- A. Edge TPUs as sensor devices for storing and transmitting the messages.
- B. Cloud Dataflow connected to the Kafka cluster to scale the processing of incoming messages.
- C. An IoT gateway connected to Cloud Pub/Sub, with Cloud Dataflow to read and process the messages from Cloud Pub/Sub.
- D. A Kafka cluster virtualized on Compute Engine in us-east with Cloud Load Balancing to connect to the devices around the world.
Answer: C
Question 122
You decided to use Cloud Datastore to ingest vehicle telemetry data in real time.
You want to build a storage system that will account for the long-term data growth, while keeping the costs low. You also want to create snapshots of the data periodically, so that you can make a point-in-time (PIT) recovery, or clone a copy of the data for Cloud Datastore in a different environment. You want to archive these snapshots for a long time.
Which two methods can accomplish this? (Choose two.)
- A. Use managed export, and store the data in a Cloud Storage bucket using Nearline or Coldline class.
- B. Use managed export, and then import to Cloud Datastore in a separate project under a unique namespace reserved for that export.
- C. Use managed export, and then import the data into a BigQuery table created just for that export, and delete temporary export files.
- D. Write an application that uses Cloud Datastore client libraries to read all the entities. Treat each entity as a BigQuery table row via BigQuery streaming insert. Assign an export timestamp for each export, and attach it as an extra column for each row. Make sure that the BigQuery table is partitioned using the export timestamp column.
- E. Write an application that uses Cloud Datastore client libraries to read all the entities. Format the exported data into a JSON file. Apply compression before storing the data in Cloud Source Repositories.
Answer: A, B
Question 123
You need to create a data pipeline that copies time-series transaction data so that it can be queried from within BigQuery by your data science team for analysis.
Every hour, thousands of transactions are updated with a new status. The size of the initial dataset is 1.5 PB, and it will grow by 3 TB per day. The data is heavily structured, and your data science team will build machine learning models based on this data. You want to maximize performance and usability for your data science team.
Which two strategies should you adopt? (Choose two.)
- A. Denormalize the data as much as possible.
- B. Preserve the structure of the data as much as possible.
- C. Use BigQuery UPDATE to further reduce the size of the dataset.
- D. Develop a data pipeline where status updates are appended to BigQuery instead of updated.
- E. Copy a daily snapshot of transaction data to Cloud Storage and store it as an Avro file. Use BigQuery’s support for external data sources to query.
Answer: A, D
Question 124
You are designing a cloud-native historical data processing system to meet the following conditions:
・The data being analyzed is in CSV, Avro, and PDF formats and will be accessed by multiple analysis tools including Dataproc, BigQuery, and Compute Engine.
・A batch pipeline moves daily data.
・Performance is not a factor in the solution.
・The solution design should maximize availability.
How should you design data storage for this solution?
- A. Create a Dataproc cluster with high availability. Store the data in HDFS, and perform analysis as needed.
- B. Store the data in BigQuery. Access the data using the BigQuery Connector on Dataproc and Compute Engine.
- C. Store the data in a regional Cloud Storage bucket. Access the bucket directly using Dataproc, BigQuery, and Compute Engine.
- D. Store the data in a multi-regional Cloud Storage bucket. Access the data directly using Dataproc, BigQuery, and Compute Engine.
Answer: D
Question 125
You have a petabyte of analytics data and need to design a storage and processing platform for it.
You must be able to perform data warehouse-style analytics on the data in Google Cloud and expose the dataset as files for batch analysis tools in other cloud providers.
What should you do?
- A. Store and process the entire dataset in BigQuery.
- B. Store and process the entire dataset in Bigtable.
- C. Store the full dataset in BigQuery, and store a compressed copy of the data in a Cloud Storage bucket.
- D. Store the warm data as files in Cloud Storage, and store the active data in BigQuery. Keep this ratio as 80% warm and 20% active.
Answer: C
Question 126
You work for a manufacturing company that sources up to 750 different components, each from a different supplier.
You’ve collected a labeled dataset that has on average 1000 examples for each unique component. Your team wants to implement an app to help warehouse workers recognize incoming components based on a photo of the component. You want to implement the first working version of this app (as Proof-Of-Concept) within a few working days.
What should you do?
- A. Use Cloud Vision AutoML with the existing dataset.
- B. Use Cloud Vision AutoML, but reduce your dataset twice.
- C. Use Cloud Vision API by providing custom labels as recognition hints.
- D. Train your own image recognition model leveraging transfer learning techniques.
Answer: A
Question 127
You are working on a niche product in the image recognition domain.
Your team has developed a model that is dominated by custom C++ TensorFlow ops your team has implemented. These ops are used inside your main training loop and are performing bulky matrix multiplications. It currently takes up to several days to train a model. You want to decrease this time significantly and keep the cost low by using an accelerator on Google Cloud.
What should you do?
- A. Use Cloud TPUs without any additional adjustment to your code.
- B. Use Cloud TPUs after implementing GPU kernel support for your customs ops.
- C. Use Cloud GPUs after implementing GPU kernel support for your customs ops.
- D. Stay on CPUs, and increase the size of the cluster you’re training your model on.
Answer: D
Question 128
You work on a regression problem in a natural language processing domain, and you have 100M labeled examples in your dataset.
You have randomly shuffled your data and split your dataset into train and test samples (in a 90/10 ratio). After you trained the neural network and evaluated your model on a test set, you discover that the root-mean-squared error (RMSE) of your model is twice as high on the train set as on the test set.
How should you improve the performance of your model?
- A. Increase the share of the test sample in the train-test split.
- B. Try to collect more data and increase the size of your dataset.
- C. Try out regularization techniques (e.g., dropout of batch normalization) to avoid overfitting.
- D. Increase the complexity of your model by, e.g., introducing an additional layer or increasing the size of vocabularies or n-grams used.
Answer: D
Question 129
You use BigQuery as your centralized analytics platform.
New data is loaded every day, and an ETL pipeline modifies the original data and prepares it for the final users. This ETL pipeline is regularly modified and can generate errors, but sometimes the errors are detected only after 2 weeks. You need to provide a method to recover from these errors, and your backups should be optimized for storage costs.
How should you organize your data in BigQuery and store your backups?
- A. Organize your data in a single table, export, and compress and store the BigQuery data in Cloud Storage.
- B. Organize your data in separate tables for each month, and export, compress, and store the data in Cloud Storage.
- C. Organize your data in separate tables for each month, and duplicate your data on a separate dataset in BigQuery.
- D. Organize your data in separate tables for each month, and use snapshot decorators to restore the table to a time prior to the corruption.
Answer: B
Question 130
The marketing team at your organization provides regular updates of a segment of your customer dataset.
The marketing team has given you a CSV with 1 million records that must be updated in BigQuery. When you use the UPDATE statement in BigQuery, you receive a quotaExceeded error.
What should you do?
- A. Reduce the number of records updated each day to stay within the BigQuery UPDATE DML statement limit.
- B. Increase the BigQuery UPDATE DML statement limit in the Quota management section of the Google Cloud Platform Console.
- C. Split the source CSV file into smaller CSV files in Cloud Storage to reduce the number of BigQuery UPDATE DML statements per BigQuery job.
- D. Import the new records from the CSV file into a new BigQuery table. Create a BigQuery job that merges the new records with the existing records and writes the results to a new BigQuery table.
Answer: D
Question 131
As your organization expands its usage of GCP, many teams have started to create their own projects.
Projects are further multiplied to accommodate different stages of deployments and target audiences. Each project requires unique access control configurations. The central IT team needs to have access to all projects. Furthermore, data from Cloud Storage buckets and BigQuery datasets must be shared for use in other projects in an ad hoc way. You want to simplify access control management by minimizing the number of policies.
