Ace Your Professional Cloud Architect Certification with Practice Exams.
Google Cloud Certified – Professional Cloud Architect – Practice Exam (Question 57)
Question 1
Your company’s test suite is a custom C++ application that runs tests throughout each day on Linux virtual machines.
The full test suite takes several hours to complete, running on a limited number of on-premises servers reserved for testing. Your company wants to move the testing infrastructure to the cloud, to reduce the amount of time it takes to fully test a change to the system, while changing the tests as little as possible.
Which cloud infrastructure should you recommend?
- A. Google Compute Engine unmanaged instance groups and Network Load Balancer
- B. Google Compute Engine managed instance groups with auto-scaling
- C. Google Cloud Dataproc to run Apache Hadoop jobs to process each test
- D. Google App Engine with Google StackDriver for logging
Correct Answer: B
Google Compute Engine enables users to launch virtual machines (VMs) on demand. VMs can be launched from the standard images or custom images created by users.
Managed instance groups offer auto scaling capabilities that allow you to automatically add or remove instances from a managed instance group based on increases or decreases in load. Autoscaling helps your applications gracefully handle increases in traffic and reduces cost when the need for resources is lower.
B: There is no mention of incoming IP data traffic for the custom C++ applications.
C: Apache Hadoop is not fit for testing C++ applications. Apache Hadoop is an open-source software framework used for distributed storage and processing of datasets of big data using the MapReduce programming model.
D: Google App Engine is intended to be used for web applications.
Google App Engine (often referred to as GAE or simply Google App Engine) is a web framework and cloud computing platform for developing and hosting web applications in Google-managed data centers.
Reference contents:
– Autoscaling groups of instances | Compute Engine Documentation
Question 2
A lead software engineer tells you that his new application design uses websockets and HTTP sessions that are not distributed across the web servers.
You want to help him ensure his application will run properly on Google Cloud Platform.
What should you do?
- A. Help the engineer to convert his websocket code to use HTTP streaming.
- B. Review the encryption requirements for websocket connections with the security team.
- C. Meet with the cloud operations team and the engineer to discuss load balancer options.
- D. Help the engineer redesign the application to use a distributed user session service that does not rely on websockets and HTTP sessions.
Correct Answer: C
Google Cloud Platform HTTP(S) load balancing provides global load balancing for HTTP(S) requests destined for your instances.
The HTTP(S) load balancer has native support for the WebSocket protocol.
A: HTTP server push, also known as HTTP streaming, is a client-server communication pattern that sends information from an HTTP server to a client asynchronously, without a client request. A server push architecture is especially effective for highly interactive web or mobile applications, where one or more clients need to receive continuous information from the server.
Reference contents:
– External HTTP(S) Load Balancing overview
Question 3
The application reliability team at your company added a debug feature to their backend service to send all server events to Google Cloud Storage for eventual analysis. The event records are at least 50 KB and at most 15 MB and are expected to peak at 3,000 events per second. You want to minimize data loss.
Which process should you implement?
- A. Append metadata to the file body. Compress individual files. Name files with serverName Timestamp. Create a new bucket if the bucket is older than 1 hour and save individual files to the new bucket. Otherwise, save files to the existing bucket.
- B. Batch every 10,000 events with a single manifest file for metadata. Compress event files and manifest files into a single archive file. Name files using serverName EventSequence. Create a new bucket if the bucket is older than 1 day and save the single archive file to the new bucket. Otherwise, save the single archive file to the existing bucket.
- C. Compress individual files. Name files with serverName EventSequence. Save files to one bucket. Set custom metadata headers for each object after saving.
- D. Append metadata to file body. Compress individual files. Name files with a random prefix pattern. Save files to one bucket.
Correct Answer: A
Question 4
A recent audit revealed that a new network was created in your GCP project.
In this network, a Google Compute Engine (GCE) instance has an SSH port open to the world. You want to discover this network’s origin.
What should you do?
- A. Search for Create VM entry in the Stackdriver alerting console.
- B. Navigate to the Activity page in the Home section. Set category to Data Access and search for Create VM entry.
- C. In the Logging section of the console, specify GCE Network as the logging section. Search for the Create Insert entry.
- D. Connect to the GCE instance using project SSH keys. Identify previous logins in system logs, and match these with the project owners list.
Correct Answer: C
A: To use the Stackdriver alerting console we must first set up alerting policies.
B: Data access logs only contain read-only operations.
Audit logs help you determine who did what, where, and when.
Cloud Audit Logging returns two types of logs:
– Admin activity logs
– Data access logs: Contains log entries for operations that perform read-only operations do not modify any data, such as get, list, and aggregated list methods.
Question 5
You want to make a copy of a production Linux virtual machine in the US-Central region.
You want to manage and replace the copy easily if there are changes on the production virtual machine. You will deploy the copy as a new instance in a different project in the US-East region.
What steps must you take?
- A. Use the Linux dd and netcat commands to copy and stream the root disk contents to a new virtual machine instance in the US-East region.
- B. Create a snapshot of the root disk and select the snapshot as the root disk when you create a new virtual machine instance in the US-East region.
- C. Create an image file from the root disk with Linux dd command, create a new virtual machine instance in the US-East region
- D. Create a snapshot of the root disk, create an image file in Google Cloud Storage from the snapshot, and create a new virtual machine instance in the US-East region using the image file of the root disk.
Correct Answer: D
Question 6
Your company runs several databases on a single MySQL instance.
They need to take backups of a specific database at regular intervals. The backup activity needs to complete as quickly as possible and cannot be allowed to impact disk performance.
How should you configure the storage?
- A. Configure a cron job to use the gcloud tool to take regular backups using persistent disk snapshots.
- B. Mount a Local SSD volume as the backup location. After the backup is complete, use gsutil to move the backup to Google Cloud Storage.
- C. Use gcsfuse to mount a Google Cloud Storage bucket as a volume directly on the instance and write backups to the mounted location using mysqldump.
- D. Mount additional persistent disk volumes onto each virtual machine (VM) instance in a RAID10 array and use LVM to create snapshots to send to Google Cloud Storage.
