Ace Your Professional Cloud Developer Certification with Practice Exams.
Google Cloud Certified – Professional Cloud Developer – Practice Exam (Question 84)
Question 1
You want to upload files from an on-premises virtual machine to Google Cloud Storage as part of a data migration.
These files will be consumed by Google Cloud Dataproc Hadoop cluster in a GCP environment.
Which command should you use?
- A. gsutil cp [LOCAL_OBJECT] gs://[DESTINATION_BUCKET_NAME]/
- B. gcloud cp [LOCAL_OBJECT] gs://[DESTINATION_BUCKET_NAME]/
- C. hadoop fs cp [LOCAL_OBJECT] gs://[DESTINATION_BUCKET_NAME]/
- D. gcloud dataproc cp [LOCAL_OBJECT] gs://[DESTINATION_BUCKET_NAME]/
Correct Answer: A
The gsutil cp command allows you to copy data between your local file. storage. boto files generated by running “gsutil config”.
Question 2
You migrated your applications to Google Cloud Platform and kept your existing monitoring platform.
You now find that your notification system is too slow for time critical problems.
What should you do?
- A. Replace your entire monitoring platform with Stackdriver.
- B. Install the Stackdriver agents on your Google Compute Engine instances.
- C. Use Stackdriver to capture and alert on logs, then ship them to your existing platform.
- D. Migrate some traffic back to your old platform and perform AB testing on the two platforms concurrently.
Correct Answer: B
Reference contents:
– Google Cloud Monitoring | Google Cloud
Question 3
You are planning to migrate a MySQL database to the managed Google Cloud SQL database for Google Cloud.
You have Google Compute Engine virtual machine instances that will connect with this Google Cloud SQL instance. You do not want to whitelist IPs for the Google Compute Engine instances to be able to access Google Cloud SQL.
What should you do?
- A. Enable private IP for the Google Cloud SQL instance.
- B. Whitelist a project to access Google Cloud SQL, and add Google Compute Engine instances in the whitelisted project.
- C. Create a role in Google Cloud SQL that allows access to the database from external instances, and assign the Google Compute Engine instances to that role.
- D. Create a Google Cloud SQL instance on one project. Create Google Compute Engine instances in a different project. Create a VPN between these two projects to allow internal access to Google Cloud SQL.
Correct Answer: C
Reference contents:
– Connecting Overview | Cloud SQL for MySQL | Google Cloud
Question 4
You have deployed an HTTP(s) Load Balancer with the gcloud commands shown below.
export NAME-load-balancer
# create network
gcloud compute networks create ${NAME}
# add instance
gcloud compute instances create ${NAME} -backend-instance-1 --subnet ${NAME} --no address
# create the instance group
gcloud compute instance-groups unmanaged create ${NAME} -i
gcloud compute instance-groups unmanaged set-named-ports ${NAME}-i --named-ports http:80 gcloud compute instance-groups unmanaged add-instances ${NAME}-i --instances ${NAME}-instance-1
# configure health checks
gcloud compute health-checks create http ${NAME}-http-hc --port 80
# create backend service
gcloud compute backend-services create ${NAME} -http-bes --health-checks ${NAME} -http-hc --protocol HTTP --port-name http --global
gcloud compute backend-services add-backend ${NAME} -http-bes --instance-group ${NAME} -i --balancing-mode RATE --max-rate 100000 --capacity-scaler 1.0 --global --instance-group-zone us-east1-d
# create urls maps and forwarding rule
gcloud compute url-maps create ${NAME}-http-urlmap --default-service ${NAME}-http-bes
gcloud compute target-http-proxies create ${NAME} -http-proxy --url-map ${NAME} -http-urlmap
gcloud compute forwarding-rules create ${NAME} -http-fw --global --ip-protocol ICP --target-http-proxy ${NAME} -http-proxy --ports 80Health checks to port 80 on the Google Compute Engine virtual machine instance are failing and no traffic is sent to your instances. You want to resolve the problem.
Which commands should you run?
- A. gcloud compute instances add-access-config ${NAME}-backend-instance-1
- B. gcloud compute instances add-tags ${NAME}-backend-instance-1 –tags http-server
- C. gcloud compute firewall-rules create allow-lb –network load-balancer –allow tcp –source-ranges 130.211.0.0/22,35.191.0.0/16 –direction INGRESS
- D. gcloud compute firewall-rules create allow-lb –network load-balancer –allow tcp –destination-ranges 130.211.0.0/22,35.191.0.0/16 –direction EGRESS
Correct Answer: C
Reference contents:
– Configuring VMs for networking use cases | VPC | Google Cloud
Question 5
Your website is deployed on Google Compute Engine.
Your marketing team wants to test conversion rates between 3 different website designs.
Which approach should you use?
- A. Deploy the website on Google App Engine and use traffic splitting.
- B. Deploy the website on Google App Engine as three separate services.
- C. Deploy the website on Google Cloud Functions and use traffic splitting.
- D. Deploy the website on Google Cloud Functions as three separate functions.
Correct Answer: A
Reference contents:
–Splitting Traffic | App Engine standard environment for Python 2 | Google Cloud
Question 6
You need to copy directory local-scripts and all of its contents from your local workstation to a Google Compute Engine virtual machine instance.
Which command should you use?
- A. gsutil cp –project “my-gcp-project” -r ~/local-scripts/ gcp-instance-name:~/server-scripts/ –zone “us-east1-b”
- B. gsutil cp –project “my-gcp-project” -R ~/local-scripts/ gcp-instance-name:~/server-scripts/ –zone “us-east1-b”
- C. gcloud compute scp –project “my-gcp-project” –recurse ~/local-scripts/ gcp-instance-name:~/server-scripts/ –zone “us-east1-b”
- D. gcloud compute mv –project “my-gcp-project” –recurse ~/local-scripts/ gcp-instance-name:~/server-scripts/ –zone “us-east1-b”
Correct Answer: C
Reference contents:
–gcloud compute copy-files | Cloud SDK Documentation | Google Cloud
Question 7
You are deploying your application to a Google Compute Engine virtual machine instance with the Stackdriver Monitoring Agent installed.
Your application is a unix process on the instance. You want to be alerted if the unix process has not run for at least 5 minutes. You are not able to change the application to generate metrics or logs.
Which alert condition should you configure?