Which two steps should you take? (Choose two.)
- A. Use Cloud Deployment Manager to automate access provision.
- B. Introduce resource hierarchy to leverage access control policy inheritance.
- C. Create distinct groups for various teams, and specify groups in Cloud IAM policies.
- D. Only use service accounts when sharing data for Cloud Storage buckets and BigQuery datasets.
- E. For each Cloud Storage bucket or BigQuery dataset, decide which projects need access. Find all the active members who have access to these projects, and create a Cloud IAM policy to grant access to all these users.
Answer: B, C
Question 132
Your United States-based company has created an application for assessing and responding to user actions.
The primary table’s data volume grows by 250,000 records per second. Many third parties use your application’s APIs to build the functionality into their own frontend applications. Your application’s APIs should comply with the following requirements:
・Single global endpoint
・ANSI SQL support
・Consistent access to the most up-to-date data
What should you do?
- A. Implement BigQuery with no region selected for storage or processing.
- B. Implement Cloud Spanner with the leader in North America and read-only replicas in Asia and Europe.
- C. Implement Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL with the master in North America and read replicas in Asia and Europe.
- D. Implement Bigtable with the primary cluster in North America and secondary clusters in Asia and Europe.
Answer: B
Question 133
A data scientist has created a BigQuery ML model and asks you to create an ML pipeline to serve predictions.
You have a REST API application with the requirement to serve predictions for an individual user ID with latency under 100 milliseconds. You use the following query to generate predictions: SELECT predicted_label, user_id FROM ML.PREDICT (MODEL ‘dataset.model’, table user_features).
How should you create the ML pipeline?
- A. Add a WHERE clause to the query, and grant the BigQuery Data Viewer role to the application service account.
- B. Create an Authorized View with the provided query. Share the dataset that contains the view with the application service account.
- C. Create a Dataflow pipeline using BigQueryIO to read results from the query. Grant the Dataflow Worker role to the application service account.
- D. Create a Dataflow pipeline using BigQueryIO to read predictions for all users from the query. Write the results to Bigtable using BigtableIO. Grant the Bigtable Reader role to the application service account so that the application can read predictions for individual users from Bigtable.
Answer: D
Question 134
You are building an application to share financial market data with consumers, who will receive data feeds.
Data is collected from the markets in real time. Consumers will receive the data in the following ways:
・Real-time event stream
・ANSI SQL access to real-time stream and historical data
・Batch historical exports
Which solution should you use?
- A. Cloud Dataflow, Cloud SQL, Cloud Spanner
- B. Cloud Pub/Sub, Cloud Storage, BigQuery
- C. Cloud Dataproc, Cloud Dataflow, BigQuery
- D. Cloud Pub/Sub, Cloud Dataproc, Cloud SQL
Answer: B
Question 135
You are building a new application that you need to collect data from in a scalable way.
Data arrives continuously from the application throughout the day, and you expect to generate approximately 150 GB of JSON data per day by the end of the year. Your requirements are:
・Decoupling producer from consumer
・Space and cost-efficient storage of the raw ingested data, which is to be stored indefinitely
・Near real-time SQL query
・Maintain at least 2 years of historical data, which will be queried with SQL
Which pipeline should you use to meet these requirements?
- A. Create an application that provides an API. Write a tool to poll the API and write data to Cloud Storage as gzipped JSON files.
- B. Create an application that writes to a Cloud SQL database to store the data. Set up periodic exports of the database to write to Cloud Storage and load into BigQuery.
- C. Create an application that publishes events to Cloud Pub/Sub, and create Spark jobs on Cloud Dataproc to convert the JSON data to Avro format, stored on HDFS on Persistent Disk.
- D. Create an application that publishes events to Cloud Pub/Sub, and create a Cloud Dataflow pipeline that transforms the JSON event payloads to Avro, writing the data to Cloud Storage and BigQuery.
Answer: D
Question 136
You are running a pipeline in Dataflow that receives messages from a Pub/Sub topic and writes the results to a BigQuery dataset in the EU.
Currently, your pipeline is located in europe-west4 and has a maximum of 3 workers, instance type n1-standard-1. You notice that during peak periods, your pipeline is struggling to process records in a timely fashion, when all 3 workers are at maximum CPU utilization.
Which two actions can you take to increase performance of your pipeline? (Choose two.)
- A. Increase the number of max workers.
- B. Use a larger instance type for your Dataflow workers.
- C. Change the zone of your Dataflow pipeline to run in us-central1.
- D. Create a temporary table in Bigtable that will act as a buffer for new data. Create a new step in your pipeline to write to this table first, and then create a new pipeline to write from Bigtable to BigQuery.
- E. Create a temporary table in Cloud Spanner that will act as a buffer for new data. Create a new step in your pipeline to write to this table first, and then create a new pipeline to write from Cloud Spanner to BigQuery.
Answer: A, B
Question 137
You have a data pipeline with a Dataflow job that aggregates and writes time series metrics to Bigtable.
You notice that data is slow to update in Bigtable. This data feeds a dashboard used by thousands of users across the organization. You need to support additional concurrent users and reduce the amount of time required to write the data.
Which two actions should you take? (Choose two.)
- A. Configure your Dataflow pipeline to use local execution.
- B. Increase the maximum number of Dataflow workers by setting maxNumWorkers in PipelineOptions.
- C. Increase the number of nodes in the Bigtable cluster.
- D. Modify your Dataflow pipeline to use the Flatten transform before writing to Bigtable.
- E. Modify your Dataflow pipeline to use the CoGroupByKey transform before writing to Bigtable.
Answer: B, C
Reference:
Understand performance | Cloud Bigtable Documentation
Question 138
You have several Spark jobs that run on a Cloud Dataproc cluster on a schedule. Some of the jobs run in sequence, and some of the jobs run concurrently.
You need to automate this process.
What should you do?
- A. Create a Cloud Dataproc Workflow Template.
- B. Create an initialization action to execute the jobs.
- C. Create a Directed Acyclic Graph in Cloud Composer.
- D. Create a Bash script that uses the Cloud SDK to create a cluster, execute jobs, and then tear down the cluster.
Answer: C
Reference:
Use workflows | Dataproc Documentation | Google Cloud
Question 139
You are building a new data pipeline to share data between two different types of applications: jobs generators and job runners.
Your solution must scale to accommodate increases in usage and must accommodate the addition of new applications without negatively affecting the performance of existing ones.
What should you do?
- A. Create an API using App Engine to receive and send messages to the applications.
- B. Use a Cloud Pub/Sub topic to publish jobs, and use subscriptions to execute them.
- C. Create a table on Cloud SQL, and insert and delete rows with the job information.
- D. Create a table on Cloud Spanner, and insert and delete rows with the job information.
Answer: B
Question 140
You need to create a new transaction table in Cloud Spanner that stores product sales data.
You are deciding what to use as a primary key.
From a performance perspective, which strategy should you choose?
- A. The current epoch time.
- B. A concatenation of the product name and the current epoch time.
- C. A random universally unique identifier number (version 4 UUID).
- D. The original order identification number from the sales system, which is a monotonically increasing integer.
Answer: C
Question 141
Data Analysts in your company have the Cloud IAM Owner role assigned to them in their projects to allow them to work with multiple GCP products in their projects.
Your organization requires that all BigQuery data access logs be retained for 6 months. You need to ensure that only audit personnel in your company can access the data access logs for all projects.
What should you do?
- A. Enable data access logs in each Data Analyst’s project. Restrict access to Stackdriver Logging via Cloud IAM roles.