Correct Answer: C
Reference contents:
– mvarrieur/MySQL-backup-to-Google-Cloud-Storage: Backup daily/weekly/monhtly all your MySQL databases to Google Cloud Storage via SH and gsutil
– Google Cloud Storage FUSE
Question 7
You are helping the QA team to roll out a new load-testing tool to test the scalability of your primary cloud services that run on Google Compute Engine with Google Cloud Bigtable.
Which three requirements should they include? (Choose 3 answers)
- A. Ensure that the load tests validate the performance of Google Cloud Bigtable.
- B. Create a separate Google Cloud project to use for the load-testing environment.
- C. Schedule the load-testing tool to regularly run against the production environment.
- D. Ensure all third-party systems your services use are capable of handling high load.
- E. Instrument the production services to record every transaction for replay by the load-testing tool.
- F. Instrument the load-testing tool and the target services with detailed logging and metrics collection.
Correct Answer: B, E, F
Question 8
Your customer is moving their corporate applications to Google Cloud Platform.
The security team wants detailed visibility of all projects in the organization. You provision the Google Cloud Resource Manager and set up yourself as the org admin.
What Google Cloud Identity and Access Management (Cloud IAM) roles should you give to the security team?
- A. Org viewer, project owner
- B. Org viewer, project viewer
- C. Org admin, project browser
- D. Project owner, network admin
Correct Answer: B
Question 9
Your company places a high value on being responsive and meeting customer needs quickly.
Their primary business objectives are release speed and agility. You want to reduce the chance of security errors being accidentally introduced.
Which two actions can you take? (Choose 2 answers)
- A. Ensure every code check-in is peer reviewed by a security SME.
- B. Use source code security analyzers as part of the CI/CD pipeline.
- C. Ensure you have stubs to unit test all interfaces between components.
- D. Enable code signing and a trusted binary repository integrated with your CI/CD pipeline.
- E. Run a vulnerability security scanner as part of your continuous-integration /continuous-delivery (CI/CD) pipeline.
Correct Answer: B, E
Question 10
You want to enable your running Google Kubernetes Engine cluster to scale as demand for your application changes.
What should you do?
- A. Add additional nodes to your Google Kubernetes Engine cluster using the following command: gcloud container clusters resize CLUSTER_Name -size 10.
- B. Add a tag to the instances in the cluster with the following command: gcloud compute instances add-tags INSTANCE – -tags enable- autoscaling max-nodes-10.
- C. Update the existing Google Kubernetes Engine cluster with the following command: gcloud alpha container clusters update mycluster – -enable- autoscaling – -min-nodes=1 – -max-nodes=10
- D. Create a new Google Kubernetes Engine cluster with the following command: gcloud alpha container clusters create mycluster – -enable- autoscaling – -min-nodes=1 – -max-nodes=10 and redeploy your application.
Correct Answer: C
Question 11
Your marketing department wants to send out a promotional email campaign.
The development team wants to minimize direct operation management. They project a wide range of possible customer responses, from 100 to 500,000 click-through per day. The link leads to a simple website that explains the promotion and collects user information and preferences.
Which infrastructure should you recommend? (Choose 2 answers)
- A. Use Google App Engine to serve the website and Google Cloud Datastore to store user data.
- B. Use a Google Container Engine cluster to serve the website and store data to persistent disk.
- C. Use a managed instance group to serve the website and Google Cloud Bigtable to store user data.
- D. Use a single Google Compute Engine virtual machine (VM) to host a web server, backend by Google Cloud SQL.
Correct Answer: A, C
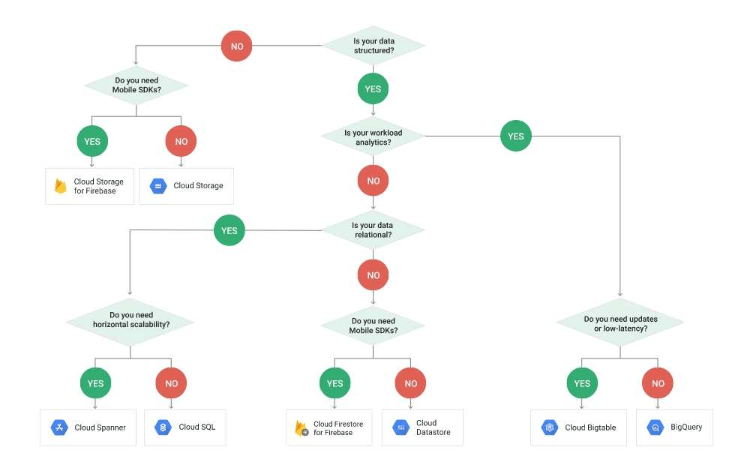
Reference contents:
– Cloud Storage Options
Question 12
Your company just finished a rapid lift and shift to Google Compute Engine for your computer needs.
You have another 9 months to design and deploy a more cloud-native solution. Specifically, you want a system that is no-ops and auto-scaling.
Which two computer products should you choose? (Choose 2 answers)
- A. Google Compute Engine with containers
- B. Google Kubernetes Engine with containers
- C. Google App Engine Standard Environment
- D. Google Compute Engine with custom instance types
- E. Google Compute Engine with managed instance groups
Correct Answer: B, C
B: With Google Container Engine, Google will automatically deploy your cluster for you, update, patch, secure the nodes.
Google Kubernetes Engine’s cluster autoscaler automatically resizes clusters based on the demands of the workloads you want to run.
C: Solutions like Google Cloud Datastore, Google BigQuery, Google App Engine, etc are truly NoOps.
Google App Engine by default scales the number of instances running up and down to match the load, thus providing consistent performance for your app at all times while minimizing idle instances and thus reducing cost.
At a high level, NoOps means that there is no infrastructure to build out and manage during usage of the platform. Typically, the compromise you make with NoOps is that you lose control of the underlying infrastructure.
Reference contents:
– How well does Google Container Engine support Google Cloud Platform’s NoOps claim?
Question 13
One of your primary business objectives is being able to trust the data stored in your application.
You want to log all changes to the application data.
How can you design your logging system to verify the authenticity of your logs?
- A. Write the log concurrently in the cloud and on premises.
- B. Use a SQL database and limit who can modify the log table.
- C. Digitally sign each timestamp and log entry and store the signature.
- D. Create a JSON dump of each log entry and store it in Google Cloud Storage.