- A. Uptime check
- B. Process health
- C. Metric absence
- D. Metric threshold
Correct Answer: B
Reference contents:
– Alerting behavior | Cloud Monitoring | Google Cloud
Question 8
You have two tables in an ANSI-SQL compliant database with identical columns that you need to quickly combine into a single table, removing duplicate rows from the result set.
What should you do?
- A. Use the JOIN operator in SQL to combine the tables.
- B. Use nested WITH statements to combine the tables.
- C. Use the UNION operator in SQL to combine the tables.
- D. Use the UNION ALL operator in SQL to combine the tables.
Correct Answer: C
Reference contents:
– SQL: UNION ALL Operator
Question 9
You have an application deployed in production.
When a new version is deployed, some issues don’t arise until the application receives traffic from users in production. You want to reduce both the impact and the number of users affected.
Which deployment strategy should you use?
- A. Blue/green deployment
- B. Canary deployment
- C. Rolling deployment
- D. Recreate deployment
Correct Answer: A
Reference contents:
– Six Strategies for Application Deployment – The New Stack
Question 10
Your company wants to expand their users outside the United States for their popular application.
The company wants to ensure 99.999% availability of the database for their application and also wants to minimize the read latency for their users across the globe.
Which two actions should they take? (Choose two.)
- A. Create a multi-regional Google Cloud Spanner instance with “nam-asia-eur1” configuration.
- B. Create a multi-regional Google Cloud Spanner instance with “nam3” configuration.
- C. Create a cluster with at least 3 Google Cloud Spanner nodes.
- D. Create a cluster with at least 1 Google Cloud Spanner node.
- E. Create a minimum of two Google Cloud Spanner instances in separate regions with at least one node.
- F. Create a Google Cloud Dataflow pipeline to replicate data across different databases.
Correct Answer: B, F
Question 11
You need to migrate an internal file upload API with an enforced 500-MB file size limit to Google App Engine.
What should you do?
- A. Use FTP to upload files.
- B. Use CPanel to upload files.
- C. Use signed URLs to upload files.
- D. Change the API to be a multipart file upload API.
Correct Answer: C
Reference contents:
– Google Cloud Platform
Question 12
You are planning to deploy your application in a Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster.
The application exposes an HTTP-based health check at /healthz. You want to use this health check endpoint to determine whether traffic should be routed to the pod by the load balancer.
Which code snippet should you include in your Pod configuration?
- A.
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /healthez
port: 80 - B.
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /healthez
port: 80 - C.
loadbalancerHealthCheck:
httpGet:
path: /healthez
port: 80 - D.
HealthCheck:
httpGet:
path: /healthez
port: 80
Correct Answer: B
For the GKE ingress controller to use your readinessProbes as health checks, the Pods for an Ingress must exist at the time of Ingress creation. If your replicas are scaled to 0, the default health check will apply.
Question 13
Your teammate has asked you to review the code below. Its purpose is to efficiently add a large number of small rows to a Google BigQuery table.
BigQuery service = BigQueryOptions.newBuilder().build().getService();
public void writeTo BigQuery(Collection<Map<String, String>> rows){
for(Map>String, String> row : row){
InsertAllRequest insertRequest = insertAllRequest.newBuilder(
"datasetId", "tableID",
InsertAllRequest.RowToInsert.of(row)).build():
service.insertAll(insertReQuest);
}
}Which improvement should you suggest your teammate make?
- A. Include multiple rows with each request.
- B. Perform the inserts in parallel by creating multiple threads.
- C. Write each row to a Google Cloud Storage object, then load into Google BigQuery.
- D. Write each row to a Google Cloud Storage object in parallel, then load into Google BigQuery.
Correct Answer: B
Question 14
You are developing a JPEG image-resizing API hosted on Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE).
Callers of the service will exist within the same GKE cluster. You want clients to be able to get the IP address of the service.
What should you do?
- A. Define a GKE Service. Clients should use the name of the A record in Google Cloud DNS to find the service’s cluster IP address.
- B. Define a GKE Service. Clients should use the service name in the URL to connect to the service.
- C. Define a GKE Endpoint. Clients should get the endpoint name from the appropriate environment variable in the client container.
- D. Define a GKE Endpoint. Clients should get the endpoint name from Google Cloud DNS.
Correct Answer: C
Question 15
You are using Google Cloud Build to build and test application source code stored in Google Cloud Source Repositories.
The build process requires a build tool not available in the Google Cloud Build environment.
What should you do?
- A. Download the binary from the internet during the build process.
- B. Build a custom Google Cloud Builder image and reference the image in your build steps.
- C. Include the binary in your Google Cloud Source Repositories repository and reference it in your build scripts.
- D. Ask to have the binary added to the Google Cloud Build environment by filing a feature request against the Google Cloud Build public Issue Tracker.
Correct Answer: B
Question 16
You are deploying your application to a Google Compute Engine virtual machine instance.
Your application is configured to write its log files to disk. You want to view the logs in Stackdriver Logging without changing the application code.
What should you do?
- A. Install the Stackdriver Logging Agent and configure it to send the application logs.
- B. Use a Stackdriver Logging Library to log directly from the application to Stackdriver Logging.
- C. Provide the log file folder path in the metadata of the instance to configure it to send the application logs.
- D. Change the application to log to /var/log so that its logs are automatically sent to Stackdriver Logging.
Correct Answer: A
Question 17
Your service adds text to images that it reads from Google Cloud Storage.
During busy times of the year, requests to Google Cloud Storage fail with an HTTP 429 “Too Many Requests” status code.
How should you handle this error?
- A. Add a cache-control header to the objects.
- B. Request a quota increase from the Google Cloud Console.
- C. Retry the request with a truncated exponential backoff strategy.
- D. Change the storage class of the Google Cloud Storage bucket to Multi-regional.
Correct Answer: C
Reference contents:
– Usage limits | Gmail API | Google Developers
Question 18
You are building an API that will be used by Android and iOS apps.
The API must:
– Support HTTPs.
– Minimize bandwidth cost.
– Integrate easily with mobile apps.
Which API architecture should you use?
- A. RESTful APIs
- B. MQTT for APIs
- C. gRPC-based APIs
- D. SOAP-based APIs
Correct Answer: A
Reference contents:
– How to Build a RESTful API for Your Mobile App?
Question 19
Your application takes an input from a user and publishes it to the user’s contacts.
This input is stored in a table in Google Cloud Spanner. Your application is more sensitive to latency and less sensitive to consistency.
How should you perform reads from Google Cloud Spanner for this application?