- B. Export the data access logs via a project-level export sink to a Cloud Storage bucket in the Data Analysts’ projects. Restrict access to the Cloud Storage bucket.
- C. Export the data access logs via a project-level export sink to a Cloud Storage bucket in newly created projects for audit logs. Restrict access to the project with the exported logs.
- D. Export the data access logs via an aggregated export sink to a Cloud Storage bucket in a newly created project for audit logs. Restrict access to the project that contains the exported logs.
Answer: D
Question 142
Each analytics team in your organization is running BigQuery jobs in their own projects.
You want to enable each team to monitor slot usage within their projects.
What should you do?
- A. Create a Cloud Monitoring dashboard based on the BigQuery metric query/scanned_bytes.
- B. Create a Cloud Monitoring dashboard based on the BigQuery metric slots/allocated_for_project.
- C. Create a log export for each project, capture the BigQuery job execution logs, create a custom metric based on the totalSlotMs, and create a Cloud Monitoring dashboard based on the custom metric.
- D. Create an aggregated log export at the organization level, capture the BigQuery job execution logs, create a custom metric based on the totalSlotMs, and create a Cloud Monitoring dashboard based on the custom metric.
Answer: B
Question 143
You are operating a streaming Cloud Dataflow pipeline.
Your engineers have a new version of the pipeline with a different windowing algorithm and triggering strategy. You want to update the running pipeline with the new version. You want to ensure that no data is lost during the update.
What should you do?
- A. Update the Cloud Dataflow pipeline inflight by passing the –update option with the –jobName set to the existing job name
- B. Update the Cloud Dataflow pipeline inflight by passing the –update option with the –jobName set to a new unique job name
- C. Stop the Cloud Dataflow pipeline with the Cancel option. Create a new Cloud Dataflow job with the updated code
- D. Stop the Cloud Dataflow pipeline with the Drain option. Create a new Cloud Dataflow job with the updated code
Answer: D
Reference:
Update an existing pipeline | Cloud Dataflow
Question 144
You need to move 2 PB of historical data from an on-premises storage appliance to Cloud Storage within six months, and your outbound network capacity is constrained to 20 Mb/sec.
How should you migrate this data to Cloud Storage?
- A. Use Transfer Appliance to copy the data to Cloud Storage.
- B. Use gsutil cp J to compress the content being uploaded to Cloud Storage.
- C. Create a private URL for the historical data, and then use Storage Transfer Service to copy the data to Cloud Storage.
- D. Use trickle or ionice along with gsutil cp to limit the amount of bandwidth gsutil utilizes to less than 20 Mb/sec so it does not interfere with the production traffic.
Answer: A
Question 145
You receive data files in CSV format monthly from a third party.
You need to cleanse this data, but every third month the schema of the files changes. Your requirements for implementing these transformations include:
・Executing the transformations on a schedule
・Enabling non-developer analysts to modify transformations
・Providing a graphical tool for designing transformations
What should you do?
- A. Use Dataprep by Trifacta to build and maintain the transformation recipes, and execute them on a scheduled basis.
- B. Load each month’s CSV data into BigQuery, and write a SQL query to transform the data to a standard schema. Merge the transformed tables together with a SQL query.
- C. Help the analysts write a Dataflow pipeline in Python to perform the transformation. The Python code should be stored in a revision control system and modified as the incoming data’s schema changes.
- D. Use Apache Spark on Dataproc to infer the schema of the CSV file before creating a Dataframe. Then implement the transformations in Spark SQL before writing the data out to Cloud Storage and loading into BigQuery.
Answer: A
Question 146
You want to migrate an on-premises Hadoop system to Cloud Dataproc.
Hive is the primary tool in use, and the data format is Optimized Row Columnar (ORC). All ORC files have been successfully copied to a Cloud Storage bucket. You need to replicate some data to the cluster’s local Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) to maximize performance.
What are two ways to start using Hive in Cloud Dataproc? (Choose two.)
- A. Run the gsutil utility to transfer all ORC files from the Cloud Storage bucket to HDFS. Mount the Hive tables locally.
- B. Run the gsutil utility to transfer all ORC files from the Cloud Storage bucket to any node of the Dataproc cluster. Mount the Hive tables locally.
- C. Run the gsutil utility to transfer all ORC files from the Cloud Storage bucket to the master node of the Dataproc cluster. Then run the Hadoop utility to copy them to HDFS. Mount the Hive tables from HDFS.
- D. Leverage Cloud Storage connector for Hadoop to mount the ORC files as external Hive tables. Replicate external Hive tables to the native ones.
- E. Load the ORC files into BigQuery. Leverage BigQuery connector for Hadoop to mount the BigQuery tables as external Hive tables. Replicate external Hive tables to the native ones.
Answer: C, D
Question 147
You are implementing several batch jobs that must be executed on a schedule.
These jobs have many interdependent steps that must be executed in a specific order. Portions of the jobs involve executing shell scripts, running Hadoop jobs, and running queries in BigQuery. The jobs are expected to run for many minutes up to several hours. If the steps fail, they must be retried a fixed number of times.
Which service should you use to manage the execution of these jobs?
- A. Cloud Scheduler
- B. Cloud Dataflow
- C. Cloud Functions
- D. Cloud Composer
Answer: D
Question 148
You work for a shipping company that has distribution centers where packages move on delivery lines to route them properly.
The company wants to add cameras to the delivery lines to detect and track any visual damage to the packages in transit. You need to create a way to automate the detection of damaged packages and flag them for human review in real time while the packages are in transit.
Which solution should you choose?
- A. Use BigQuery machine learning to be able to train the model at scale, so you can analyze the packages in batches.
- B. Train an AutoML model on your corpus of images, and build an API around that model to integrate with the package tracking applications.
- C. Use the Cloud Vision API to detect for damage, and raise an alert through Cloud Functions. Integrate the package tracking applications with this function.
- D. Use TensorFlow to create a model that is trained on your corpus of images. Create a Python notebook in Cloud Datalab that uses this model so you can analyze for damaged packages.
Answer: B
Question 149
You are migrating your data warehouse to BigQuery.
You have migrated all of your data into tables in a dataset. Multiple users from your organization will be using the data. They should only see certain tables based on their team membership.
How should you set user permissions?
- A. Assign the users/groups data viewer access at the table level for each table.
- B. Create SQL views for each team in the same dataset in which the data resides, and assign the users/groups data viewer access to the SQL views.
- C. Create authorized views for each team in the same dataset in which the data resides, and assign the users/groups data viewer access to the authorized views.
- D. Create authorized views for each team in datasets created for each team. Assign the authorized views data viewer access to the dataset in which the data resides. Assign the users/groups data viewer access to the datasets in which the authorized views reside.
Answer: A
Question 150
You want to build a managed Hadoop system as your data lake.
The data transformation process is composed of a series of Hadoop jobs executed in sequence. To accomplish the design of separating storage from compute, you decided to use the Cloud Storage connector to store all input data, output data, and intermediary data. However, you noticed that one Hadoop job runs very slowly with Cloud Dataproc, when compared with the on-premises bare-metal Hadoop environment (8-core nodes with 100-GB RAM). Analysis shows that this particular Hadoop job is disk I/O intensive. You want to resolve the issue.
What should you do?
- A. Allocate sufficient memory to the Hadoop cluster, so that the intermediary data of that particular Hadoop job can be held in memory.
- B. Allocate sufficient persistent disk space to the Hadoop cluster, and store the intermediate data of that particular Hadoop job on native HDFS.
- C. Allocate more CPU cores of the virtual machine instances of the Hadoop cluster so that the networking bandwidth for each instance can scale up.