Correct Answer: D
Write a log entry. If the log does not exist, it is created. You can specify a severity for the log entry, and you can write a structured log entry by specifying — payload-type=json and writing your message as a JSON string: gcloud logging write LOG STRING gcloud logging write LOG JSON-STRING –payload-type=json
Reference contents:
– Command-line interface | Cloud Logging
Question 14
Your company has decided to make a major revision of their API in order to create better experiences for their developers.
They need to keep the old version of the API available and deployable, while allowing new customers and testers to try out the new API. They want to keep the same SSL and DNS records in place to serve both APIs.
What should they do?
- A. Configure a new load balancer for the new version of the API.
- B. Reconfigure old clients to use a new endpoint for the new API.
- C. Have the old API forward traffic to the new API based on the path.
- D. Use separate backend pools for each API path behind the load balancer.
Correct Answer: D
Question 15
Your company plans to migrate a multi-petabyte data set to the cloud.
The data set must be available 24hrs a day. Your business analysts have experience only with using a SQL interface.
How should you store the data to optimize it for ease of analysis?
- A. Load data into Google BigQuery.
- B. Insert data into Google Cloud SQL.
- C. Put flat files into Google Cloud Storage.
- D. Stream data into Google Cloud Datastore.
Correct Answer: A
Google BigQuery is Google’s serverless, highly scalable, low cost enterprise data warehouse designed to make all your data analysts productive. Because there is no infrastructure to manage, you can focus on analyzing data to find meaningful insights using familiar SQL and you don’t need a database administrator.
Google BigQuery enables you to analyze all your data by creating a logical data warehouse over managed, columnar storage as well as data from object storage, and spreadsheets.
Reference contents:
– BigQuery: Cloud Data Warehouse
Question 16
The operations manager asks you for a list of recommended practices that she should consider when migrating a J2EE application to the cloud.
Which three practices should you recommend? (Choose 3 answers)
- A. Port the application code to run on Google App Engine.
- B. Integrate Google Cloud Dataflow into the application to capture real-time metrics.
- C. Instrument the application with a monitoring tool like Stackdriver Debugger.
- D. Select an automation framework to reliably provision the cloud infrastructure.
- E. Deploy a continuous integration tool with automated testing in a staging environment.
- F. Migrate from MySQL to a managed NoSQL database like Google Cloud Datastore or Google Cloud Bigtable.
Correct Answer: A, D, E
Reference contents:
– Deploying a Java App | App Engine standard environment for Java 8
– Getting Started: Cloud SQL
Question 17
A news feed web service has the following code running on Google App Engine.
During peak load, users report that they can see news articles they already viewed.
What is the most likely cause of this problem?
import news
from flask import Flask, redirect, request
from flask.ext.api import status
from google.appengine.api import users
app = Flask (_name_)
sessions = { }
@app.route ("/")
def homepage():
user = users.get_current_user()
if not user:
return "Invalid login",
status.HTTP_401_UNAUTHORIZED
if user not in sessions :
sessions (user] = { "viewed": []}
news_articles = news.get_new_news (user, sessions [user] ["viewed"])
sessions [user] ["viewed"] + [n["id"] for n in news_articles]
return news.render (news_articles)
if _name_ == "_main_":
app.run()- A. The session variable is local to just a single instance.
- B. The session variable is being overwritten in Google Cloud Datastore.
- C. The URL of the API needs to be modified to prevent caching.
- D. The HTTP Expires header needs to be set to -1 stop caching.
Correct Answer: B
Reference contents:
– Google App Engine Cache List in Session Variable
Question 18
An application development team believes their current logging tool will not meet their needs for their new cloud-based product.
They want a better tool to capture errors and help them analyze their historical log data. You want to help them find a solution that meets their needs.
What should you do?
- A. Direct them to download and install the Google StackDriver logging agent.
- B. Send them a list of online resources about logging best practices.
- C. Help them define their requirements and assess viable logging tools.
- D. Help them upgrade their current tool to take advantage of any new features.
Correct Answer: A
The Stackdriver Logging agent streams logs from your VM instances and from selected third party software packages to Stackdriver Logging. Using the agent is optional but we recommend it. The agent runs under both Linux and Microsoft Windows.
Stackdriver Logging allows you to store, search, analyze, monitor, and alert on log data and events from Google Cloud Platform and Amazon Web Services (AWS). Our API also allows ingestion of any custom log data from any source. Stackdriver Logging is a fully managed service that performs at scale and can ingest application and system log data from thousands of VMs. Even better, you can analyze all that log data in real time.
Reference contents:
– Installing the Cloud Logging agent on a single VM
– The hidden superpowers of Stackdriver Logging | by Alex Van Boxel | Google Cloud – Community
Question 19
You need to reduce the number of unplanned rollbacks of erroneous production deployments in your company’s web hosting platform.
Improvement to the QA/ Test processes accomplished an 80% reduction.
Which additional two approaches can you take to further reduce the rollbacks? (Choose 2 answers)
- A. Introduce a green-blue deployment model.
- B. Replace the QA environment with canary releases.
- C. Fragment the monolithic platform into microservices.
- D. Reduce the platform’s dependency on relational database systems.
- E. Replace the platform’s relational database systems with a NoSQL database.
Correct Answer: A, C
Reference contents:
– Implementing deployment and testing strategies on GKE | Solutions
– Application deployment and testing strategies | Solutions
Question 20
To reduce costs, the Director of Engineering has required all developers to move their development infrastructure resources from on-premises virtual machines (VMs) to Google Cloud Platform.
These resources go through multiple start/stop events during the day and require state to persist. You have been asked to design the process of running a development environment in Google Cloud while providing cost visibility to the finance department.
Which two steps should you take? (Choose 2 answers)
- A. Use the – -no-auto-delete flag on all persistent disks and stop the VM.
- B. Use the – -auto-delete flag on all persistent disks and terminate the VM.
- C. Apply VM CPU utilization label and include it in the Google BigQuery billing export.
- D. Use Google BigQuery billing export and labels to associate cost to groups.
- E. Store all state into the local SSD, snapshot the persistent disks, and terminate the VM.
- F. Store all state in Google Cloud Storage, snapshot the persistent disks, and terminate the VM.
Correct Answer: C, E
C: Billing export to Google BigQuery enables you to export your daily usage and cost estimates automatically throughout the day to a Google BigQuery dataset you specify.