- A. Perform Read-Only transactions.
- B. Perform stale reads using single-read methods.
- C. Perform strong reads using single-read methods.
- D. Perform stale reads using read-write transactions.
Correct Answer: D
Reference contents:
– Best practices for using Cloud Spanner as a gaming database | Google Cloud
Question 20
Your application is deployed in a Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster.
When a new version of your application is released, your CI/CD tool updates the spec.template.spec.containers[0].image value to reference the Docker image of your new application version. When the Deployment object applies the change, you want to deploy at least 1 replica of the new version and maintain the previous replicas until the new replica is healthy.
Which change should you make to the GKE Deployment object shown below?
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deploment
metadata:
name: ecommerce-frontend-deployment
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: ecommerce-frontend
spec:
containers:
- name: ecommerce-frontend-webapp
image:ecommerce-frontend-webapp:1.7.9
ports:
- containerPort: 80- A. Set the Deployment strategy to RollingUpdate with maxSurge set to 0, maxUnavailable set to 1.
- B. Set the Deployment strategy to RollingUpdate with maxSurge set to 1, maxUnavailable set to 0.
- C. Set the Deployment strategy to Recreate with maxSurge set to 0, maxUnavailable set to 1.
- D. Set the Deployment strategy to Recreate with maxSurge set to 1, maxUnavailable set to 0.
Correct Answer: D
Question 21
You plan to make a simple HTML application available on the internet.
This site keeps information about FAQs for your application. The application is static and contains images, HTML, CSS, and Javascript. You want to make this application available on the internet with as few steps as possible.
What should you do?
- A. Upload your application to Google Cloud Storage.
- B. Upload your application to an Google App Engine environment.
- C. Create a Google Compute Engine instance with Apache web server installed. Configure Apache web server to host the application.
- D. Containerize your application first. Deploy this container to GKE and assign an external IP address to the GKE pod hosting the application.
Correct Answer: A
Reference contents:
– Hosting a static website | Cloud Storage | Google Cloud
Question 22
Your company has deployed a new API to Google App Engine Standard environment.
During testing, the API is not behaving as expected. You want to monitor the application over time to diagnose the problem within the application code without redeploying the application.
Which tool should you use?
- A. Stackdriver Trace
- B. Stackdriver Monitoring
- C. Stackdriver Debug Snapshots
- D. Stackdriver Debug Logpoints
Correct Answer: B
Reference contents:
– GCP Stackdriver Tutorial : Debug Snapshots, Traces, Logging and Logpoints
Question 23
You want to use the Stackdriver Logging Agent to send an application’s log file to Stackdriver from a Google Compute Engine virtual machine instance.
After installing the Stackdriver Logging Agent, what should you do first?
- A. Enable the Error Reporting API on the project.
- B. Grant the instance full access to all Google Cloud APIs.
- C. Configure the application log file as a custom source.
- D. Create a Stackdriver Logs Export Sink with a filter that matches the application’s log entries.
Correct Answer: B
Question 24
Your company has a Google BigQuery data mart that provides analytics information to hundreds of employees.
One user wants to run jobs without interrupting important workloads. This user isn’t concerned about the time it takes to run these jobs. You want to fulfill this request while minimizing cost to the company and the effort required on your part.
What should you do?
- A. Ask the user to run the jobs as batch jobs.
- B. Create a separate project for the user to run jobs.
- C. Add the user as a job.user role in the existing project.
- D. Allow the user to run jobs when important workloads are not running.
Correct Answer: B
Question 25
You want to notify on-call engineers about a service degradation in production while minimizing development time.
What should you do?
- A. Use Google Cloud Functions to monitor resources and raise alerts.
- B. Use Google Cloud Pub/Sub to monitor resources and raise alerts.
- C. Use Stackdriver Error Reporting to capture errors and raise alerts.
- D. Use Stackdriver Monitoring to monitor resources and raise alerts.
Correct Answer: A
Question 26
You are writing a single-page web application with a user-interface that communicates with a third-party API for content using XMLHttpRequest.
The data displayed on the UI by the API results is less critical than other data displayed on the same web page, so it is acceptable for some requests to not have the API data displayed in the UI. However, calls made to the API should not delay rendering of other parts of the user interface. You want your application to perform well when the API response is an error or a timeout.
What should you do?
- A. Set the asynchronous option for your requests to the API to false and omit the widget displaying the API results when a timeout or error is encountered.
- B. Set the asynchronous option for your request to the API to true and omit the widget displaying the API results when a timeout or error is encountered.
- C. Catch timeout or error exceptions from the API call and keep trying with exponential backoff until the API response is successful.
- D. Catch timeout or error exceptions from the API call and display the error response in the UI widget.
Correct Answer: A
Question 27
You are creating a Google App Engine application that writes a file to any user’s Google Drive.
How should the application authenticate to the Google Drive API?
- A. With an OAuth Client ID that uses the https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.file scope to obtain an access token for each user.
- B. With an OAuth Client ID with delegated domain-wide authority.
- C. With the Google App Engine service account and https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.file scope that generates a signed JWT.
- D. With the Google App Engine service account with delegated domain-wide authority.
Correct Answer: B
Reference contents:
– Authenticate your users | Google Drive API | Google Developers
Question 28
You are creating a Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster and run this command:
gcloud container clusters create large-cluster--num-bides 200The command fails with the error:
insufficient regional quota to satisfy request: resource "CPUS": request requires '200.0' and is short '176..0'. project has quota of '24.0' with '24.0' available.
You want to resolve the issue. What should you do?
- A. Request additional GKE quota in the Google Cloud Console.
- B. Request additional Google Compute Engine quota in the Google Cloud Console.
- C. Open a support case to request additional GKE quota.
- D. Decouple services in the cluster, and rewrite new clusters to function with fewer cores.
Correct Answer: A
Question 29
You are parsing a log file that contains three columns: a timestamp, an account number (a string), and a transaction amount (a number).
You want to calculate the sum of all transaction amounts for each unique account number efficiently.
Which data structure should you use?
- A. A linked list
- B. A hash table
- C. A two-dimensional array
- D. A comma-delimited string
Correct Answer: B
Question 30
Your company has a Google BigQuery dataset named “Master” that keeps information about employee travel and expenses.
This information is organized by the employee department. That means employees should only be able to view information for their department. You want to apply a security framework to enforce this requirement with the minimum number of steps.
What should you do?