- D. Allocate additional network interface card (NIC), and configure link aggregation in the operating system to use the combined throughput when working with Cloud Storage.
Answer: B
Question 151
You work for an advertising company, and you’ve developed a Spark ML model to predict click-through rates at advertisement blocks.
You’ve been developing everything at your on-premises data center, and now your company is migrating to Google Cloud. Your data center will be closing soon, so a rapid lift-and-shift migration is necessary. However, the data you’ve been using will be migrated to BigQuery. You periodically retrain your Spark ML models, so you need to migrate existing training pipelines to Google Cloud.
What should you do?
- A. Use Vertex AI for training existing Spark ML models.
- B. Rewrite your models on TensorFlow, and start using Vertex AI.
- C. Use Dataproc for training existing Spark ML models, but start reading data directly from BigQuery.
- D. Spin up a Spark cluster on Compute Engine, and train Spark ML models on the data exported from BigQuery.
Answer: C
Question 152
You work for a global shipping company.
You want to train a model on 40 TB of data to predict which ships in each geographic region are likely to cause delivery delays on any given day. The model will be based on multiple attributes collected from multiple sources. Telemetry data, including location in GeoJSON format, will be pulled from each ship and loaded every hour. You want to have a dashboard that shows how many and which ships are likely to cause delays within a region. You want to use a storage solution that has native functionality for prediction and geospatial processing.
Which storage solution should you use?
- A. BigQuery
- B. Cloud Bigtable
- C. Cloud Datastore
- D. Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL
Answer: A
Question 153
You operate an IoT pipeline built around Apache Kafka that normally receives around 5000 messages per second.
You want to use Google Cloud Platform to create an alert as soon as the moving average over 1 hour drops below 4000 messages per second.
What should you do?
- A. Consume the stream of data in Dataflow using Kafka IO. Set a sliding time window of 1 hour every 5 minutes. Compute the average when the window closes, and send an alert if the average is less than 4000 messages.
- B. Consume the stream of data in Dataflow using Kafka IO. Set a fixed time window of 1 hour. Compute the average when the window closes, and send an alert if the average is less than 4000 messages.
- C. Use Kafka Connect to link your Kafka message queue to Pub/Sub. Use a Dataflow template to write your messages from Pub/Sub to Bigtable. Use Cloud Scheduler to run a script every hour that counts the number of rows created in Bigtable in the last hour. If that number falls below 4000, send an alert.
- D. Use Kafka Connect to link your Kafka message queue to Pub/Sub. Use a Dataflow template to write your messages from Pub/Sub to BigQuery. Use Cloud Scheduler to run a script every five minutes that counts the number of rows created in BigQuery in the last hour. If that number falls below 4000, send an alert.
Answer: A
Question 154
You plan to deploy Cloud SQL using MySQL.
You need to ensure high availability in the event of a zone failure.
What should you do?
- A. Create a Cloud SQL instance in one zone, and create a failover replica in another zone within the same region.
- B. Create a Cloud SQL instance in one zone, and create a read replica in another zone within the same region.
- C. Create a Cloud SQL instance in one zone, and configure an external read replica in a zone in a different region.
- D. Create a Cloud SQL instance in a region, and configure automatic backup to a Cloud Storage bucket in the same region.
Answer: A
Question 155
Your company is selecting a system to centralize data ingestion and delivery.
You are considering messaging and data integration systems to address the requirements. The key requirements are:
・The ability to seek to a particular offset in a topic, possibly back to the start of all data ever captured
・Support for publish/subscribe semantics on hundreds of topics
・Retain per-key ordering
Which system should you choose?
- A. Apache Kafka
- B. Cloud Storage
- C. Dataflow
- D. Firebase Cloud Messaging
Answer: A
Question 156
You are planning to migrate your current on-premises Apache Hadoop deployment to the cloud.
You need to ensure that the deployment is as fault-tolerant and cost-effective as possible for long-running batch jobs. You want to use a managed service.
What should you do?
- A. Deploy a Dataproc cluster. Use a standard persistent disk and 50% preemptible workers. Store data in Cloud Storage, and change references in scripts from hdfs:// to gs://
- B. Deploy a Dataproc cluster. Use an SSD persistent disk and 50% preemptible workers. Store data in Cloud Storage, and change references in scripts from hdfs:// to gs://
- C. Install Hadoop and Spark on a 10-node Compute Engine instance group with standard instances. Install the Cloud Storage connector, and store the data in Cloud Storage. Change references in scripts from hdfs:// to gs://
- D. Install Hadoop and Spark on a 10-node Compute Engine instance group with preemptible instances. Store data in HDFS. Change references in scripts from hdfs:// to gs://
Answer: A
Question 157
Your team is working on a binary classification problem.
You have trained a support vector machine (SVM) classifier with default parameters, and received an area under the Curve (AUC) of 0.87 on the validation set. You want to increase the AUC of the model.
What should you do?
- A. Perform hyperparameter tuning.
- B. Train a classifier with deep neural networks, because neural networks would always beat SVMs.
- C. Deploy the model and measure the real-world AUC; it’s always higher because of generalization.
- D. Scale predictions you get out of the model (tune a scaling factor as a hyperparameter) in order to get the highest AUC.
Answer: A
Question 158
You need to deploy additional dependencies to all nodes of a Cloud Dataproc cluster at startup using an existing initialization action.
Company security policies require that Cloud Dataproc nodes do not have access to the Internet so public initialization actions cannot fetch resources.
What should you do?
- A. Deploy the Cloud SQL Proxy on the Cloud Dataproc master.
- B. Use an SSH tunnel to give the Cloud Dataproc cluster access to the Internet.
- C. Copy all dependencies to a Cloud Storage bucket within your VPC security perimeter.
- D. Use Resource Manager to add the service account used by the Cloud Dataproc cluster to the Network User role.
Answer: C
Question 159
You need to choose a database for a new project that has the following requirements:
・Fully managed
・Able to automatically scale up
・Transactionally consistent
・Able to scale up to 6 TB
・Able to be queried using SQL
Which database do you choose?
- A. Cloud SQL
- B. Cloud Bigtable
- C. Cloud Spanner
- D. Cloud Datastore
Answer: A
Question 160
You work for a mid-sized enterprise that needs to move its operational system transaction data from an on-premises database to GCP.
The database is about 20 TB in size.
Which database should you choose?
- A. Cloud SQL
- B. Cloud Bigtable
- C. Cloud Spanner
- D. Cloud Datastore
Answer: A
Question 161
You need to choose a database to store time series CPU and memory usage for millions of computers.
You need to store this data in one-second interval samples. Analysts will be performing real-time, ad hoc analytics against the database. You want to avoid being charged for every query executed and ensure that the schema design will allow for future growth of the dataset.
Which database and data model should you choose?
- A. Create a table in BigQuery, and append the new samples for CPU and memory to the table.
- B. Create a wide table in BigQuery, create a column for the sample value at each second, and update the row with the interval for each second.
- C. Create a narrow table in Bigtable with a row key that combines the Computer Engine computer identifier with the sample time at each second.
- D. Create a wide table in Bigtable with a row key that combines the computer identifier with the sample time at each minute, and combine the values for each second as column data.
Answer: C
Question 162
You want to archive data in Cloud Storage.
Because some data is very sensitive, you want to use the `Trust No One` (TNO) approach to encrypt your data to prevent the cloud provider staff from decrypting your data.
What should you do?
- A. Use gcloud kms keys to create a symmetric key. Then use gcloud kms encrypt to encrypt each archival file with the key and unique additional authenticated data (AAD). Use gsutil cp to upload each encrypted file to the Cloud Storage bucket, and keep the AAD outside of Google Cloud.