Labels applied to resources that generate usage metrics are forwarded to the billing system so that you can break down your billing charges based upon label criteria. For example, the Google Compute Engine service reports metrics on VM instances. If you deploy a project with 2,000 VMs, each of which is labeled distinctly, then only the first 1,000 label maps seen within the 1 hour window will be preserved.
E: You cannot stop an instance that has a local SSD attached. Instead, you must migrate your critical data off of the local SSD to a persistent disk or to another instance before you delete the instance completely.
You can stop an instance temporarily so you can come back to it at a later time. A stopped instance does not incur charges, but all of the resources that are attached to the instance will still be charged. Alternatively, if you are done using an instance, delete the instance and its resources to stop incurring charges.
Reference contents:
– Export Cloud Billing data to BigQuery
– Stopping and starting an instance | Compute Engine Documentation
Question 21
Your company wants to track whether someone is present in a meeting room reserved for a scheduled meeting.
There are 1000 meeting rooms across 5 offices on 3 continents. Each room is equipped with a motion sensor that reports its status every second. The data from the motion detector includes only a sensor ID and several different discrete items of information. Analysts will use this data, together with information about account owners and office locations.
Which database type should you use?
- A. Flat file
- B. NoSQL
- C. Relational
- D. Blobstore
Correct Answer: B
Relational databases were not designed to cope with the scale and agility challenges that face modern applications, nor were they built to take advantage of the commodity storage and processing power available today.
NoSQL fits well for:
– Developers are working with applications that create massive volumes of new, rapidly changing data types structured, semi-structured, unstructured and polymorphic data.
D: The Blobstore API allows your application to serve data objects, called blobs, that are much larger than the size allowed for objects in the Google Cloud Datastore service.
Blobs are useful for serving large files, such as video or image files, and for allowing users to upload large data files.
Reference contents:
– What is NoSQL? NoSQL Databases Explained
Question 22
You set up an auto scaling instance group to serve web traffic for an upcoming launch.
After configuring the instance group as a backend service to an HTTP(S) load balancer, you notice that virtual machine (VM) instances are being terminated and re-launched every minute. The instances do not have a public IP address. You have verified the appropriate web response is coming from each instance using the curl command. You want to ensure the backend is configured correctly.
What should you do?
- A. Ensure that a firewall rule exists to allow source traffic on HTTP/HTTPS to reach the load balancer.
- B. Assign a public IP to each instance and configure a firewall rule to allow the load balancer to reach the instance public IP.
- C. Ensure that a firewall rule exists to allow load balancer health checks to reach the instances in the instance group.
- D. Create a tag on each instance with the name of the load balancer. Configure a firewall rule with the name of the load balancer as the source and the instance tag as the destination.
Correct Answer: C
The best practice when configuring a health check is to check health and serve traffic on the same port. However, it is possible to perform health checks on one port, but serve traffic on another. If you do use two different ports, ensure that firewall rules and services running on instances are configured appropriately. If you run health checks and serve traffic on the same port, but decide to switch ports at some point, be sure to update both the backend service and the health check.
Backend services that do not have a valid global forwarding rule referencing it will not be health checked and will have no health status.
Reference contents:
– Backend services overview | Load Balancing
– Health checks overview | Load Balancing
– External HTTP(S) Load Balancing overview
Question 23
You write a Python script to connect to Google BigQuery from a Google Compute Engine virtual machine.
The script is printing errors that it cannot connect to Google BigQuery.
What should you do to fix the script?
- A. Install the latest Google BigQuery API client library for Python.
- B. Run your script on a new virtual machine with the Google BigQuery access scope enabled.
- C. Create a new service account with Google BigQuery access and execute your script with that user.
- D. Install the bq component for gcloud with the command gcloud components install bq.
Correct Answer: A
Applications that use Google BigQuery must be associated with a Google Cloud Console project with the Google BigQuery API enabled.
Reference contents:
– Quickstart: Using client libraries | BigQuery
Question 24
Your customer is moving an existing corporate application to Google Cloud Platform from an on-premises data center.
The business owners require minimal user disruption. There are strict security team requirements for storing passwords.
What authentication strategy should they use?
- A. Use G Suite Password Sync to replicate passwords into Google.
- B. Federate authentication via SAML 2.0 to the existing Identity Provider.
- C. Provision users in Google using the Google Cloud Directory Sync tool.
- D. Ask users to set their Google password to match their corporate password.
Correct Answer: C
Provision users to Google’s directory
The global Directory is available to both Google Cloud Platform and G Suite resources and can be provisioned by a number of means. Provisioned users can take advantage of rich authentication features including single sign-on (SSO), OAuth, and two-factor verification.
You can provision users automatically using one of the following tools and services:
– Google Cloud Directory Sync (GCDS)
– Google Admin SDK
– A third-party connector
GCDS is a connector that can provision users and groups on your behalf for both Google Cloud Platform and G Suite. Using GCDS, you can automate the addition, modification, and deletion of users, groups, and non-employee contacts. You can synchronize the data from your LDAP directory server to your Google Cloud Platform domain by using LDAP queries. This synchronization is one-way: the data in your LDAP directory server is never modified.
Reference contents:
– Best practices for enterprise organizations | Documentation
Question 25
Your company has successfully migrated to the cloud and wants to analyze their data stream to optimize operations.
They do not have any existing code for this analysis, so they are exploring all their options. These options include a mix of batch and stream processing, as they are running some hourly jobs and live- processing some data as it comes in.
Which technology should they use for this?
- A. Google Cloud Dataproc
- B. Google Cloud Dataflow
- C. Google Container Engine with Google Cloud Bigtable
- D. Google Compute Engine with Google BigQuery
Correct Answer: B
Google Cloud Dataflow is a fully-managed service for transforming and enriching data in stream (real time) and batch (historical) modes with equal reliability and expressiveness — no more complex workarounds or compromises needed.
Reference contents:
– Qwiklab: Processing Data with Google Cloud Dataflow
Question 26
Your customer is receiving reports that their recently updated Google App Engine application is taking approximately 30 seconds to load for some of their users.
This behavior was not reported before the update.
What strategy should you take?
- A. Work with your ISP to diagnose the problem.
- B. Open a support ticket to ask for network capture and flow data to diagnose the problem, then roll back your application.