- A. Create a separate dataset for each department. Create a view with an appropriate WHERE clause to select records from a particular dataset for the specific department. Authorize this view to access records from your Master dataset. Give employees the permission to this department-specific dataset.
- B. Create a separate dataset for each department. Create a data pipeline for each department to copy appropriate information from the Master dataset to the specific dataset for the department. Give employees the permission to this department-specific dataset.
- C. Create a dataset named Master dataset. Create a separate view for each department in the Master dataset. Give employees access to the specific view for their department.
- D. Create a dataset named Master dataset. Create a separate table for each department in the Master dataset. Give employees access to the specific table for their department.
Correct Answer: B
Question 31
You have an application in production. It is deployed on Google Compute Engine virtual machine instances controlled by a managed instance group.
Traffic is routed to the instances via a HTTP(s) load balancer. Your users are unable to access your application. You want to implement a monitoring technique to alert you when the application is unavailable.
Which technique should you choose?
- A. Smoke tests
- B. Stackdriver uptime checks
- C. Google Cloud Load Balancing – heath checks
- D. Managed instance group – heath checks
Correct Answer: B
Reference contents:
– Stackdriver Monitoring Automation Part 3: Uptime Checks | by Charles | Google Cloud – Community
Question 32
You are load testing your server application.
During the first 30 seconds, you observe that a previously inactive Google Cloud Storage bucket is now servicing 2000 write requests per second and 7500 read requests per second. Your application is now receiving intermittent 5xx and 429 HTTP responses from the Google Cloud Storage JSON API as the demand escalates. You want to decrease the failed responses from the Google Cloud Storage API.
What should you do?
- A. Distribute the uploads across a large number of individual storage buckets.
- B. Use the XML API instead of the JSON API for interfacing with Google Cloud Storage.
- C. Pass the HTTP response codes back to clients that are invoking the uploads from your application.
- D. Limit the upload rate from your application clients so that the dormant bucket’s peak request rate is reached more gradually.
Correct Answer: A
Reference contents:
– Request rate and access distribution guidelines | Cloud Storage | Google Cloud
Question 33
Your application is controlled by a managed instance group.
You want to share a large read-only data set between all the instances in the managed instance group. You want to ensure that each instance can start quickly and can access the data set via its filesystem with very low latency. You also want to minimize the total cost of the solution.
What should you do?
- A. Move the data to a Google Cloud Storage bucket, and mount the bucket on the filesystem using Google Cloud Storage FUSE.
- B. Move the data to a Google Cloud Storage bucket, and copy the data to the boot disk of the instance via a startup script.
- C. Move the data to a Google Compute Engine persistent disk, and attach the disk in read-only mode to multiple Google Compute Engine virtual machine instances.
- D. Move the data to a Google Compute Engine persistent disk, take a snapshot, create multiple disks from the snapshot, and attach each disk to its own instance.
Correct Answer: C
Question 34
You are developing an HTTP API hosted on a Google Compute Engine virtual machine instance that needs to be invoked by multiple clients within the same Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). You want clients to be able to get the IP address of the service.
What should you do?
- A. Reserve a static external IP address and assign it to an HTTP(S) load balancing service’s forwarding rule. Clients should use this IP address to connect to the service.
- B. Reserve a static external IP address and assign it to an HTTP(S) load balancing service’s forwarding rule. Then, define an A record in Google Cloud DNS. Clients should use the name of the A record to connect to the service.
- C. Ensure that clients use Google Compute Engine internal DNS by connecting to the instance name with the url https://[INSTANCE_NAME].[ZONE].c. [PROJECT_ID].internal/.
- D. Ensure that clients use Google Compute Engine internal DNS by connecting to the instance name with the url https://[API_NAME]/[API_VERSION]/.
Correct Answer: D
Question 35
Your application is logging to Stackdriver.
You want to get the count of all requests on all /api/alpha/* endpoints.
What should you do?
- A. Add a Stackdriver counter metric for path:/api/alpha/.
- B. Add a Stackdriver counter metric for endpoint:/api/alpha/*.
- C. Export the logs to Google Cloud Storage and count lines matching /api/alpha.
- D. Export the logs to Google Cloud Pub/Sub and count lines matching /api/alpha.
Correct Answer: C
Question 36
You want to re-architect a monolithic application so that it follows a microservices model. You want to accomplish this efficiently while minimizing the impact of this change to the business.
Which approach should you take?
- A. Deploy the application to Google Compute Engine and turn on autoscaling.
- B. Replace the application’s features with appropriate microservices in phases.
- C. Refactor the monolithic application with appropriate microservices in a single effort and deploy it.
- D. Build a new application with the appropriate microservices separate from the monolith and replace it when it is complete.
Correct Answer: C
Reference contents:
– Migrating a monolithic application to microservices on Google Kubernetes Engine | Google Cloud
Question 37
Your existing application keeps user state information in a single MySQL database.
This state information is very user-specific and depends heavily on how long a user has been using an application. The MySQL database is causing challenges to maintain and enhance the schema for various users.
Which storage option should you choose?
- A. Google Cloud SQL
- B. Google Cloud Storage
- C. Google Cloud Spanner
- D. Google Cloud Datastore/Firestore
Correct Answer: A
Reference contents:
– Migration from MySQL to Cloud SQL | Solutions | Google Cloud
Question 38
You are building a new API.
You want to minimize the cost of storing and reduce the latency of serving images.
Which architecture should you use?
- A. Google App Engine backed by Google Cloud Storage.
- B. Google Compute Engine backed by Persistent Disk.
- C. Transfer Appliance backed by Filestore.
- D. Google Cloud Content Delivery Network (CDN) backed by Google Cloud Storage.
Correct Answer: B
Question 39
Your company’s development teams want to use Google Cloud Build in their projects to build and push Docker images to Google Cloud Container Registry.
The operations team requires all Docker images to be published to a centralized, securely managed Docker registry that the operations team manages.
What should you do?
- A. Use Google Cloud Container Registry to create a registry in each development team’s project. Configure the Google Cloud Build build to push the Docker image to the project’s registry. Grant the operations team access to each development team’s registry.
- B. Create a separate project for the operations team that has Google Cloud Container Registry configured. Assign appropriate permissions to the Google Cloud Build service account in each developer team’s project to allow access to the operation team’s registry.
- C. Create a separate project for the operations team that has Container Registry configured. Create a Service Account for each development team and assign the appropriate permissions to allow it access to the operations team’s registry. Store the service account key file in the source code repository and use it to authenticate against the operations team’s registry.