- B. Use gcloud kms keys to create a symmetric key. Then use gcloud kms encrypt to encrypt each archival file with the key. Use gsutil cp to upload each encrypted file to the Cloud Storage bucket. Manually destroy the key previously used for encryption, and rotate the key once.
- C. Specify customer-supplied encryption key (CSEK) in the .boto configuration file. Use gsutil cp to upload each archival file to the Cloud Storage bucket. Save the CSEK in Cloud Memorystore as permanent storage of the secret.
- D. Specify customer-supplied encryption key (CSEK) in the .boto configuration file. Use gsutil cp to upload each archival file to the Cloud Storage bucket. Save the CSEK in a different project that only the security team can access.
Answer: A
Question 163
You have data pipelines running on BigQuery, Dataflow, and Dataproc.
You need to perform health checks and monitor their behavior, and then notify the team managing the pipelines if they fail. You also need to be able to work across multiple projects. Your preference is to use managed products or features of the platform.
What should you do?
- A. Export the information to Cloud Monitoring, and set up an Alerting policy.
- B. Run a Virtual Machine in Compute Engine with Airflow, and export the information to Cloud Monitoring.
- C. Export the logs to BigQuery, and set up App Engine to read that information and send emails if you find a failure in the logs.
- D. Develop an App Engine application to consume logs using GCP API calls, and send emails if you find a failure in the logs.
Answer: A
Question 164
You are working on a linear regression model on BigQuery ML to predict a customer’s likelihood of purchasing your company’s products.
Your model uses a city name variable as a key predictive component. In order to train and serve the model, your data must be organized in columns. You want to prepare your data using the least amount of coding while maintaining the predictable variables.
What should you do?
- A. Create a new view with BigQuery that does not include a column with city information.
- B. Use SQL in BigQuery to transform the state column using a one-hot encoding method, and make each city a column with binary values.
- C. Use TensorFlow to create a categorical variable with a vocabulary list. Create the vocabulary file and upload that as part of your model to BigQuery ML.
- D. Use Cloud Data Fusion to assign each city to a region that is labeled as 1, 2, 3, 4, or 5, and then use that number to represent the city in the model.
Answer: B
Question 165
You work for a large bank that operates in locations throughout North America.
You are setting up a data storage system that will handle bank account transactions. You require ACID compliance and the ability to access data with SQL.
Which solution is appropriate?
- A. Store transaction data in Cloud Spanner. Enable stale reads to reduce latency.
- B. Store transaction in Cloud Spanner. Use locking read-write transactions.
- C. Store transaction data in BigQuery. Disabled the query cache to ensure consistency.
- D. Store transaction data in Cloud SQL. Use a federated query BigQuery for analysis.
Answer: B
Question 166
A shipping company has live package-tracking data that is sent to an Apache Kafka stream in real time.
This is then loaded into BigQuery. Analysts in your company want to query the tracking data in BigQuery to analyze geospatial trends in the lifecycle of a package. The table was originally created with ingest-date partitioning. Over time, the query processing time has increased. You need to implement a change that would improve query performance in BigQuery.
What should you do?
- A. Implement clustering in BigQuery on the ingest date column.
- B. Implement clustering in BigQuery on the package-tracking ID column.
- C. Tier older data onto Cloud Storage files and create a BigQuery table using Cloud Storage as an external data source.
- D. Re-create the table using data partitioning on the package delivery date.
Answer: B
Question 167
Your company currently runs a large on-premises cluster using Spark, Hive, and HDFS in a colocation facility.
The cluster is designed to accommodate peak usage on the system; however, many jobs are batch in nature, and usage of the cluster fluctuates quite dramatically. Your company is eager to move to the cloud to reduce the overhead associated with on-premises infrastructure and maintenance and to benefit from the cost savings. They are also hoping to modernize their existing infrastructure to use more serverless offerings in order to take advantage of the cloud. Because of the timing of their contract renewal with the colocation facility, they have only 2 months for their initial migration.
How would you recommend they approach their upcoming migration strategy so they can maximize their cost savings in the cloud while still executing the migration in time?
- A. Migrate the workloads to Dataproc plus HDFS; modernize later.
- B. Migrate the workloads to Dataproc plus Cloud Storage; modernize later.
- C. Migrate the Spark workload to Dataproc plus HDFS, and modernize the Hive workload for BigQuery.
- D. Modernize the Spark workload for Dataflow and the Hive workload for BigQuery.
Answer: B
Question 168
You work for a financial institution that lets customers register online.
As new customers register, their user data is sent to Pub/Sub before being ingested into BigQuery. For security reasons, you decide to redact your customers’ Government issued Identification Number while allowing customer service representatives to view the original values when necessary.
What should you do?
- A. Use BigQuery’s built-in AEAD encryption to encrypt the SSN column. Save the keys to a new table that is only viewable by permissioned users.
- B. Use BigQuery column-level security. Set the table permissions so that only members of the Customer Service user group can see the SSN column.
- C. Before loading the data into BigQuery, use Cloud Data Loss Prevention (DLP) to replace input values with a cryptographic hash.
- D. Before loading the data into BigQuery, use Cloud Data Loss Prevention (DLP) to replace input values with a cryptographic format-preserving encryption token.
Answer: B
Question 169
You are migrating a table to BigQuery and are deciding on the data model.
Your table stores information related to purchases made across several store locations and includes information like the time of the transaction, items purchased, the store ID, and the city and state in which the store is located. You frequently query this table to see how many of each item were sold over the past 30 days and to look at purchasing trends by state, city, and individual store.
How would you model this table for the best query performance?
- A. Partition by transaction time; cluster by state first, then city, then store ID.
- B. Partition by transaction time; cluster by store ID first, then city, then state.
- C. Top-level cluster by state first, then city, then store ID.
- D. Top-level cluster by store ID first, then city, then state.
Answer: A
Question 170
You are updating the code for a subscriber to a Pub/Sub feed.
You are concerned that upon deployment the subscriber may erroneously acknowledge messages, leading to message loss. Your subscriber is not set up to retain acknowledged messages.
What should you do to ensure that you can recover from errors after deployment?
- A. Set up the Pub/Sub emulator on your local machine. Validate the behavior of your new subscriber logic before deploying it to production.
- B. Create a Pub/Sub snapshot before deploying new subscriber code. Use a Seek operation to re-deliver messages that became available after the snapshot was created.
- C. Use Cloud Build for your deployment. If an error occurs after deployment, use a Seek operation to locate a timestamp logged by Cloud Build at the start of the deployment.
- D. Enable dead-lettering on the Pub/Sub topic to capture messages that aren’t successfully acknowledged. If an error occurs after deployment, re-deliver any messages captured by the dead-letter queue.
Answer: B
Reference:
Replaying and purging messages | Cloud Pub/Sub Documentation
Question 171
You work for a large real estate firm and are preparing 6 TB of home sales data to be used for machine learning.
You will use SQL to transform the data and use BigQuery ML to create a machine learning model. You plan to use the model for predictions against a raw dataset that has not been transformed.
How should you set up your workflow in order to prevent skew at prediction time?
- A. When creating your model, use BigQuery’s TRANSFORM clause to define preprocessing steps. At prediction time, use BigQuery’s ML.EVALUATE clause without specifying any transformations on the raw input data.
- B. When creating your model, use BigQuery’s TRANSFORM clause to define preprocessing steps. Before requesting predictions, use a saved query to transform your raw input data, and then use ML.EVALUATE.
- C. Use a BigQuery view to define your preprocessing logic. When creating your model, use the view as your model training data. At prediction time, use BigQuery’s ML.EVALUATE clause without specifying any transformations on the raw input data.