- C. Roll back to an earlier known good release initially, then use Stackdriver Trace and Logging to diagnose the problem in a development/test/staging environment.
- D. Roll back to an earlier known good release, then push the release again at a quieter period to investigate. Then use Stackdriver Trace and Logging to diagnose the problem.
Correct Answer: C
Stackdriver Logging allows you to store, search, analyze, monitor, and alert on log data and events from Google Cloud Platform and Amazon Web Services (AWS). Our API also allows ingestion of any custom log data from any source. Stackdriver Logging is a fully managed service that performs at scale and can ingest application and system log data from thousands of VMs. Even better, you can analyze all that log data in real time.
Reference contents:
– Google Cloud Logging
Question 27
A production database virtual machine on Google Compute Engine has an ext4-formatted persistent disk for data files.
The database is about to run out of storage space.
How can you remediate the problem with the least amount of downtime?
- A. In the Google Cloud Console, increase the size of the persistent disk and use the resize2fs command in Linux.
- B. Shut down the virtual machine, use the Google Cloud Console to increase the persistent disk size, then restart the virtual machine.
- C. In the Google Cloud Console, increase the size of the persistent disk and verify the new space is ready to use with the fdisk command in Linux.
- D. In the Google Cloud Console, create a new persistent disk attached to the virtual machine, format and mount it, and configure the database service to move the files to the new disk.
- E. In the Google Cloud Console, create a snapshot of the persistent disk restore the snapshot to a new larger disk, unmount the old disk, mount the new disk and restart the database service.
Correct Answer: A
On Linux instances, connect to your instance and manually resize your partitions and file systems to use the additional disk space that you added.
Extend the file system on the disk or the partition to use the added space. If you grew a partition on your disk, specify the partition. If your disk does not have a partition table, specify only the disk ID. sudo resize2fs /dev/[DISK_ID][PARTITION_NUMBER] where [DISK_ID] is the device name and [PARTITION_NUMBER] is the partition number for the device where you are resizing the file system.
Reference contents:
– Adding or resizing zonal persistent disks | Compute Engine Documentation
Question 28
Your application needs to process credit card transactions.
You want the smallest scope of Payment Card Industry (PCI) compliance without compromising the ability to analyze transactional data and trends relating to which payment methods are used.
How should you design your architecture?
- A. Create a tokenizer service and store only tokenized data.
- B. Create separate projects that only process credit card data.
- C. Create separate subnetworks and isolate the components that process credit card data
- D. Streamline the audit discovery phase by labeling all of the virtual machines (VMs) that process PCI data.
- E. Enable Logging export to Google BigQuery and use ACLs and views to scope the data shared with the auditor.
Correct Answer: A
Reference contents:
– Six Ways to Reduce PCI DSS Audit Scope by Tokenizing Cardholder data
Question 29
You have been asked to select the storage system for the click-data of your company’s large portfolio of websites.
This data is streamed in from a custom website analytics package at a typical rate of 6,000 clicks per minute. With bursts of up to 8,500 clicks per second. It must have been stored for future analysis by your data science and user experience teams.
Which storage infrastructure should you choose?
- A. Google Cloud SQL
- B. Google Cloud Bigtable
- C. Google Cloud Storage
- D. Google Cloud Datastore
Correct Answer: B
Google Cloud Bigtable is a scalable, fully-managed NoSQL wide-column database that is suitable for both real-time access and analytics workloads.
Good for:
– Low-latency read/write access
– High-throughput analytics
– Native time series support
Common workloads:
– IoT, finance, adtech
– Personalization, recommendations
– Monitoring
– Geospatial datasets
– Graphs
C: Google Cloud Storage is a scalable, fully-managed, highly reliable, and cost-efficient object / blob store.
Is good for:
– Images, pictures, and videos
– Objects and blobs
– Unstructured data
D: Google Cloud Datastore is a scalable, fully-managed NoSQL document database for your web and mobile applications.
Is good for:
– Semi-structured application data
– Hierarchical data
– Durable key-value data
Common workloads:
– User profiles
– Product catalogs
– Game state
Reference contents:
– Cloud Storage Options
Question 30
You are creating a solution to remove backup files older than 90 days from your backup Google Cloud Storage bucket.
You want to optimize ongoing Google Cloud Storage spend.
What should you do?
- A. Write a lifecycle management rule in XML and push it to the bucket with gsutil.
- B. Write a lifecycle management rule in JSON and push it to the bucket with gsutil.
- C. Schedule a cron script using gsutil ls gs://backups/** to find and remove items older than 90 days.
- D. Schedule a cron script using gsutil ls gs://backups/** to find and remove items older than 90 days and schedule it with cron.
Correct Answer: B
Question 31
Your company is forecasting a sharp increase in the number and size of Apache Spark and Hadoop jobs being run on your local datacenter.
You want to utilize the cloud to help you scale this upcoming demand with the least amount of operations work and code change.
Which product should you use?
- A. Google Cloud Dataflow
- B. Google Cloud Dataproc
- C. Google Compute Engine
- D. Google Kubernetes Engine
Correct Answer: B
Google Cloud Dataproc is a fast, easy-to-use, low-cost and fully managed service that lets you run the Apache Spark and Apache Hadoop ecosystem on Google Cloud Platform. Google Cloud Dataproc provisions big or small clusters rapidly, supports many popular job types, and is integrated with other Google Cloud Platform services, such as Google Cloud Storage and Stackdriver Logging, thus helping you reduce TCO.
Reference contents:
– Dataproc FAQ | Dataproc Documentation
Question 32
The database administration team has asked you to help them improve the performance of their new database server running on Google Compute Engine.
The database is for importing and normalizing their performance statistics and is built with MySQL running on Debian Linux. They have an n1-standard-8 virtual machine with 80 GB of SSD persistent disk.
What should they change to get better performance from this system?
- A. Increase the virtual machine’s memory to 64 GB.
- B. Create a new virtual machine running PostgreSQL.
- C. Dynamically resize the SSD persistent disk to 500 GB.
- D. Migrate their performance metrics warehouse to Google BigQuery.
- E. Modify all of their batch jobs to use bulk inserts into the database.
Correct Answer: C
Question 33
You want to optimize the performance of an accurate, real-time, weather-charting application.
The data comes from 50,000 sensors sending 10 readings a second, in the format of a timestamp and sensor reading.