- D. Create a separate project for the operations team that has the open source Docker Registry deployed on a Google Compute Engine virtual machine instance. Create a username and password for each development team. Store the username and password in the source code repository and use it to authenticate against the operations team’s Docker registry.
Correct Answer: A
Reference contents:
– Google Cloud Container Registry | Google Cloud
Question 40
You are planning to deploy your application in a Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster.
Your application can scale horizontally, and each instance of your application needs to have a stable network identity and its own persistent disk.
Which GKE object should you use?
- A. Deployment
- B. StatefulSet
- C. ReplicaSet
- D. ReplicaController
Correct Answer: B
Reference contents:
– Chapter 10. StatefulSets: deploying replicated stateful applications · Kubernetes in Action
Question 41
You are using Google Cloud Build to build a Docker image.
You need to modify the build to execute unit and run integration tests. When there is a failure, you want the build history to clearly display the stage at which the build failed.
What should you do?
- A. Add RUN commands in the Dockerfile to execute unit and integration tests.
- B. Create a Google Cloud Build build config file with a single build step to compile unit and integration tests.
- C. Create a Google Cloud Build build config file that will spawn a separate Google Cloud Build pipeline for unit and integration tests.
- D. Create a Google Cloud Build build config file with separate Google Cloud Build steps to compile and execute unit and integration tests.
Correct Answer: D
Question 42
Your code is running on Google Cloud Functions in project A.
It is supposed to write an object in a Google Cloud Storage bucket owned by project B. However, the write call is failing with the error “403 Forbidden”.
What should you do to correct the problem?
- A. Grant your user account the roles/storage.objectCreator role for the Google Cloud Storage bucket.
- B. Grant your user account the roles/iam.serviceAccountUser role for the service-PROJECTA@gcf-admin-robot.iam.gserviceaccount.com service account.
- C. Grant the service-PROJECTA@gcf-admin-robot.iam.gserviceaccount.com service account the roles/storage.objectCreator role for the Google Cloud Storage bucket.
- D. Enable the Google Cloud Storage API in project B.
Correct Answer: B
Question 43
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
HipLocal’s .net-based auth service fails under intermittent load.
What should they do?
- A. Use Google App Engine for autoscaling.
- B. Use Google Cloud Functions for autoscaling.
- C. Use a Google Compute Engine cluster for the service.
- D. Use a dedicated Google Compute Engine virtual machine instance for the service.
Correct Answer: D
Reference contents:
– Autoscaling an Instance Group with Custom Cloud Monitoring Metrics
Question 44
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
HipLocal’s APIs are showing occasional failures, but they cannot find a pattern.
They want to collect some metrics to help them troubleshoot.
What should they do?
- A. Take frequent snapshots of all of the VMs.
- B. Install the Stackdriver Logging agent on the VMs.
- C. Install the Stackdriver Monitoring agent on the VMs.
- D. Use Stackdriver Trace to look for performance bottlenecks.
Correct Answer: C
Question 45
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
HipLocal has connected their Hadoop infrastructure to GCP using Google Cloud Interconnect in order to query data stored on persistent disks.
Which IP strategy should they use?
- A. Create manual subnets.
- B. Create an auto mode subnet.
- C. Create multiple peered VPCs.
- D. Provision a single instance for NAT.
Correct Answer: A
Question 46
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
Which service should HipLocal use to enable access to internal apps?
- A. Google Cloud VPN
- B. Google Cloud Armor
- C. Virtual Private Cloud
- D. Google Cloud Identity-Aware Proxy
Correct Answer: D
Reference contents:
– Overview of IAP for on-premises apps | Identity-Aware Proxy | Google Cloud
Question 47
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
HipLocal wants to reduce the number of on-call engineers and eliminate manual scaling.
Which two services should they choose? (Choose two.)
- A. Use Google App Engine services.
- B. Use serverless Google Cloud Functions.
- C. Use Knative to build and deploy serverless applications.
- D. Use Google Kubernetes Engine for automated deployments.
- E. Use a large Google Compute Engine cluster for deployments.
Correct Answer: B, C
Question 48
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
In order to meet their business requirements, how should HipLocal store their application state?
- A. Use local SSDs to store state.
- B. Put a memcache layer in front of MySQL.
- C. Move the state storage to Google Cloud Spanner.
- D. Replace the MySQL instance with Google Cloud SQL.
Correct Answer: B
Question 49
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
Which service should HipLocal use for their public APIs?
- A. Google Cloud Armor
- B. Google Cloud Functions
- C. Google Cloud Endpoints
- D. Shielded Virtual Machines
Correct Answer: D
Question 50
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
HipLocal wants to improve the resilience of their MySQL deployment, while also meeting their business and technical requirements.
Which configuration should they choose?
- A. Use the current single instance MySQL on Google Compute Engine and several read-only MySQL servers on Google Compute Engine.
- B. Use the current single instance MySQL on Google Compute Engine, and replicate the data to Google Cloud SQL in an external master configuration.
- C. Replace the current single instance MySQL instance with Google Cloud SQL, and configure high availability.
- D. Replace the current single instance MySQL instance with Google Cloud SQL, and Google provides redundancy without further configuration.
Correct Answer: B
Question 51
Your application is running in multiple Google Kubernetes Engine clusters.
It is managed by a Deployment in each cluster. The Deployment has created multiple replicas of your Pod in each cluster. You want to view the logs sent to stdout for all of the replicas in your Deployment in all clusters.
Which command should you use?
- A. kubectl logs [PARAM]
- B. gcloud logging read [PARAM]
- C. kubectl exec “”it [PARAM] journalctl
- D. gcloud compute ssh [PARAM] “”-command= “sudo journalctl”
Correct Answer: D
Question 52
You are using Google Cloud Build to create a new Docker image on each source code commit to a Google Cloud Source Repositories repository.
Your application is built on every commit to the master branch. You want to release specific commits made to the master branch in an automated method.
What should you do?
- A. Manually trigger the build for new releases.
- B. Create a build trigger on a Git tag pattern. Use a Git tag convention for new releases.
- C. Create a build trigger on a Git branch name pattern. Use a Git branch naming convention for new releases.
- D. Commit your source code to a second Google Cloud Source Repositories repository with a second Google Cloud Build trigger. Use this repository for new releases only.