- D. Preprocess all data using Dataflow. At prediction time, use BigQuery’s ML.EVALUATE clause without specifying any further transformations on the input data.
Answer: A
Question 172
You are analyzing the price of a company’s stock.
Every 5 seconds, you need to compute a moving average of the past 30 seconds’ worth of data. You are reading data from Pub/Sub and using DataFlow to conduct the analysis.
How should you set up your windowed pipeline?
- A. Use a fixed window with a duration of 5 seconds. Emit results by setting the following trigger: AfterProcessingTime.pastFirstElementInPane().plusDelayOf (Duration.standardSeconds(30))
- B. Use a fixed window with a duration of 30 seconds. Emit results by setting the following trigger: AfterWatermark.pastEndOfWindow().plusDelayOf (Duration.standardSeconds(5))
- C. Use a sliding window with a duration of 5 seconds. Emit results by setting the following trigger: AfterProcessingTime.pastFirstElementInPane().plusDelayOf (Duration.standardSeconds(30))
- D. Use a sliding window with a duration of 30 seconds and a period of 5 seconds. Emit results by setting the following trigger: AfterWatermark.pastEndOfWindow ()
Answer: D
Question 173
You are designing a pipeline that publishes application events to a Pub/Sub topic.
Although message ordering is not important, you need to be able to aggregate events across disjoint hourly intervals before loading the results to BigQuery for analysis.
What technology should you use to process and load this data to BigQuery while ensuring that it will scale with large volumes of events?
- A. Create a Cloud Function to perform the necessary data processing that executes using the Pub/Sub trigger every time a new message is published to the topic.
- B. Schedule a Cloud Function to run hourly, pulling all available messages from the Pub/Sub topic and performing the necessary aggregations.
- C. Schedule a batch Dataflow job to run hourly, pulling all available messages from the Pub/Sub topic and performing the necessary aggregations.
- D. Create a streaming Dataflow job that reads continually from the Pub/Sub topic and performs the necessary aggregations using tumbling windows.
Answer: D
Question 174
You work for a large financial institution that is planning to use Dialogflow to create a chatbot for the company’s mobile app.
You have reviewed old chat logs and tagged each conversation for intent based on each customer’s stated intention for contacting customer service. About 70% of customer requests are simple requests that are solved within 10 intents. The remaining 30% of inquiries require much longer, more complicated requests.
Which intents should you automate first?
- A. Automate the 10 intents that cover 70% of the requests so that live agents can handle more complicated requests.
- B. Automate the more complicated requests first because those require more of the agents’ time.
- C. Automate a blend of the shortest and longest intents to be representative of all intents.
- D. Automate intents in places where common words such as ‘payment’ appear only once so the software isn’t confused.
Answer: A
Question 175
Your company is implementing a data warehouse using BigQuery, and you have been tasked with designing the data model.
You move your on-premises sales data warehouse with a star data schema to BigQuery but notice performance issues when querying the data of the past 30 days.
Based on Google’s recommended practices, what should you do to speed up the query without increasing storage costs?
- A. Denormalize the data.
- B. Shard the data by customer ID.
- C. Materialize the dimensional data in views.
- D. Partition the data by transaction date.
Answer: D
Reference:
Schema and data transfer overview | BigQuery | Google Cloud
Question 176
You have uploaded 5 years of log data to Cloud Storage.
A user reported that some data points in the log data are outside of their expected ranges, which indicates errors. You need to address this issue and be able to run the process again in the future while keeping the original data for compliance reasons.
What should you do?
- A. Import the data from Cloud Storage into BigQuery. Create a new BigQuery table, and skip the rows with errors.
- B. Create a Compute Engine instance and create a new copy of the data in Cloud Storage. Skip the rows with errors.
- C. Create a Dataflow workflow that reads the data from Cloud Storage, checks for values outside the expected range, sets the value to an appropriate default, and writes the updated records to a new dataset in Cloud Storage.
- D. Create a Dataflow workflow that reads the data from Cloud Storage, checks for values outside the expected range, sets the value to an appropriate default, and writes the updated records to the same dataset in Cloud Storage.
Answer: C
Question 177
You want to rebuild your batch pipeline for structured data on Google Cloud.
You are using PySpark to conduct data transformations at scale, but your pipelines are taking over twelve hours to run. To expedite development and pipeline run time, you want to use a serverless tool and SOL syntax. You have already moved your raw data into Cloud Storage.
How should you build the pipeline on Google Cloud while meeting speed and processing requirements?
- A. Convert your PySpark commands into SparkSQL queries to transform the data, and then run your pipeline on Dataproc to write the data into BigQuery.
- B. Ingest your data into Cloud SQL, convert your PySpark commands into SparkSQL queries to transform the data, and then use federated queues from BigQuery for machine learning.
- C. Ingest your data into BigQuery from Cloud Storage, convert your PySpark commands into BigQuery SQL queries to transform the data, and then write the transformations to a new table.
- D. Use Apache Beam Python SDK to build the transformation pipelines, and write the data into BigQuery.
Answer: C
Question 178
You are testing a Dataflow pipeline to ingest and transform text files.
The files are compressed by gzip, errors are written to a dead-letter queue, and you are using SideInputs to join data.
You noticed that the pipeline is taking longer to complete than expected; what should you do to expedite the Dataflow job?
- A. Switch to compressed Avro files.
- B. Reduce the batch size.
- C. Retry records that throw an error.
- D. Use CoGroupByKey instead of the SideInput.
Answer: D
Question 179
You are building a real-time prediction engine that streams files, which may contain PII (personal identifiable information) data, into Cloud Storage and eventually into BigQuery.
You want to ensure that the sensitive data is masked but still maintains referential integrity, because names and emails are often used as join keys.
How should you use the Cloud Data Loss Prevention API (DLP API) to ensure that the PII data is not accessible by unauthorized individuals?
- A. Create a pseudonym by replacing the PII data with cryptogenic tokens, and store the non-tokenized data in a locked-down button.
- B. Redact all PII data, and store a version of the unredacted data in a locked-down bucket.
- C. Scan every table in BigQuery, and mask the data it finds that has PII.
- D. Create a pseudonym by replacing PII data with a cryptographic format-preserving token.
Answer: D
Question 180
You are migrating an application that tracks library books and information about each book, such as author or year published, from an on-premises data warehouse to BigQuery.
In your current relational database, the author information is kept in a separate table and joined to the book information on a common key.
Based on Google’s recommended practice for schema design, how would you structure the data to ensure optimal speed of queries about the author of each book that has been borrowed?
- A. Keep the schema the same, maintain the different tables for the book and each of the attributes, and query as you are doing today.
- B. Create a table that is wide and includes a column for each attribute, including the author’s first name, last name, date of birth, etc.
- C. Create a table that includes information about the books and authors, but nest the author fields inside the author column.
- D. Keep the schema the same, create a view that joins all of the tables, and always query the view.
Answer: C
Question 181
You need to give new website users a globally unique identifier (GUID) using a service that takes in data points and returns a GUID.
This data is sourced from both internal and external systems via HTTP calls that you will make via microservices within your pipeline. There will be tens of thousands of messages per second and that can be multi-threaded. and you worry about the backpressure on the system.
How should you design your pipeline to minimize that backpressure?
- A. Call out to the service via HTTP.
- B. Create the pipeline statically in the class definition.
- C. Create a new object in the startBundle method of DoFn.
- D. Batch the job into ten-second increments.
Answer: D
Question 182
You are migrating your data warehouse to Google Cloud and decommissioning your on-premises data center.