Where should you store the data?
- A. Google BigQuery
- B. Google Cloud SQL
- C. Google Cloud Bigtable
- D. Google Cloud Storage
Correct Answer: C
Google Cloud Bigtable is a scalable, fully-managed NoSQL wide-column database that is suitable for both real-time access and analytics workloads.
Good for:
– Low-latency read/write access
– High-throughput analytics
– Native time series support
Common workloads:
– IoT, finance, adtech
– Personalization, recommendations
– Monitoring
– Geospatial datasets
Graphs
Reference contents:
– Cloud Storage Options
Question 34
Your company’s user-feedback portal comprises a standard LAMP stack replicated across two zones.
It is deployed in the us-central1 region and uses autoscaled managed instance groups on all layers, except the database. Currently, only a small group of select customers have access to the portal. The portal meets a 99,99% availability SLA under these conditions. However next quarter, your company will be making the portal available to all users, including unauthenticated users. You need to develop a resiliency testing strategy to ensure the system maintains the SLA once they introduce additional user load.
What should you do?
- A. Capture existing users input, and replay captured user load until autoscale is triggered on all layers. At the same time, terminate all resources in one of the zones.
- B. Create synthetic random user input, replay synthetic load until autoscale logic is triggered on at least one layer, and introduce “chaos” to the system by terminating random resources on both zones.
- C. Expose the new system to a larger group of users, and increase group size each day until autoscale logic is triggered on all layers. At the same time, terminate random resources on both zones.
- D. Capture existing users input, and replay captured user load until resource utilization crosses 80%. Also, derive an estimated number of users based on existing user’s usage of the app, and deploy enough resources to handle 200% of expected load.
Correct Answer: D
Question 35
One of the developers on your team deployed their application in Google Container Engine with the Dockerfile below.
They report that their application deployments are taking too long.
FROM ./src
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y python python-pip
RUN pip install -r requirements.txtYou want to optimize this Dockerfile for faster deployment times without adversely affecting the app’s functionality.
Which two actions should you take? (Choose 2 answers)
- A. Remove Python after running pip.
- B. Remove dependencies from requirements.txt.
- C. Use a slimmed-down base image like Alpine Linux.
- D. Use larger machine types for your Google Container Engine node pools.
- E. Copy the source after the package dependencies (Python and pip) are installed.
Correct Answer: C, E
The speed of deployment can be changed by limiting the size of the uploaded app, limiting the complexity of the build necessary in the Dockerfile, if present, and by ensuring a fast and reliable internet connection.
Alpine Linux is built around musl libc and busybox. This makes it smaller and more resource efficient than traditional GNU/Linux distributions. A container requires no more than 8 MB and a minimal installation to disk requires around 130 MB of storage. Not only do you get a fully-fledged Linux environment but a large selection of packages from the repository.
Reference contents:
–Google App Engine is slow to deploy, hangs on “Updating service [someproject]…”
– about
Question 36
Your solution is producing performance bugs in production that you did not see in staging and test environments.
You want to adjust your test and deployment procedures to avoid this problem in the future.
What should you do?
- A. Deploy fewer changes to production.
- B. Deploy smaller changes to production.
- C. Increase the load on your test and staging environments.
- D. Deploy changes to a small subset of users before rolling out to production.
Correct Answer: D
Question 37
A small number of API requests to your microservices-based application take a very long time.
You know that each request to the API can traverse many services. You want to know which service takes the longest in those cases.
What should you do?
- A. Set timeouts on your application so that you can fail requests faster.
- B. Send custom metrics for each of your requests to Stackdriver Monitoring.
- C. Use Stackdriver Monitoring to look for insights that show when your API latencies are high.
- D. Instrument your application with Stackdriver Trace in order to break down the request latencies at each microservice.
Correct Answer: D
Reference contents:
– Quickstart | Cloud Trace
Question 38
During a high traffic portion of the day, one of your relational databases crashes, but the replica is never promoted to a master.
You want to avoid this in the future.
What should you do?
- A. Use a different database.
- B. Choose larger instances for your database.
- C. Create snapshots of your database more regularly.
- D. Implement routinely scheduled failovers of your databases.
Correct Answer: B
Question 39
Your organization requires that metrics from all applications be retained for 5 years for future analysis in possible legal proceedings.
Which approach should you use?
- A. Grant the security team access to the logs in each Project.
- B. Configure Stackdriver Monitoring for all Projects, and export to Google BigQuery.
- C. Configure Stackdriver Monitoring for all Projects with the default retention policies.
- D. Configure Stackdriver Monitoring for all Projects, and export to Google Cloud Storage.
Correct Answer: B
Stackdriver Logging provides you with the ability to filter, search, and view logs from your cloud and open source application services. Allows you to define metrics based on log contents that are incorporated into dashboards and alerts. Enables you to export logs to Google BigQuery, Google Cloud Storage, and Google Cloud Pub/Sub.
Reference contents:
– Operations: Cloud Monitoring & Logging
Question 40
Your company has decided to build a backup replica of their on-premises user authentication PostgreSQL database on Google Cloud Platform.
The database is 4 TB, and large updates are frequent. Replication requires private address space communication.
Which networking approach should you use?
- A. Dedicated Interconnect
- B. Cloud VPN connected to the data center network.
- C. A NAT and TLS translation gateway installed on-premises.
- D. A Google Compute Engine instance with a VPN server installed connected to the data center network.
Correct Answer: A
Google Cloud Dedicated Interconnect provides direct physical connections and RFC 1918 communication between your on-premises network and Google’s network. Dedicated Interconnect enables you to transfer large amounts of data between networks, which can be more cost effective than purchasing additional bandwidth over the public Internet or using VPN tunnels.
Benefits:
-Traffic between your on-premises network and your VPC network doesn’t traverse the public Internet. Traffic traverses a dedicated connection with fewer hops, meaning there are less points of failure where traffic might get dropped or disrupted.
– Your VPC network’s internal (RFC 1918) IP addresses are directly accessible from your on-premises network. You don’t need to use a NAT device or VPN tunnel to reach internal IP addresses. Currently, you can only reach internal IP addresses over a dedicated connection. To reach Google external IP addresses, you must use a separate connection.