Correct Answer: C
Question 53
You are designing a schema for a table that will be moved from MySQL to Cloud Bigtable. The MySQL table is as follows:
AccountActivity
(
Account_id int,
Event_timestamp datetime,
Transaction_type string,
Amount numeric (18,4)
) primary key (Account_id, Event_timestamp)How should you design a row key for Cloud Bigtable for this table?
- A. Set Account_id as a key.
- B. Set Account_id_Event_timestamp as a key.
- C. Set Event_timestamp_Account_id as a key.
- D. Set Event_timestamp as a key.
Correct Answer: C
Question 54
You want to view the memory usage of your application deployed on Google Compute Engine.
What should you do?
- A. Install the Stackdriver Client Library.
- B. Install the Stackdriver Monitoring Agent.
- C. Use the Stackdriver Metrics Explorer.
- D. Use the Google Cloud Console.
Correct Answer: C
Reference contents:
– Google Cloud Platform: how to monitor memory usage of VM instances
Question 55
You have an analytics application that runs hundreds of queries on Google BigQuery every few minutes using Google BigQuery API.
You want to find out how much time these queries take to execute.
What should you do?
- A. Use Stackdriver Monitoring to plot slot usage.
- B. Use Stackdriver Trace to plot API execution time.
- C. Use Stackdriver Trace to plot query execution time.
- D. Use Stackdriver Monitoring to plot query execution times.
Correct Answer: D
Question 56
You are designing a schema for a Google Cloud Spanner customer database.
You want to store a phone number array field in a customer table. You also want to allow users to search customers by phone number.
How should you design this schema?
- A. Create a table named Customers. Add an Array field in a table that will hold phone numbers for the customer.
- B. Create a table named Customers. Create a table named Phones. Add a CustomerId field in the Phones table to find the CustomerId from a phone number.
- C. Create a table named Customers. Add an Array field in a table that will hold phone numbers for the customer. Create a secondary index on the Array field.
- D. Create a table named Customers as a parent table. Create a table named Phones, and interleave this table into the Customer table. Create an index on the phone number field in the Phones table.
Correct Answer: C
Question 57
You are deploying a single website on Google App Engine that needs to be accessible via the URL http://www.altostrat.com.
What should you do?
- A. Verify domain ownership with Webmaster Central. Create a DNS CNAME record to point to the Google App Engine canonical name ghs.googlehosted.com.
- B. Verify domain ownership with Webmaster Central. Define an A record pointing to the single global Google App Engine IP address.
- C. Define a mapping in dispatch.yaml to point the domain www.altostrat.com to your Google App Engine service. Create a DNS CNAME record to point to the Google App Engine canonical name ghs.googlehosted.com.
- D. Define a mapping in dispatch.yaml to point the domain www.altostrat.com to your Google App Engine service. Define an A record pointing to the single global Google App Engine IP address.
Correct Answer: A
Reference contents:
– Mapping Custom Domains | App Engine flexible environment for .NET docs | Google Cloud
Question 58
You are running an application on Google App Engine that you inherited.
You want to find out whether the application is using insecure binaries or is vulnerable to XSS attacks.
Which service should you use?
- A. Google Cloud Amor
- B. Stackdriver Debugger
- C. Google Cloud Security Scanner
- D. Stackdriver Error Reporting
Correct Answer: C
Reference contents:
– Google Cloud Security Command Center | Google Cloud
Question 59
You are working on a social media application.
You plan to add a feature that allows users to upload images. These images will be 2 MB “” 1 GB in size. You want to minimize their infrastructure operations overhead for this feature.
What should you do?
- A. Change the application to accept images directly and store them in the database that stores other user information.
- B. Change the application to create signed URLs for Google Cloud Storage. Transfer these signed URLs to the client application to upload images to Google Cloud Storage.
- C. Set up a web server on GCP to accept user images and create a file store to keep uploaded files. Change the application to retrieve images from the file store.
- D. Create a separate bucket for each user in Google Cloud Storage. Assign a separate service account to allow write access on each bucket. Transfer service account credentials to the client application based on user information. The application uses this service account to upload images to Google Cloud Storage.
Correct Answer: B
Reference contents:
– News, Features and Announcements | Google Cloud
Question 60
Your application is built as a custom machine image.
You have multiple unique deployments of the machine image. Each deployment is a separate managed instance group with its own template. Each deployment requires a unique set of configuration values. You want to provide these unique values to each deployment but use the same custom machine image in all deployments. You want to use out-of-the-box features of Google Compute Engine.
What should you do?
- A. Place the unique configuration values in the persistent disk.
- B. Place the unique configuration values in a Google Cloud Bigtable table.
- C. Place the unique configuration values in the instance template startup script.
- D. Place the unique configuration values in the instance template instance metadata.
Correct Answer: A
Reference contents:
– Instance groups | Compute Engine Documentation | Google Cloud
Question 61
Your application performs well when tested locally, but it runs significantly slower when you deploy it to Google App Engine standard environment.
You want to diagnose the problem.
What should you do?
- A. File a ticket with GCP Support indicating that the application performs faster locally.
- B. Use Stackdriver Debugger Snapshots to look at a point-in-time execution of the application.
- C. Use Stackdriver Trace to determine which functions within the application have higher latency.
- D. Add logging commands to the application and use Stackdriver Logging to check where the latency problem occurs.
Correct Answer: D
Question 62
You have an application running in Google App Engine.
Your application is instrumented with Stackdriver Trace. The /product-details request reports details about four known unique products at /sku-details as shown below. You want to reduce the time it takes for the request to complete.
What should you do?
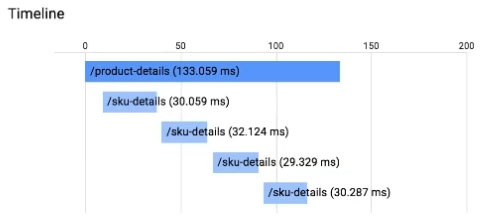
- A. Increase the size of the instance class.
- B. Change the Persistent Disk type to SSD.
- C. Change /product-details to perform the requests in parallel.
- D. Store the /sku-details information in a database, and replace the webservice call with a database query.
Correct Answer: C
Question 63
Your company has a data warehouse that keeps your application information in Google BigQuery. The Google BigQuery data warehouse keeps 2 PBs of user data. Recently, your company expanded your user base to include EU users and needs to comply with these requirements:
– Your company must be able to delete all user account information upon user request.