Because this is a priority for your company, you know that bandwidth will be made available for the initial data load to the cloud. The files being transferred are not large in number, but each file is 90 GB. Additionally, you want your transactional systems to continually update the warehouse on Google Cloud in real time.
What tools should you use to migrate the data and ensure that it continues to write to your warehouse?
- A. Storage Transfer Service for the migration; Pub/Sub and Cloud Data Fusion for the real-time updates.
- B. BigQuery Data Transfer Service for the migration; Pub/Sub and Dataproc for the real-time updates.
- C. gsutil for the migration; Pub/Sub and Dataflow for the real-time updates.
- D. gsutil for both the migration and the real-time updates.
Answer: C
Question 183
You are using Bigtable to persist and serve stock market data for each of the major indices.
To serve the trading application, you need to access only the most recent stock prices that are streaming in.
How should you design your row key and tables to ensure that you can access the data with the simplest query?
- A. Create one unique table for all of the indices, and then use the index and timestamp as the row key design.
- B. Create one unique table for all of the indices, and then use a reverse timestamp as the row key design.
- C. For each index, have a separate table and use a timestamp as the row key design.
- D. For each index, have a separate table and use a reverse timestamp as the row key design.
Answer: A
Question 184
You are building a report-only data warehouse where the data is streamed into BigQuery via the streaming API.
Following Google’s best practices, you have both a staging and a production table for the data. How should you design your data loading to ensure that there is only one master dataset without affecting performance on either the ingestion or reporting pieces?
- A. Have a staging table that is an append-only model, and then update the production table every three hours with the changes written to staging.
- B. Have a staging table that is an append-only model, and then update the production table every ninety minutes with the changes written to staging.
- C. Have a staging table that moves the staged data over to the production table and deletes the contents of the staging table every three hours.
- D. Have a staging table that moves the staged data over to the production table and deletes the contents of the staging table every thirty minutes.
Answer: C
Question 185
You issue a new batch job to Dataflow.
The job starts successfully, processes a few elements, and then suddenly fails and shuts down. You navigate to the Dataflow monitoring interface where you find errors related to a particular DoFn in your pipeline.
What is the most likely cause of the errors?
- A. Job validation
- B. Exceptions in worker code
- C. Graph or pipeline construction
- D. Insufficient permissions
Answer: B
Question 186
Your new customer has requested daily reports that show their net consumption of Google Cloud compute resources and who used the resources.
You need to quickly and efficiently generate these daily reports.
What should you do?
- A. Do daily exports of Cloud Logging data to BigQuery. Create views filtering by project, log type, resource, and user.
- B. Filter data in Cloud Logging by project, resource, and user; then export the data in CSV format.
- C. Filter data in Cloud Logging by project, log type, resource, and user, then import the data into BigQuery.
- D. Export Cloud Logging data to Cloud Storage in CSV format. Cleanse the data using Dataprep, filtering by project, resource, and user.
Answer: A
Question 187
The Development and External teams have the project viewer Identity and Access Management (IAM) role in a folder named Visualization.
You want the Development Team to be able to read data from both Cloud Storage and BigQuery, but the External Team should only be able to read data from BigQuery.
What should you do?
- A. Remove Cloud Storage IAM permissions to the External Team on the acme-raw-data project.
- B. Create Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) firewall rules on the acme-raw-data project that deny all ingress traffic from the External Team CIDR range.
- C. Create a VPC Service Controls perimeter containing both projects and BigQuery as a restricted API. Add the External Team users to the perimeter’s Access Level.
- D. Create a VPC Service Controls perimeter containing both projects and Cloud Storage as a restricted API. Add the Development Team users to the perimeter’s Access Level.
Answer: D
Question 188
Your startup has a web application that currently serves customers out of a single region in Asia.
You are targeting funding that will allow your startup to serve customers globally. Your current goal is to optimize for cost, and your post-funding goal is to optimize for global presence and performance.
You must use a native JDBC driver.
What should you do?
- A. Use Cloud Spanner to configure a single region instance initially, and then configure multi-region Cloud Spanner instances after securing funding.
- B. Use a Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL highly available instances first, and Bigtable with US, Europe, and Asia replication after securing funding.
- C. Use a Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL zonal instance first, and Bigtable with US, Europe, and Asia after securing funding.
- D. Use a Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL zonal instance first, and Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL with highly available configuration after securing funding.
Answer: A
Question 189
You need to migrate 1 PB of data from an on-premises data center to Google Cloud. Data transfer time during the migration should take only a few hours.
You want to follow Google-recommended practices to facilitate the large data transfer over a secure connection.
What should you do?
- A. Establish a Cloud Interconnect connection between the on-premises data center and Google Cloud, and then use the Storage Transfer Service.
- B. Use a Transfer Appliance and have engineers manually encrypt, decrypt, and verify the data.
- C. Establish a Cloud VPN connection, start gcloud compute scp jobs in parallel, and run checksums to verify the data.
- D. Reduce the data into 3 TB batches, transfer the data using gsutil, and run checksums to verify the data.
Answer: A
Question 190
You are loading CSV files from Cloud Storage to BigQuery.
The files have known data quality issues, including mismatched data types, such as STRINGs and INT64s in the same column, and inconsistent formatting of values such as phone numbers or addresses. You need to create the data pipeline to maintain data quality and perform the required cleansing and transformation.
What should you do?
- A. Use Data Fusion to transform the data before loading it into BigQuery.
- B. Use Data Fusion to convert the CSV files to a self-describing data format, such as AVRO, before loading the data to BigQuery.
- C. Load the CSV files into a staging table with the desired schema, perform the transformations with SQL, and then write the results to the final destination table.
- D. Create a table with the desired schema, load the CSV files into the table, and perform the transformations in place using SQL.
Answer: A
Question 191
You are developing a new deep learning model that predicts a customer’s likelihood to buy on your ecommerce site.
After running an evaluation of the model against both the original training data and new test data, you find that your model is overfitting the data. You want to improve the accuracy of the model when predicting new data.
What should you do?
- A. Increase the size of the training dataset, and increase the number of input features.
- B. Increase the size of the training dataset, and decrease the number of input features.
- C. Reduce the size of the training dataset, and increase the number of input features.
- D. Reduce the size of the training dataset, and decrease the number of input features.
Answer: B
Question 192
You are implementing a chatbot to help an online retailer streamline their customer service.
The chatbot must be able to respond to both text and voice inquiries. You are looking for a low-code or no-cade option, and you want to be able to easily train the chatbot to provide answers to keywords.
What should you do?
- A. Use the Cloud Speech-to-Text API to build a Python application in App Engine.
- B. Use the Cloud Speech-to-Text API to build a Python application in a Compute Engine instance.
- C. Use Dialogflow for simple queries and the Cloud Speech-to-Text API for complex queries.
- D. Use Dialogflow to implement the chatbot, defining the intents based on the most common queries collected.
Answer: D
Question 193
An aerospace company uses a proprietary data format to store its flight data.
You need to connect this new data source to BigQuery and stream the data into BigQuery. You want to efficiently import the data into BigQuery while consuming as few resources as possible.
What should you do?
- A. Write a shell script that triggers a Cloud Function that performs periodic ETL batch jobs on the new data source.
- B. Use a standard Dataflow pipeline to store the raw data in BigQuery, and then transform the format later when the data is used.
- C. Use Apache Hive to write a Dataproc job that streams the data into BigQuery in CSV format.
- D. Use an Apache Beam custom connector to write a Dataflow pipeline that streams the data into BigQuery in Avro format.
Answer: D
Question 194
An online brokerage company requires a high volume trade processing architecture.
You need to create a secure queuing system that triggers jobs. The jobs will run in Google Cloud and call the company’s Python API to execute trades. You need to efficiently implement a solution.