– You can scale your connection to Google based on your needs. Connection capacity is delivered over one or more 10 Gbps Ethernet connections, with a maximum of eight connections (80 Gbps total per interconnect).
– The cost of egress traffic from your VPC network to your on-premises network is reduced. A dedicated connection is generally the least expensive method if you have a high-volume of traffic to and from Google’s network.
Reference contents:
– Dedicated Interconnect overview
Question 41
Auditors visit your teams every 12 months and ask to review all the Google Cloud Identity and Access Management (Cloud IAM) policy changes in the previous 12 months.
You want to streamline and expedite the analysis and audit process.
What should you do?
- A. Create custom Google Stackdriver alerts and send them to the auditor.
- B. Enable Logging export to Google BigQuery and use ACLs and views to scope the data shared with the auditor.
- C. Use Google Cloud Functions to transfer log entries to Google Cloud SQL and use ACLs and views to limit an auditor’s view.
- D. Enable Google Cloud Storage (GCS) log export to audit logs into a GCS bucket and delegate access to the bucket.
Correct Answer: D
Question 42
You are designing a large distributed application with 30 microservices.
Each of your distributed microservices needs to connect to a database back-end. You want to store the credentials securely.
Where should you store the credentials?
- A. In the source code.
- B. In an environment variable.
- C. In a secret management system.
- D. In a config file that has restricted access through ACLs.
Correct Answer: C
Reference contents:
– Secret Manager conceptual overview | Secret Manager Documentation
Question 43
A lead engineer wrote a custom tool that deploys virtual machines in the legacy data center.
He wants to migrate the custom tool to the new cloud environment. You want to advocate for the adoption of Google Cloud Deployment Manager.
What are two business risks of migrating to Google Cloud Deployment Manager? (Choose 2 answers)
- A. Google Cloud Deployment Manager uses Python.
- B. Google Cloud Deployment Manager APIs could be deprecated in the future.
- C. Google Cloud Deployment Manager is unfamiliar to the company’s engineers.
- D. Google Cloud Deployment Manager requires a Google APIs service account to run.
- E. Google Cloud Deployment Manager can be used to permanently delete cloud resources.
- F. Google Cloud Deployment Manager only supports automation of Google Cloud resources.
Correct Answer: B, F
Question 44
A development manager is building a new application.
He asks you to review his requirements and identify what cloud technologies he can use to meet them. The application mus:
– Be based on open-source technology for cloud portability
– Dynamically scale compute capacity based on demand
– Support continuous software delivery
– Run multiple segregated copies of the same application stack
– Deploy application bundles using dynamic templates
– Route network traffic to specific services based on URL
Which combination of technologies will meet all of his requirements?
- A. Google Kubernetes Engine, Jenkins, and Helm
- B. Google Kubernetes Engine and Google Cloud Load Balancing
- C. Google Kubernetes Engine and Google Cloud Deployment Manager
- D. Google Kubernetes Engine, Jenkins, and Google Cloud Load Balancing
Correct Answer: D
Jenkins is an open-source automation server that lets you flexibly orchestrate your build, test, and deployment pipelines. Google Kubernetes Engine is a hosted version of Kubernetes, a powerful cluster manager and orchestration system for containers.
When you need to set up a continuous delivery (CD) pipeline, deploying Jenkins on Google Kubernetes Engine provides important benefits over a standard VM-based deployment.
A: Helm is a tool for managing Kubernetes charts. Charts are packages of pre-configured Kubernetes resources.
Use Helm to:
– Find and use popular software packaged as Kubernetes charts
– Share your own applications as Kubernetes charts
– Create reproducible builds of your Kubernetes applications
– Intelligently manage your Kubernetes manifest files
– Manage releases of Helm packages
Reference contents:
– Jenkins on Kubernetes Engine | Solutions
Question 45
You have created several pre-emptible Linux virtual machine instances using Google Compute Engine.
You want to properly shut down your application before the virtual machines are preempted.
What should you do?
- A. Create a shutdown script named k99.shutdown in the /etc/rc.6.d/ directory.
- B. Create a shutdown script registered as a xinetd service in Linux and configure a Stackdriver endpoint check to call the service.
- C. Create a shutdown script and use it as the value for a new metadata entry with the key shutdown-script in the Google Cloud Console when you create the new virtual machine instance.
- D. Create a shutdown script, registered as a xinetd service in Linux, and use the gcloud compute instances add-metadata command to specify the service URL as the value for a new metadata entry with the key shutdown-script-url.
Correct Answer: C
A startup script, or a shutdown script, is specified through the metadata server, using startup script metadata keys.
Reference contents:
– Running startup scripts | Compute Engine Documentation
Question 46
Your organization has a 3-tier web application deployed in the same network on Google Cloud Platform.
Each tier (web, API, and database) scales independently of the others. Network traffic should flow through the web to the API tier and then on to the database tier. Traffic should not flow between the web and the database tier.
How should you configure the network?
- A. Add each tier to a different subnetwork.
- B. Set up software based firewalls on individual VMs.
- C. Add tags to each tier and set up routes to allow the desired traffic flow.
- D. Add tags to each tier and set up firewall rules to allow the desired traffic flow.
Correct Answer: D
Google Cloud Platform(GCP) enforces firewall rules through rules and tags. GCP rules and tags can be defined once and used across all regions.
Reference contents:
– Google Cloud for OpenStack Users
– Building three-tier architectures with security groups | AWS News Blog
Question 47
Your development team has installed a new Linux kernel module on the batch servers in Google Compute Engine (GCE) virtual machines (VMs) to speed up the nightly batch process.
Two days after the installation, 50% of the batch servers failed the nightly batch run. You want to collect details on the failure to pass back to the development team.
Which three actions should you take? (Choose 3 answers)
- A. Use Stackdriver Logging to search for the module log entries.
- B. Read the debug GCE Activity log using the API or Google Cloud Console.
- C. Use gcloud or Google Cloud Console to connect to the serial console and observe the logs.
- D. Identify whether a live migration event of the failed server occurred, using in the activity log.
- E. Adjust the Google Stackdriver timeline to match the failure time, and observe the batch server metrics.
- F. Export a debug VM into an image, and run the image on a local server where kernel log messages will be displayed on the native screen.
Correct Answer: A, C, E
Question 48
Your company wants to try out the cloud with low risk.