– All EU user data must be stored in a single region specifically for EU users.
Which two actions should you take? (Choose two.)
- A. Use Google BigQuery federated queries to query data from Google Cloud Storage.
- B. Create a dataset in the EU region that will keep information about EU users only.
- C. Create a Google Cloud Storage bucket in the EU region to store information for EU users only.
- D. Re-upload your data using to a Google Cloud Dataflow pipeline by filtering your user records out.
- E. Use DML statements in Google BigQuery to update/delete user records based on their requests.
Correct Answer: C, E
Reference contents:
– BigQuery for data warehouse practitioners | Solutions | Google Cloud
Question 64
Your Google App Engine standard configuration is as follows:
service: production
instance_class: B1
You want to limit the application to 5 instances.
Which code snippet should you include in your configuration?
- A. manual_scaling: instances: 5 min_pending_latency: 30ms
- B. manual_scaling: max_instances: 5 idle_timeout: 10m
- C. basic_scaling: instances: 5 min_pending_latency: 30ms
- D. basic_scaling: max_instances: 5 idle_timeout: 10m
Correct Answer: C
Question 65
Your analytics system executes queries against a Google BigQuery dataset.
The SQL query is executed in batch and passes the contents of a SQL file to the Google BigQuery CLI. Then it redirects the Google BigQuery CLI output to another process. However, you are getting a permission error from the Google BigQuery CLI when the queries are executed.
You want to resolve the issue. What should you do?
- A. Grant the service account Google BigQuery Data Viewer and Google BigQuery Job User roles.
- B. Grant the service account Google BigQuery Data Editor and Google BigQuery Data Viewer roles.
- C. Create a view in Google BigQuery from the SQL query and SELECT* from the view in the CLI.
- D. Create a new dataset in Google BigQuery, and copy the source table to the new dataset Query the new dataset and table from the CLI.
Correct Answer: B
Question 66
Your application is running on Google Compute Engine and is showing sustained failures for a small number of requests. You have narrowed the cause down to a single Google Compute Engine instance, but the instance is unresponsive to SSH.
What should you do next?
- A. Reboot the machine.
- B. Enable and check the serial port output.
- C. Delete the machine and create a new one.
- D. Take a snapshot of the disk and attach it to a new machine.
Correct Answer: A
Question 67
You configured your Google Compute Engine instance group to scale automatically according to overall CPU usage.
However, your application’s response latency increases sharply before the cluster has finished adding up instances. You want to provide a more consistent latency experience for your end users by changing the configuration of the instance group autoscaler.
Which two configuration changes should you make? (Choose two.)
- A. Add the label “AUTOSCALE” to the instance group template.
- B. Decrease the cool-down period for instances added to the group.
- C. Increase the target CPU usage for the instance group autoscaler.
- D. Decrease the target CPU usage for the instance group autoscaler.
- E. Remove the health-check for individual VMs in the instance group.
Correct Answer: A, C
Question 68
You have an application controlled by a managed instance group.
When you deploy a new version of the application, costs should be minimized and the number of instances should not increase. You want to ensure that, when each new instance is created, the deployment only continues if the new instance is healthy.
What should you do?
- A. Perform a rolling-action with maxSurge set to 1, maxUnavailable set to 0.
- B. Perform a rolling-action with maxSurge set to 0, maxUnavailable set to 1
- C. Perform a rolling-action with maxHealthy set to 1, maxUnhealthy set to 0.
- D. Perform a rolling-action with maxHealthy set to 0, maxUnhealthy set to 1.
Correct Answer: A
Reference contents:
– Automatically rolling out updates to instances in a MIG | Google Cloud
Question 69
Your application requires service accounts to be authenticated to GCP products via credentials stored on its host Google Compute Engine virtual machine instances.
You want to distribute these credentials to the host instances as securely as possible.
What should you do?
- A. Use HTTP signed URLs to securely provide access to the required resources.
- B. Use the instance’s service account Application Default Credentials to authenticate to the required resources.
- C. Generate a P12 file from the Google Cloud Console after the instance is deployed, and copy the credentials to the host instance before starting the application.
- D. Commit the credential JSON file into your application’s source repository, and have your CI/CD process package it with the software that is deployed to the instance.
Correct Answer: B
Reference contents:
– Authorizing requests to Compute Engine | Compute Engine Documentation | Google Cloud
Question 70
Your application is deployed in a Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) cluster.
You want to expose this application publicly behind a Cloud Load Balancing HTTP(S) load balancer.
What should you do?
- A. Configure a GKE Ingress resource.
- B. Configure a GKE Service resource.
- C. Configure a GKE Ingress resource with type: LoadBalancer.
- D. Configure a GKE Service resource with type: LoadBalancer.
Correct Answer: A
Reference contents:
– GKE Ingress for HTTP(S) Load Balancing | Google Cloud
Question 71
Your company is planning to migrate their on-premises Hadoop environment to the cloud.
Increasing storage cost and maintenance of data stored in HDFS is a major concern for your company. You also want to make minimal changes to existing data analytics jobs and existing architecture.
How should you proceed with the migration?
- A. Migrate your data stored in Hadoop to Google BigQuery. Change your jobs to source their information from Google BigQuery instead of the on-premises Hadoop environment.
- B. Create Google Compute Engine instances with HDD instead of SSD to save costs. Then perform a full migration of your existing environment into the new one in Google Compute Engine instances.
- C. Create a Google Cloud Dataproc cluster on Google Cloud Platform, and then migrate your Hadoop environment to the new Google Cloud Dataproc cluster. Move your HDFS data into larger HDD disks to save on storage costs.
- D. Create a Google Cloud Dataproc cluster on Google Cloud Platform, and then migrate your Hadoop code objects to the new cluster. Move your data to Google Cloud Storage and leverage the Google Cloud Dataproc connector to run jobs on that data.
Correct Answer: D
Question 72
Your data is stored in Google Cloud Storage buckets.
Fellow developers have reported that data downloaded from Google Cloud Storage is resulting in slow API performance.You want to research the issue to provide details to the GCP support team.
Which command should you run?
- A. gsutil test “”o output.json gs://my-bucket
- B. gsutil perfdiag “”o output.json gs://my-bucket
- C. gcloud compute scp example-instance:~/test-data “”o output.json gs://my-bucket
- D. gcloud services test “”o output.json gs://my-bucket
Correct Answer: B
Reference contents:
– Sometimes get super-slow download rates from Google Cloud Storage, severely impacting workflow
Question 73
You are using Google Cloud Build build to promote a Docker image to Development, Test, and Production environments.