What should you do?
- A. Use a Pub/Sub push subscription to trigger a Cloud Function to pass the data to the Python API.
- B. Write an application hosted on a Compute Engine instance that makes a push subscription to the Pub/Sub topic.
- C. Write an application that makes a queue in a NoSQL database.
- D. Use Cloud Composer to subscribe to a Pub/Sub topic and call the Python API.
Answer: A
Question 195
Your company wants to be able to retrieve large result sets of medical information from your current system, which has over 10 TBs in the database, and store the data in new tables for further query.
The database must have a low-maintenance architecture and be accessible via SQL. You need to implement a cost-effective solution that can support data analytics for large result sets.
What should you do?
- A. Use Cloud SQL, but first organize the data into tables. Use JOIN in queries to retrieve data.
- B. Use BigQuery as a data warehouse. Set output destinations for caching large queries.
- C. Use a MySQL cluster installed on a Compute Engine managed instance group for scalability.
- D. Use Cloud Spanner to replicate the data across regions. Normalize the data in a series of tables.
Answer: B
Question 196
You have 15 TB of data in your on-premises data center that you want to transfer to Google Cloud.
Your data changes weekly and is stored in a POSIX-compliant source. The network operations team has granted you 500 Mbps bandwidth to the public internet. You want to follow Google-recommended practices to reliably transfer your data to Google Cloud on a weekly basis.
What should you do?
- A. Use Cloud Scheduler to trigger the gsutil command. Use the -m parameter for optimal parallelism.
- B. Use Transfer Appliance to migrate your data into a Google Kubernetes Engine cluster, and then configure a weekly transfer job.
- C. Install Storage Transfer Service for on-premises data in your data center, and then configure a weekly transfer job.
- D. Install Storage Transfer Service for on-premises data on a Google Cloud virtual machine, and then configure a weekly transfer job.
Answer: C
Question 197
You are designing a system that requires an ACID-compliant database.
You must ensure that the system requires minimal human intervention in case of a failure.
What should you do?
- A. Configure a Cloud SQL for MySQL instance with point-in-time recovery enabled.
- B. Configure a Cloud SQL for PostgreSQL instance with high availability enabled.
- C. Configure a Bigtable instance with more than one cluster.
- D. Configure a BigQuery table with a multi-region configuration.
Answer: B
Question 198
You are implementing workflow pipeline scheduling using open source-based tools and Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE).
You want to use a Google managed service to simplify and automate the task. You also want to accommodate Shared VPC networking considerations.
What should you do?
- A. Use Dataflow for your workflow pipelines. Use Cloud Run triggers for scheduling.
- B. Use Dataflow for your workflow pipelines. Use shell scripts to schedule workflows.
- C. Use Cloud Composer in a Shared VPC configuration. Place the Cloud Composer resources in the host project.
- D. Use Cloud Composer in a Shared VPC configuration. Place the Cloud Composer resources in the service project.
Answer: D
Question 199
You are using BigQuery and Data Studio to design a customer-facing dashboard that displays large quantities of aggregated data.
You expect a high volume of concurrent users. You need to optimize the dashboard to provide quick visualizations with minimal latency.
What should you do?
- A. Use BigQuery BI Engine with materialized views.
- B. Use BigQuery BI Engine with logical views.
- C. Use BigQuery BI Engine with streaming data.
- D. Use BigQuery BI Engine with authorized views.
Answer: A
Question 200
Government regulations in the banking industry mandate the protection of clients’ personally identifiable information (PII).
Your company requires PII to be access controlled, encrypted, and compliant with major data protection standards. In addition to using Cloud Data Loss Prevention (Cloud DLP), you want to follow Google-recommended practices and use service accounts to control access to PII.
What should you do?
- A. Assign the required Identity and Access Management (IAM) roles to every employee, and create a single service account to access project resources.
- B. Use one service account to access a Cloud SQL database, and use separate service accounts for each human user.
- C. Use Cloud Storage to comply with major data protection standards. Use one service account shared by all users.
- D. Use Cloud Storage to comply with major data protection standards. Use multiple service accounts attached to IAM groups to grant the appropriate access to each group.
Answer: A
Question 201
You need to migrate a Redis database from an on-premises data center to a Memorystore for Redis instance.
You want to follow Google-recommended practices and perform the migration for minimal cost, time and effort.
What should you do?
- A. Make an RDB backup of the Redis database, use the gsutil utility to copy the RDB file into a Cloud Storage bucket, and then import the RDB file into the Memorystore for Redis instance.
- B. Make a secondary instance of the Redis database on a Compute Engine instance and then perform a live cutover.
- C. Create a Dataflow job to read the Redis database from the on-premises data center and write the data to a Memorystore for Redis instance.
- D. Write a shell script to migrate the Redis data and create a new Memorystore for Redis instance.
Answer: A
Question 202
Your platform on your on-premises environment generates 100 GB of data daily, composed of millions of structured JSON text files.
Your on-premises environment cannot be accessed from the public internet. You want to use Google Cloud products to query and explore the platform data.
What should you do?
- A. Use Cloud Scheduler to copy data daily from your on-premises environment to Cloud Storage. Use the BigQuery Data Transfer Service to import data into BigQuery.
- B. Use a Transfer Appliance to copy data from your on-premises environment to Cloud Storage. Use the BigQuery Data Transfer Service to import data into BigQuery.
- C. Use Transfer Service for on-premises data to copy data from your on-premises environment to Cloud Storage. Use the BigQuery Data Transfer Service to import data into BigQuery.
- D. Use the BigQuery Data Transfer Service dataset copy to transfer all data into BigQuery.
Answer: C
Question 203
A TensorFlow machine learning model on Compute Engine virtual machines (n2-standard-32) takes two days to complete training.
The model has custom TensorFlow operations that must run partially on a CPU. You want to reduce the training time in a cost-effective manner.
What should you do?
- A. Change the VM type to n2-highmem-32.
- B. Change the VM type to e2-standard-32.
- C. Train the model using a VM with a GPU hardware accelerator.
- D. Train the model using a VM with a TPU hardware accelerator.
Answer: C
Question 204
You want to create a machine learning model using BigQuery ML and create an endpoint for hosting the model using Vertex AI.
This will enable the processing of continuous streaming data in near-real time from multiple vendors. The data may contain invalid values.
What should you do?
- A. Create a new BigQuery dataset and use streaming inserts to land the data from multiple vendors. Configure your BigQuery ML model to use the “ingestion” dataset as the framing data.
- B. Use BigQuery streaming inserts to land the data from multiple vendors where your BigQuery dataset ML model is deployed.
- C. Create a Pub/Sub topic and send all vendor data to it. Connect a Cloud Function to the topic to process the data and store it in BigQuery.
- D. Create a Pub/Sub topic and send all vendor data to it. Use Dataflow to process and sanitize the Pub/Sub data and stream it to BigQuery.
Answer: D
Question 205
You have a data processing application that runs on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE).
Containers need to be launched with their latest available configurations from a container registry. Your GKE nodes need to have GPUs, local SSDs, and 8 Gbps bandwidth. You want to efficiently provision the data processing infrastructure and manage the deployment process.
What should you do?
- A. Use Compute Engine startup scripts to pull container images, and use gcloud commands to provision the infrastructure.
- B. Use Cloud Build to schedule a job using Terraform build to provision the infrastructure and launch with the most current container images.
- C. Use GKE to autoscale containers, and use gcloud commands to provision the infrastructure.
- D. Use Dataflow to provision the data pipeline, and use Cloud Scheduler to run the job.
Answer: B

Comments are closed