They want to archive approximately 100 TB of their log data to the cloud and test the analytics features available to them there, while also retaining that data as a long-term disaster recovery backup.
Which two steps should you take? (Choose 2 answers)
- A. Load logs into Google BigQuery.
- B. Load logs into Google Cloud SQL.
- C. Import logs into Google Stackdriver.
- D. Insert logs into Google Cloud Bigtable.
- E. Upload log files into Google Cloud Storage.
Correct Answer: A, E
Question 49
You created a pipeline that can deploy your source code changes to your infrastructure in instance groups for self-healing.
One of the changes negatively affects your key performance indicator. You are not sure how to fix it, and investigation could take up to a week.
What should you do?
- A. Log in to a server, and iterate on the fox locally.
- B. Revert the source code change, and rerun the deployment pipeline.
- C. Log into the servers with the bad code change, and swap in the previous code.
- D. Change the instance group template to the previous one, and delete all instances.
Correct Answer: B
Question 50
Your organization wants to control IAM policies for different departments independently, but centrally.
Which approach should you take?
- A. Multiple Organizations with multiple Folders.
- B. Multiple Organizations, one for each department.
- C. A single Organization with Folders for each department.
- D. A single Organization with multiple projects, each with a central owner.
Correct Answer: C
Folders are nodes in the Google Cloud Platform Resource Hierarchy. A folder can contain projects, other folders, or a combination of both. You can use folders to group projects under an organization in a hierarchy. For example, your organization might contain multiple departments, each with its own set of GCP resources. Folders allow you to group these resources on a per-department basis. Folders are used to group resources that share common IAM policies. While a folder can contain multiple folders or resources, a given folder or resource can have exactly one parent.
Reference contents:
– Creating and managing Folders | Resource Manager Documentation
Question 51
You deploy your custom Java application to Google App Engine.
It fails to deploy and gives you the following stack trace.
What should you do?
java.lang.SecurityException: SHA1 diest digest error for com/Altostart/CloakeServlet.class
at com.google.appengine.runtime.Request.prosess-d36f818a24b8cf1d (Request.java)
at sun.security.util.ManifestEntryVerifier.verify (ManifestEntryVerifier.java:210)
at.java.util.har.JarVerifier.prosessEntry (JarVerifier.java:218)
at java.util.jar.JarVerifier.update (JarVerifier.java:205)
at java.util.jar.JarVerifiersVerifierStream.read (JarVerifier.java:428)
at sun.misc.Resource.getBytes (Resource.java:124)
at java.net.URL.ClassLoader.defineClass (URCClassLoader.java:273)
at sun.reflect.GenerateMethodAccessor5.invoke (Unknown Source)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImp1.invoke (DelegatingMethodAccessorImp1.java:43)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke (Method.java:616)
at java.lang.ClassLoader.loadClass (ClassLoader.java:266)- A. Upload missing JAR files and redeploy your application.
- B. Digitally sign all of your JAR files and redeploy your application.
- C. Recompile the CLoakedServlet class using an MD5 hash instead of SHA1.
Correct Answer: B
Question 52
You are designing a mobile chat application.
You want to ensure people cannot spoof chat messages, by providing a message were sent by a specific user.
What should you do?
- A. Tag messages client side with the originating user identifier and the destination user.
- B. Encrypt the message client side using block-based encryption with a shared key.
- C. Use public key infrastructure (PKI) to encrypt the message client side using the originating user’s private key.
- D. Use a trusted certificate authority to enable SSL connectivity between the client application and the server.
Correct Answer: C
Question 53
As part of implementing their disaster recovery plan, your company is trying to replicate their production MySQL database from their private data center to their GCP project using a Google Cloud VPN connection.
They are experiencing latency issues and a small amount of packet loss that is disrupting the replication.
What should they do?
- A. Configure their replication to use UDP.
- B. Configure a Dedicated Interconnect.
- C. Restore their database daily using Google Cloud SQL.
- D. Add additional VPN connections and load balance them.
- E. Send the replicated transaction to Google Cloud Pub/Sub.
Correct Answer: B
Question 54
Your customer support tool logs all email and chat conversations to Google Cloud Bigtable for retention and analysis.
What is the recommended approach for sanitizing this data of personally identifiable information or payment card information before initial storage?
- A. Hash all data using SHA256.
- B. Encrypt all data using elliptic curve cryptography.
- C. De-identify the data with the Google Cloud Data Loss Prevention API.
- D. Use regular expressions to find and redact phone numbers, email addresses, and credit card numbers.
Correct Answer: C
Reference contents:
– PCI Data Security Standard compliance | Architectures
Question 55
You are using Google Cloud Shell and need to install a custom utility for use in a few weeks.
Where can you store the file so it is in the default execution path and persists across sessions?
- A. ~/bin
- B. Google Cloud Storage
- C. /google/scripts
- D. /usr/local/bin
Correct Answer: A
Question 56
You want to create a private connection between your instances on Google Compute Engine and your on-premises data center.
You require a connection of at least 20 Gbps. You want to follow Google-recommended practices.
How should you set up the connection?
- A. Create a VPC and connect it to your on-premises data center using Dedicated Interconnect.
- B. Create a VPC and connect it to your on-premises data center using a single Cloud VPN.
- C. Create a Cloud Content Delivery Network (Cloud CDN) and connect it to your on-premises data center using Dedicated Interconnect.
- D. Create a Cloud Content Delivery Network (Cloud CDN) and connect it to your on-premises datacenter using a single Cloud VPN.
Correct Answer: A
Question 57
You are analyzing and defining business processes to support your startup’s trial usage of GCP, and you don’t yet know what consumer demand for your product will be.
Your manager requires you to minimize GCP service costs and adhere to Google best practices.
What should you do?
- A. Utilize free tier and sustained use discounts. Provision a staff position for service cost management.
- B. Utilize free tier and sustained use discounts. Provide training to the team about service cost management.
- C. Utilize free tier and committed use discounts. Provision a staff position for service cost management.
- D. Utilize free tier and committed use discounts. Provide training to the team about service cost management.
Correct Answer: A
![[GCP] Google Cloud Certified:Professional Cloud Architect](https://www.cloudsmog.net/wp-content/uploads/google-cloud-certified_professional-cloud-architect-1200x675.jpg)
Comments are closed