You need to ensure that the same Docker image is deployed to each of these environments.
How should you identify the Docker image in your build?
- A. Use the latest Docker image tag.
- B. Use a unique Docker image name.
- C. Use the digest of the Docker image.
- D. Use a semantic version Docker image tag.
Correct Answer: D
Question 74
Your company has created an application that uploads a report to a Google Cloud Storage bucket.
When the report is uploaded to the bucket, you want to publish a message to a Google Cloud Pub/Sub topic. You want to implement a solution that will take a small amount of effort to implement.
What should you do?
- A. Configure the Google Cloud Storage bucket to trigger Google Cloud Pub/Sub notifications when objects are modified.
- B. Create a Google App Engine application to receive the file; when it is received, publish a message to the Google Cloud Pub/Sub topic.
- C. Create a Google Cloud Functions that is triggered by the Google Cloud Storage bucket. In the Google Cloud Functions, publish a message to the Google Cloud Pub/Sub topic.
- D. Create an application deployed in a Google Kubernetes Engine cluster to receive the file; when it is received, publish a message to the Google Cloud Pub/Sub topic.
Correct Answer: C
Reference contents:
– Pub/Sub notifications for Cloud Storage | Google Cloud
Question 75
Your teammate has asked you to review the code below, which is adding a credit to an account balance in Google Cloud Datastore.
Which improvement should you suggest your teammate make?
public Entity creditAccount (long accountId, long creditAmount) {
Entity account = datastore.get
(keyFactory.newKey (accountid)) ;
account = Entity.builder (account).set(
"balance", account.getLong ("balance") + credit Amount) .build()
datastore.put (account);
return account;
}- A. Get the entity with an ancestor query.
- B. Get and put the entity in a transaction.
- C. Use a strongly consistent transactional database.
- D. Don’t return the account entity from the function.
Correct Answer: A
Question 76
Your company stores their source code in a Google Cloud Source Repositories repository.
Your company wants to build and test their code on each source code committed to the repository and requires a solution that is managed and has minimal operations overhead.
Which method should they use?
- A. Use Google Cloud Build with a trigger configured for each source code commit.
- B. Use Jenkins deployed via the Google Cloud Platform Marketplace, configured to watch for source code commits.
- C. Use a Google Compute Engine virtual machine instance with an open source continuous integration tool, configured to watch for source code commits.
- D. Use a source code commit trigger to push a message to a Google Cloud Pub/Sub topic that triggers an Google App Engine service to build the source code.
Correct Answer: A
Question 77
You are writing a Google Compute Engine hosted application in project A that needs to securely authenticate to a Google Cloud Pub/Sub topic in project B.
What should you do?
- A. Configure the instances with a service account owned by project B. Add the service account as a Google Cloud Pub/Sub publisher to project A.
- B. Configure the instances with a service account owned by project A. Add the service account as a publisher on the topic.
- C. Configure Application Default Credentials to use the private key of a service account owned by project B. Add the service account as a Google Cloud Pub/Sub publisher to project A.
- D. Configure Application Default Credentials to use the private key of a service account owned by project A. Add the service account as a publisher on the topic.
Correct Answer: B
Question 78
You are developing a corporate tool on Google Compute Engine for the finance department, which needs to authenticate users and verify that they are in the finance department.
All company employees use G Suite.
What should you do?
- A. Enable Google Cloud Identity-Aware Proxy on the HTTP(s) load balancer and restrict access to a Google Group containing users in the finance department. Verify the provided JSON Web Token within the application.
- B. Enable Google Cloud Identity-Aware Proxy on the HTTP(s) load balancer and restrict access to a Google Group containing users in the finance department. Issue client-side certificates to everybody in the finance team and verify the certificates in the application.
- C. Configure Google Cloud Armor Security Policies to restrict access to only corporate IP address ranges. Verify the provided JSON Web Token within the application.
- D. Configure Google Cloud Armor Security Policies to restrict access to only corporate IP address ranges. Issue client side certificates to everybody in the finance team and verify the certificates in the application.
Correct Answer: C
Question 79
Your API backend is running on multiple cloud providers.
You want to generate reports for the network latency of your API.
Which two steps should you take? (Choose two.)
- A. Use Zipkin collector to gather data.
- B. Use Fluentd agent to gather data.
- C. Use Stackdriver Trace to generate reports.
- D. Use Stackdriver Debugger to generate report.
- E. Use Stackdriver Profiler to generate report.
Correct Answer: C, E
Question 80
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
Which database should HipLocal use for storing user activity?
- A. Google BigQuery
- B. Google Cloud SQL
- C. Google Cloud Spanner
- D. Google Cloud Datastore
Correct Answer: C
Question 81
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
HipLocal is configuring their access controls.
Which firewall configuration should they implement?
- A. Block all traffic on port 443.
- B. Allow all traffic into the network.
- C. Allow traffic on port 443 for a specific tag.
- D. Allow all traffic on port 443 into the network.
Correct Answer: C
Question 82
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
HipLocal’s data science team wants to analyze user reviews.
How should they prepare the data?
- A. Use the Google Cloud Data Loss Prevention API for redaction of the review dataset.
- B. Use the Google Cloud Data Loss Prevention API for de-identification of the review dataset.
- C. Use the Google Cloud Natural Language Processing API for redaction of the review dataset.
- D. Use the Google Cloud Natural Language Processing API for de-identification of the review dataset.
Correct Answer: D
Question 83
For this question, refer to the HipLocal case study.
In order for HipLocal to store application state and meet their stated business requirements, which database service should they migrate to?
- A. Google Cloud Spanner
- B. Google Cloud Datastore
- C. Google Cloud Memorystore as a cache
- D. Separate Google Cloud SQL clusters for each region
Correct Answer: A
Question 84
You have an application deployed in production.
When a new version is deployed, you want to ensure that all production traffic is routed to the new version of your application. You also want to keep the previous version deployed so that you can revert to it if there is an issue with the new version.
Which deployment strategy should you use?
- A. Blue/green deployment
- B. Canary deployment
- C. Rolling deployment
- D. Recreate deployment
![[GCP] Google Cloud Certified - Professional Cloud Developer](https://www.cloudsmog.net/wp-content/uploads/google-cloud-certified_professional-cloud-developer-1200x675.jpg)
Comments are closed